Nigeria held the top spot in global cashew production from 2001 to 2010. This highlights a period of strong agricultural output, though the country has since been overtaken by India and Côte d'Ivoire. In recent years, Côte d'Ivoire has emerged as the world’s leading cashew producer, holding the top spot for three consecutive years as of 2022. This shift highlights the country's growing role in global cashew production. India and Mozambique once dominated global production, with India leading for 35 of the past 62 years.
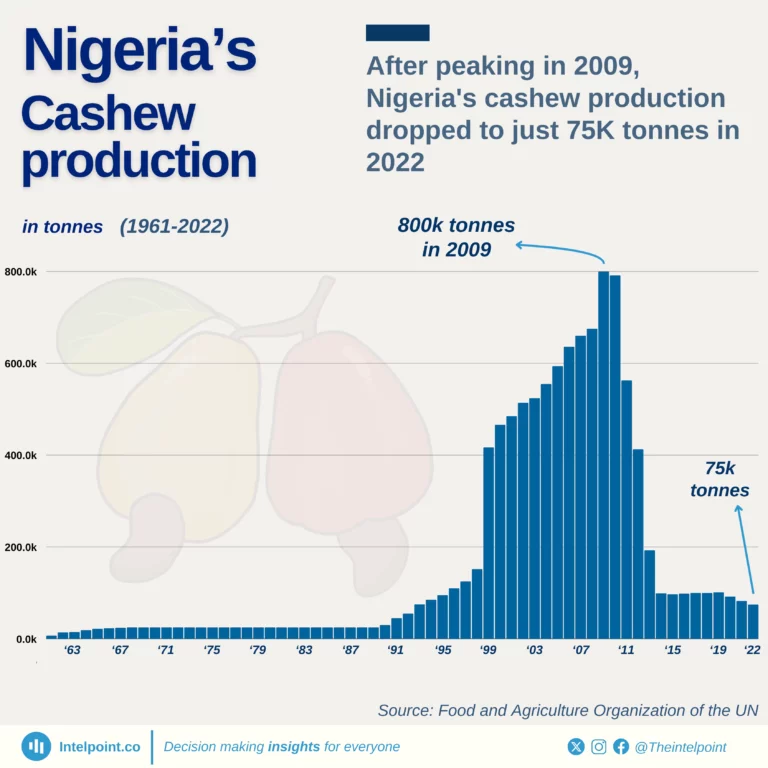
Once the world’s leading cashew producer, Nigeria saw production fall below 100k tonnes in 2022 after hitting a high of 800,000 tonnes in 2009. Despite this decline, experts believe the sector could generate $2.4 billion in foreign exchange annually if production is increased.
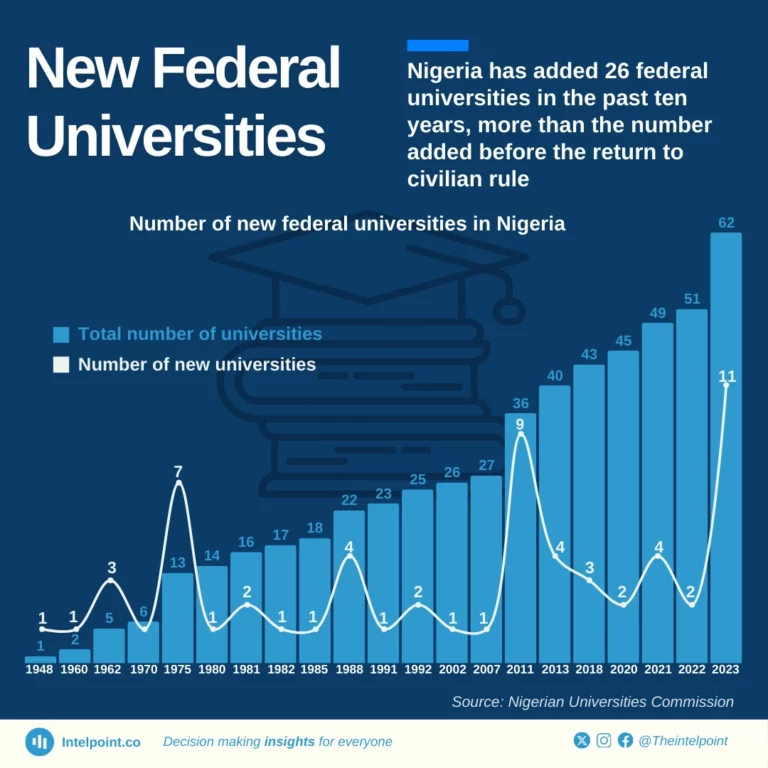
The short-lived administration of General Muritala Mohammed established the most universities in a year of any military administration. In 1975, a federal university was established in Calabar, Ilorin, Jos, Kano, Maiduguri, Port Harcourt, and Sokoto.
The Goodluck Jonathan-led administration moved to ensure a federal university in every state without one, creating 12 universities in three years—a move criticised by the Academic Staff Union of Universities (ASUU).
The creation of specialised universities marked the 2015-2023 Muhammadu Buhari administration through the upgrade of colleges of education and the establishment of health sciences and agricultural universities.
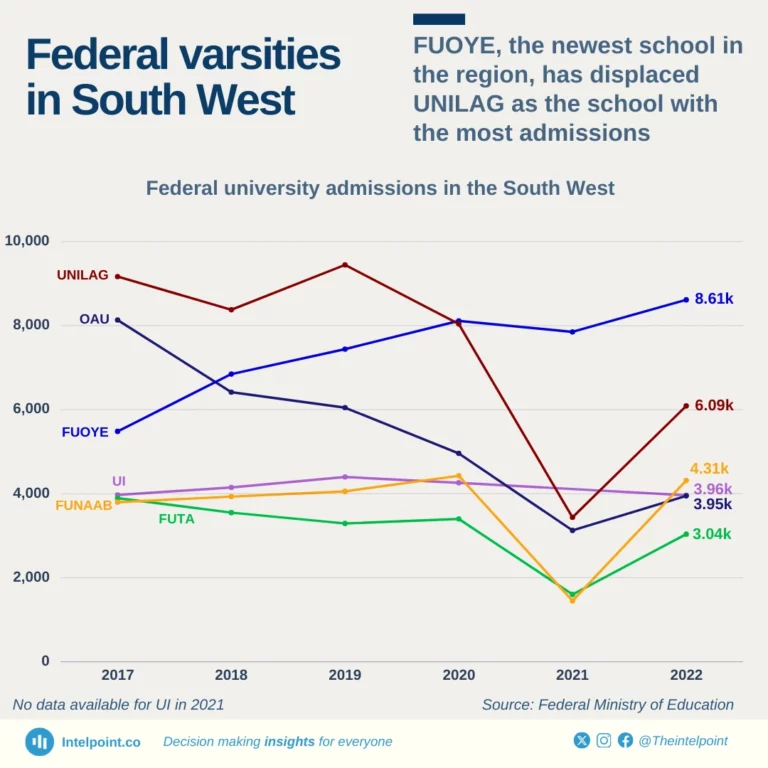
UNILAG and OAU admitted the most students in the South West in 2017, with 9,168 and 8,135, respectively. However, OAU has seen a steady decline in its admissions, reaching a low of 3,127 in 2021 when UNILAG also saw a significant dip in admissions.
FUOYE, the region's only federal university established in the 2000s, increased admissions from 5,483 in 2017 to 8,614 in 2022, admitting the highest number of students in the region. UI, Nigeria's oldest university, has maintained a steady admission count between 3,900 and 4,400 in the years under consideration.
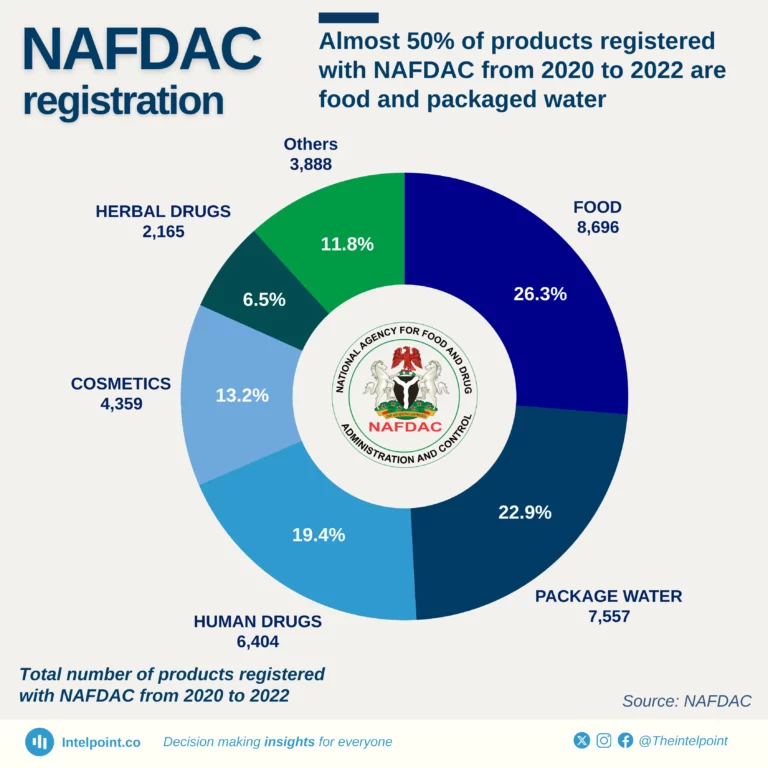
Food and packaged water dominate NAFDAC registration, as close to 50% of all products registered between 2020 and 2022 were either food or packaged water. This suggests a significant focus on ensuring the safety and quality of these essential commodities. Human drugs also make up a substantial portion of registered products, reflecting the importance of regulating medications to protect public health. Cosmetics and herbal drugs follow closely with 13.2% and 6.5%, respectively.
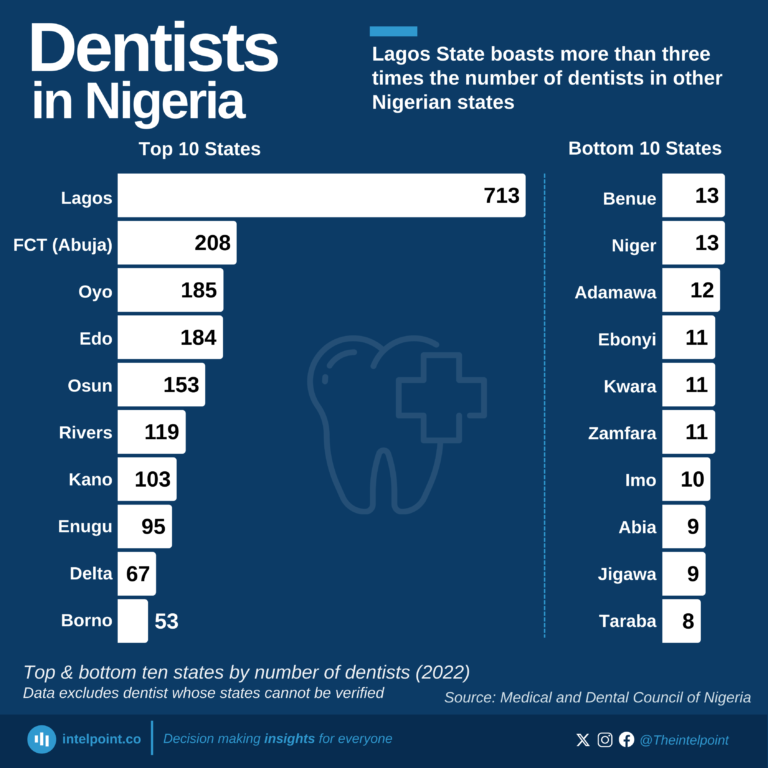
Lagos State leads the dental healthcare workforce in Nigeria with an impressive 713 dentists, a figure over three times higher than any other state. This dominance shows Lagos' position as a hub for healthcare professionals. Trailing far behind are the FCT (Abuja) with 208 dentists and Oyo with 185.
The gap becomes even more glaring when examining the bottom states like Taraba, with only eight dentists, and others such as Jigawa and Abia, with just nine each. These numbers paint a concerning picture for residents of these regions, who may face long travel distances or extended waiting times to access basic dental care. Interestingly, Borno State, which faces security challenges, has 53 dentists, surpassing several other states.
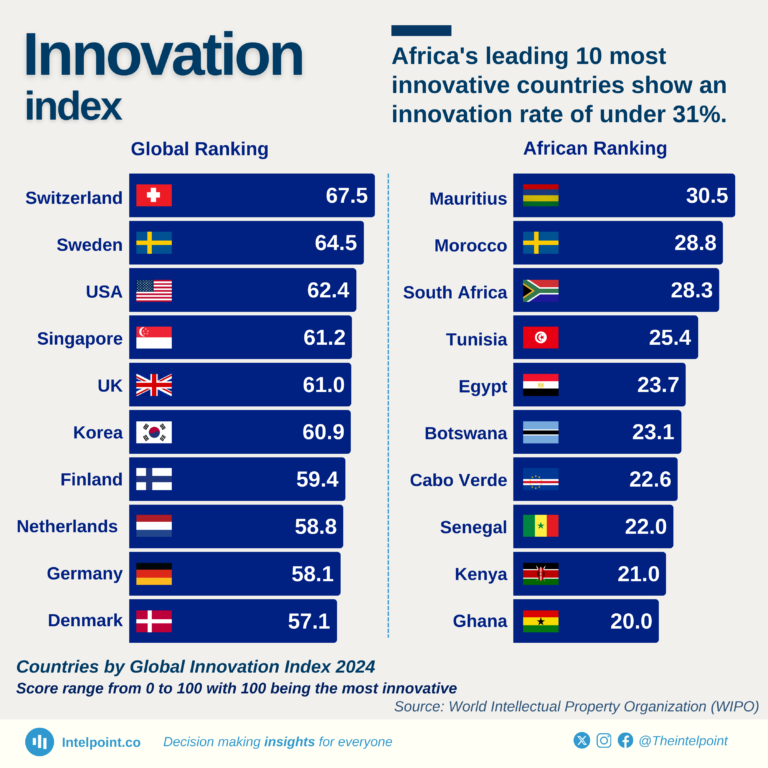
The Global Innovation Index 2024 reveals a striking contrast in innovation performance between countries globally and across Africa. Switzerland leads the global rankings with an impressive score of 67.5, followed by Sweden (64.5) and the USA (62.4), highlighting their sustained investments in research, development, and technological advancement.
In Africa, Mauritius takes the top spot with a score of 30.5, followed closely by Morocco (28.8) and South Africa (28.3). However, even Africa's most innovative nations achieve less than half the score of global leaders, indicating a significant innovation gap.
Nigeria ranks 15th in the African ranking and 113th globally, out of 133 countries, with a score of 17.1.
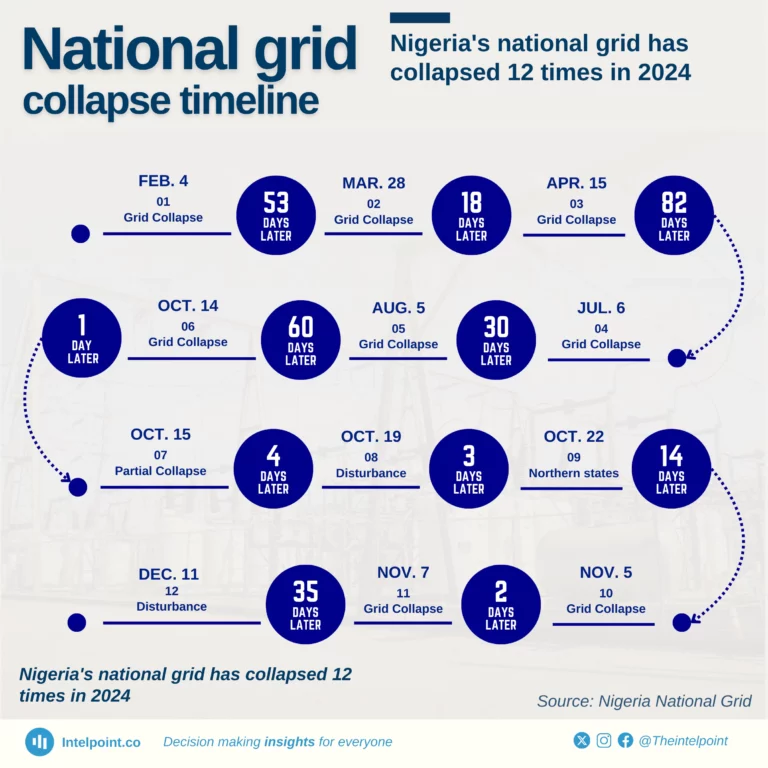
Nigeria's national grid has experienced 12 collapses so far in 2024, a troubling trend that reveals the fragility of the country's energy infrastructure. The timeline highlights intervals ranging from as short as one day to as long as 82 days between incidents. Notably, two consecutive collapses occurred on October 14 and October 15, while a total of 9 collapses occurred in the second half of the year.
Yesterday's collapse came 35 days after November 7, when the grid went down for the 11th time.
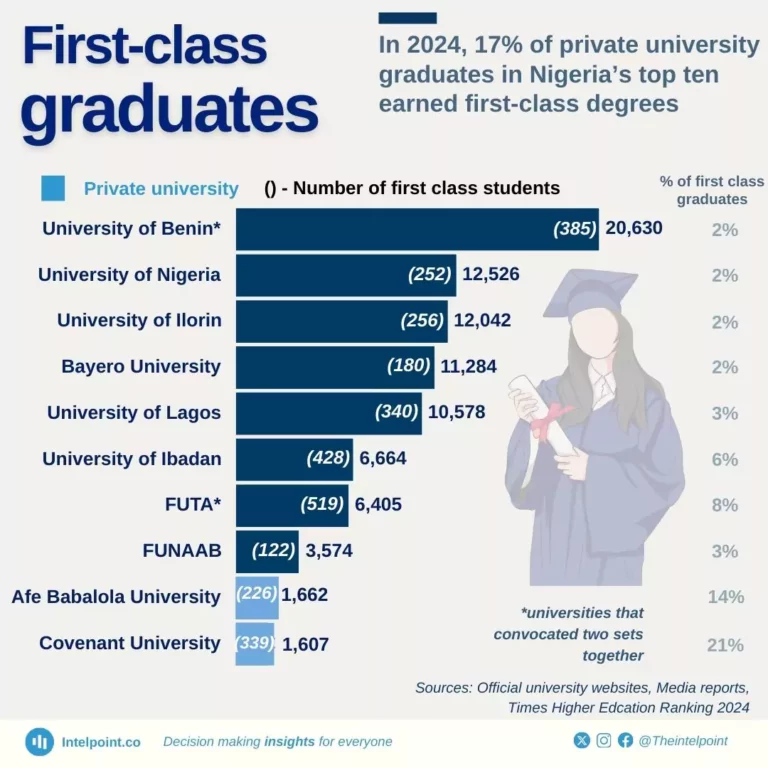
In 2024, the top ten universities in Nigeria graduated 3,047 first-class students. Seventeen per cent of private university students in Nigeria earned first-class degrees, compared to 3% in federal/state universities.
The University of Benin convocated the most first-class students (385), while the Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta (FUNAAB) had the least, with 122.
Covenant University had the highest proportion, with one in five students graduating with a first class.