Enugu and Kwara lead as the states with the most tourist centres in Nigeria, boasting 17 tourist sites each. States like Edo (16), Kogi (15), and Oyo (15) closely follow, showcasing Nigeria's rich and varied attractions across different regions.
Lagos, often called Nigeria's commercial capital, features prominently with 13 tourist centres.

In 2022, derailments accounted for 44% of all train accidents, increasing from 35% in 2021 to 38% in 2020. This shows the need to prioritise railway infrastructure maintenance. Locomotive failures also contributed to train accidents, making up 35% of cases in 2022. Although this is slightly lower than the 36% recorded in 2020, it still represents a significant proportion of rail incidents.
The world's top ten semiconductor vendors control nearly 50% of the market share. Intel has maintained its position as the market leader, though its share has declined significantly from 15.4% in 2013 to 9.1% in 2023, and Samsung Electronics, its closest rival, has experienced a similar downward trend.
Apple and Nvidia have emerged as formidable contenders in the semiconductor business, joining the ranks of leading players in less than five years.

Cinemas provide consumers with entertainment outside their homes, allowing them to watch the latest blockbusters with friends on a large screen. They also help movie producers get their films in front of thousands of people.
In Nigeria, independent cinemas form the largest group, with names recognisable mostly within the towns where they exist. However, cinema chains are growing. Filmhouse Cinemas has 12 locations in five states, while Genesis Cinemas operates in six states, albeit with fewer locations than Filmhouse Cinemas. Unlike the other top five, Kada Cinemas has no cinemas in Lagos.

Seven Nigerian commercial banks have international authorisation. Per the new capital requirements, these banks must raise their shareholders' funds to ₦500 billion by April 2026, up from ₦50 billion, to retain their licences.
All seven banks have footprints in the UK, where FCMB and Fidelity Bank operate, underutilising their licence. Ghana and Sierra Leone are the only countries where all the big five have a presence.
While UBA is present in more countries than any other bank, Access is catching up quickly and poised to overtake it. In the past two years, it has expanded into over five countries, with plans to grow its presence to nearly 30 countries by 2027.
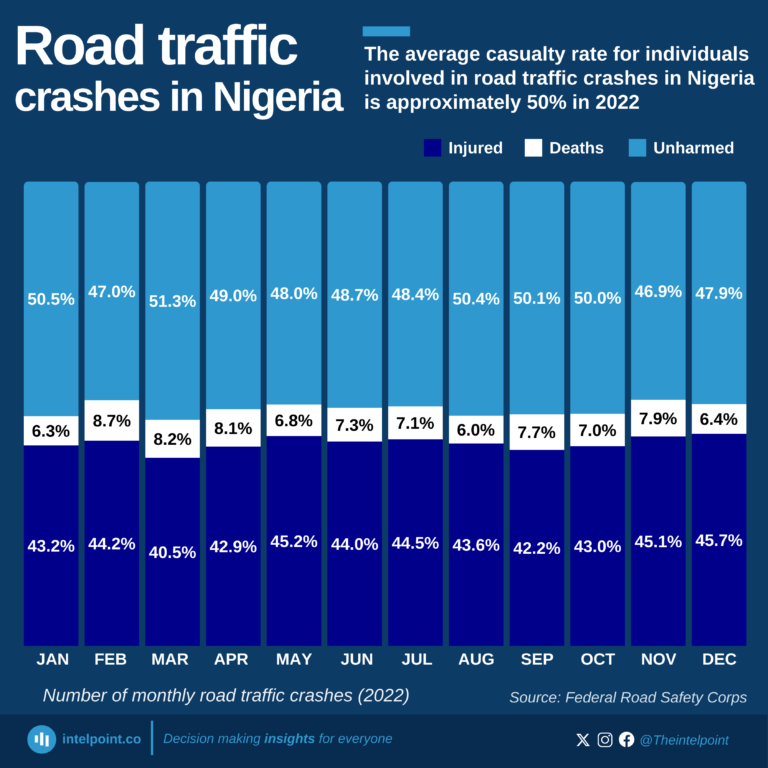
Road traffic crashes in Nigeria remain a significant concern, with an average casualty rate of approximately 50% throughout 2022. This means half of the people involved in crashes either sustained injuries or lost their lives. While the remaining half walked away unharmed, February and November had the highest casualty rates at 53%, though with just a slight increase from other months.
A closer look at the data reveals that injuries far outweigh fatalities across all months. This pattern shows the heavy burden on hospitals and emergency services, which often struggle to manage the influx of victims. December, a festive season marked by increased travel, saw a casualty rate of 52%, with deaths accounting for 6.4% and injuries rising to 45.7%. This reaffirms the need for extra caution during peak travel when road congestion and reckless driving are heightened.

With the top ten states receiving 40% of the ₦82b shared in EMTL, Lagos led with ₦7.68b, followed by Kano with ₦3.46b. Oyo, Rivers, and Kaduna rounded out the top five, each securing over ₦2b. These states are driving the lion’s share of the revenue. In stark contrast, the bottom ten states, including Bayelsa and Ebonyi, saw much smaller allocations, with each receiving less than ₦2b.
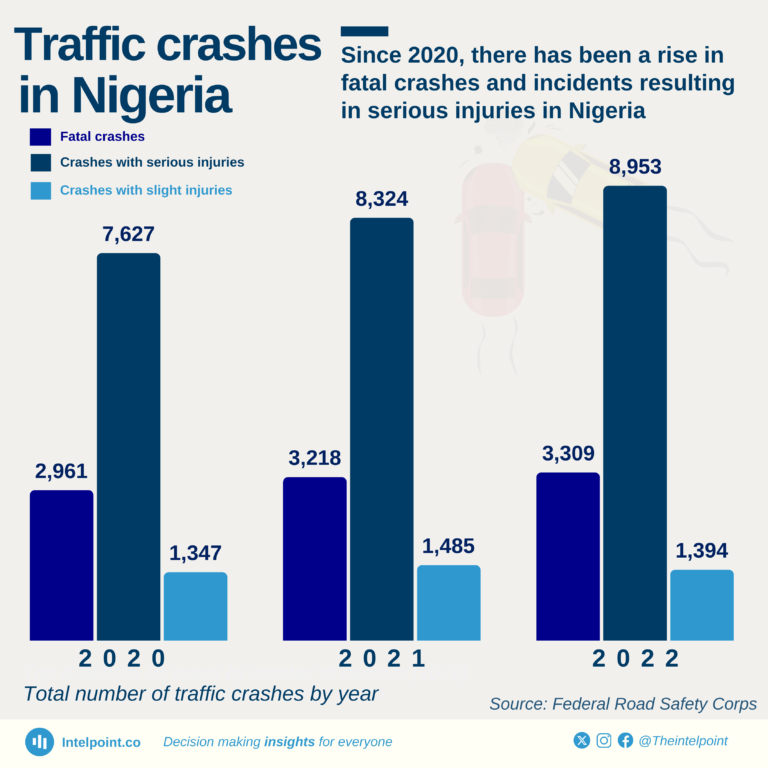
Data from the Federal Road Safety Corps (FRSC) highlights a worrying rise in traffic crashes in Nigeria between 2020 and 2022. Fatal crashes and crashes resulting in serious injuries have increased consistently, emphasising a growing public safety challenge on the nation’s roads.
In 2020, Nigeria recorded 11,935 crashes with 2,961 fatalities and 7,627 serious injuries. By 2022, the numbers climbed further to 13,656 total crashes, with 3,309 fatal incidents (a 12% rise) and 8,953 serious injuries (a 17% increase).
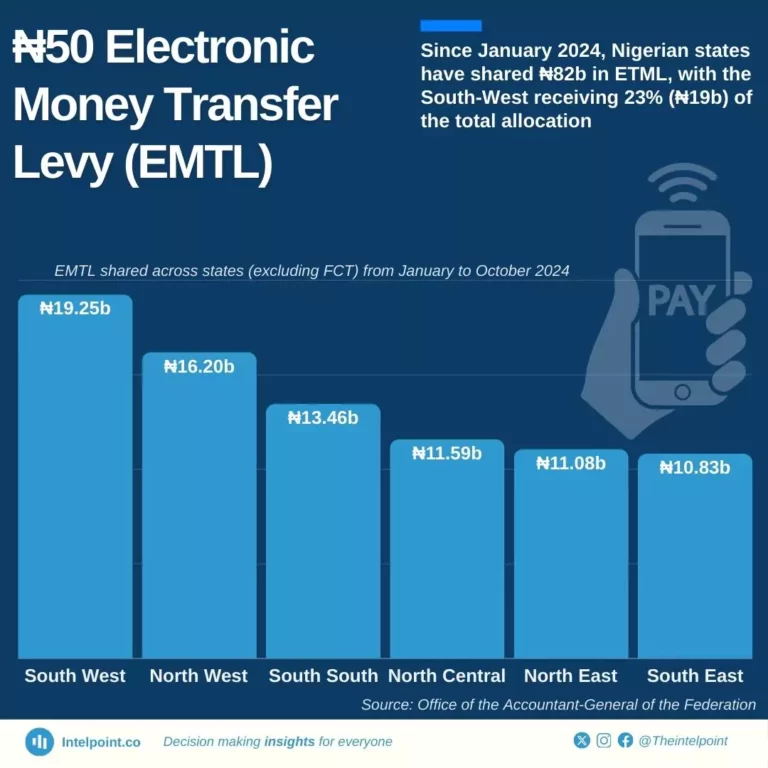
On December 1, 2024, fintech companies including OPay, PalmPay, and Moniepoint announced plans to begin implementing the Electronic Money Transfer Levy (EMTL), a ₦50 charge applied to electronic transfers of ₦10,000 and above. The announcement sparked widespread reactions from Nigerians who expressed concerns about the rising cost of living.
Since January 2024, however, Nigerian states (excluding FCT) have shared ₦82b in EMTL revenue. The South West received the highest allocation of ₦19b, while the South East received the lowest, at ₦11b.
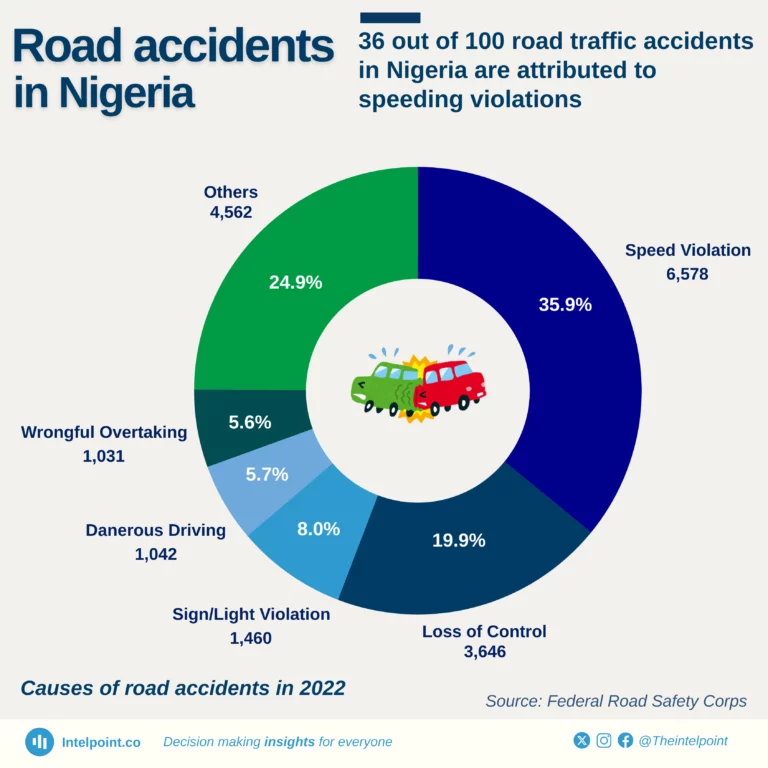
In 2022, approximately 36% of road accidents in Nigeria were caused by speeding violations, accounting for 6,578 cases. This reveals the need for drivers to prioritise safety over the rush to reach their destinations. Loss of control closely follows as another significant cause, contributing to 19.9% of accidents.
While speeding dominates, other seemingly smaller actions like wrongful overtaking (5.6%), dangerous driving (5.7%), and sign/light violations (8.0%) still add up to the dangers.

Temu has embarked on an extraordinary global expansion, cementing its place as a leading e-commerce platform across multiple markets. From its launch in the US in 2022, Temu has quickly become one of the most downloaded shopping apps in the country.
However, Temu's rapid rise has not been without its challenges. Regulators in the EU, US, and South Korea have closely scrutinised the company, examining potential links to labour issues, data protection concerns, and intellectual property violations. Despite these hurdles, Temu has continued to forge ahead, becoming Meta's top advertiser for the year and making a splash with its second Super Bowl campaign in 2024.
As Temu expands into new regions, the company must navigate an evolving regulatory landscape to maintain its momentum and solidify its position as a global e-commerce powerhouse.
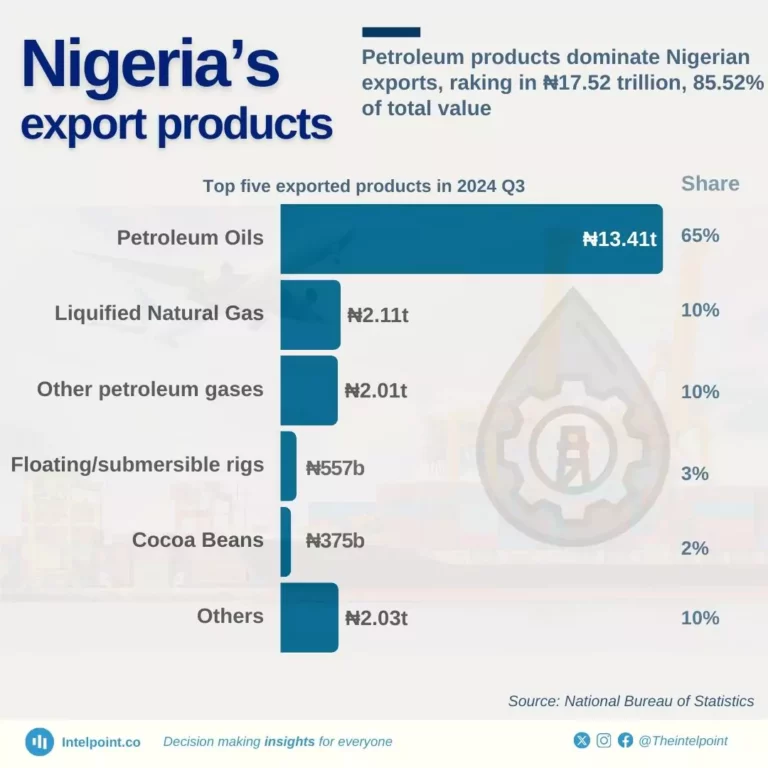
Nigeria's export value increased by 16.8% quarter-on-quarter to ₦20.49 trillion in Q3 2024. Petroleum products (oils, liquefied natural gas, and other petroleum gases) made up 85.52% of its exports, valued at ₦17.53 trillion.
This figure highlights Nigeria's heavy reliance on the oil and gas sector for revenue, emphasising the need for diversification to reduce dependence on a single industry.