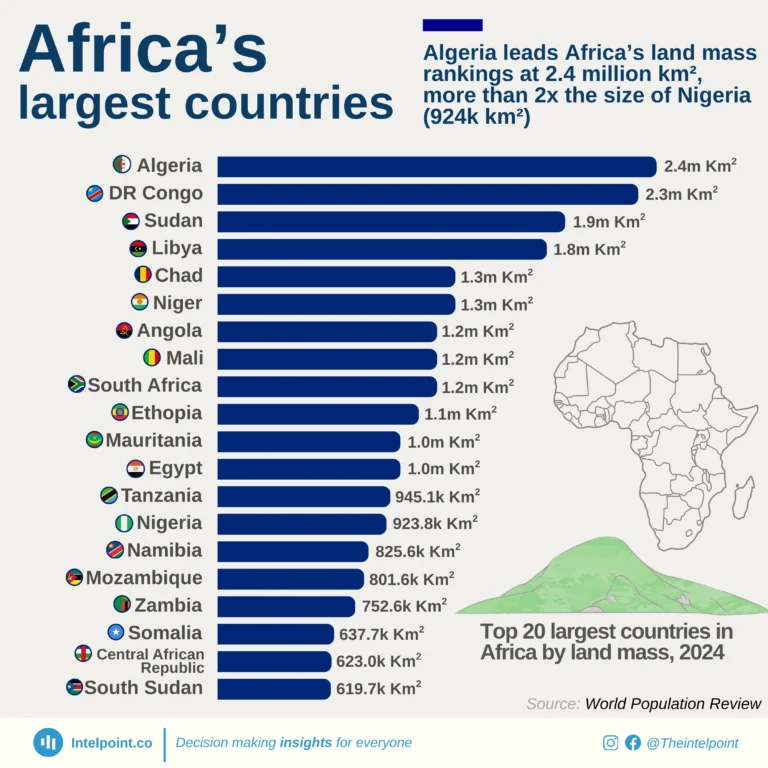
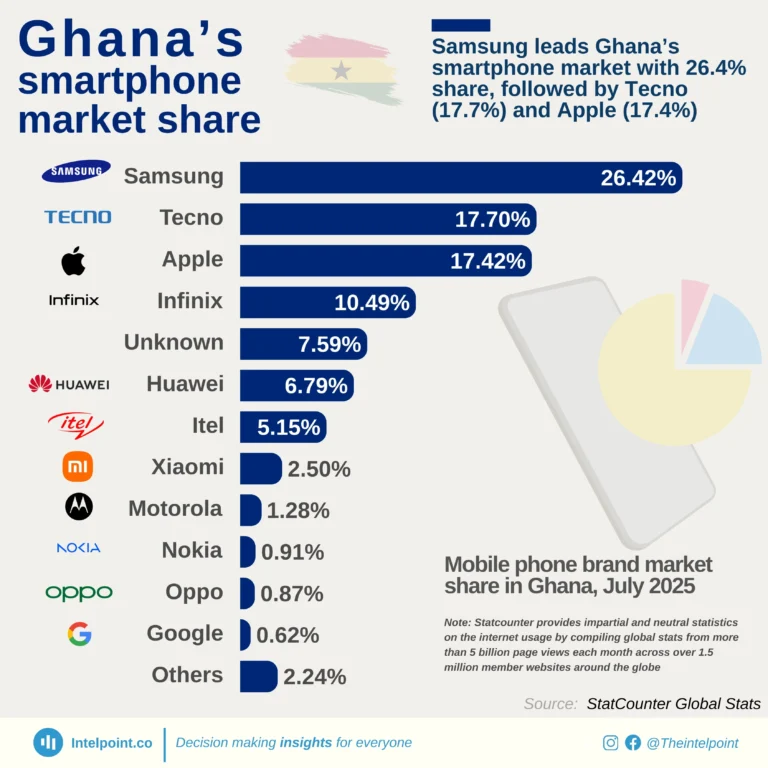
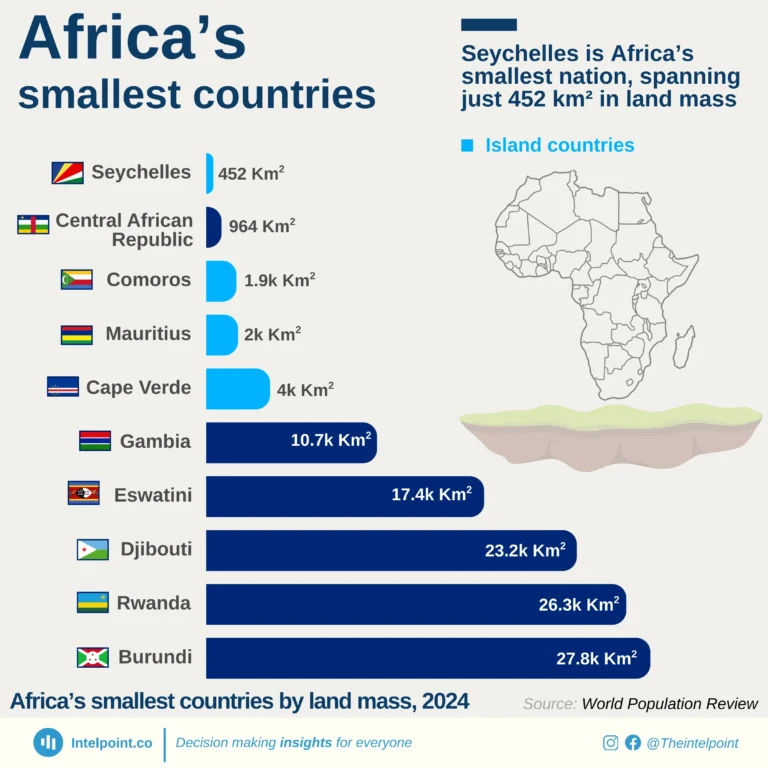
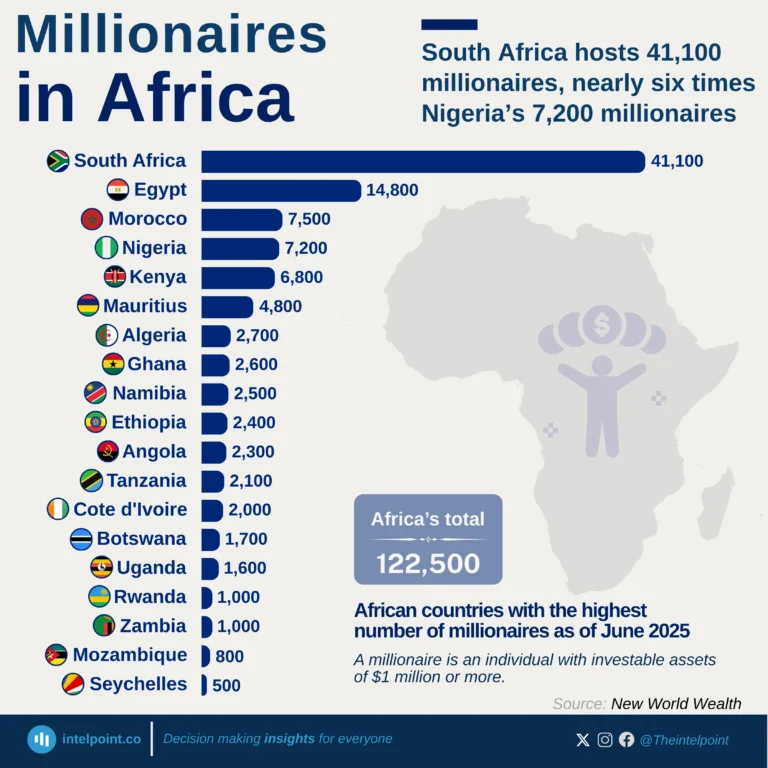
The Global Innovation Index 2024 reveals a striking contrast in innovation performance between countries globally and across Africa. Switzerland leads the global rankings with an impressive score of 67.5, followed by Sweden (64.5) and the USA (62.4), highlighting their sustained investments in research, development, and technological advancement.
In Africa, Mauritius takes the top spot with a score of 30.5, followed closely by Morocco (28.8) and South Africa (28.3). However, even Africa's most innovative nations achieve less than half the score of global leaders, indicating a significant innovation gap.
Nigeria ranks 15th in the African ranking and 113th globally, out of 133 countries, with a score of 17.1.