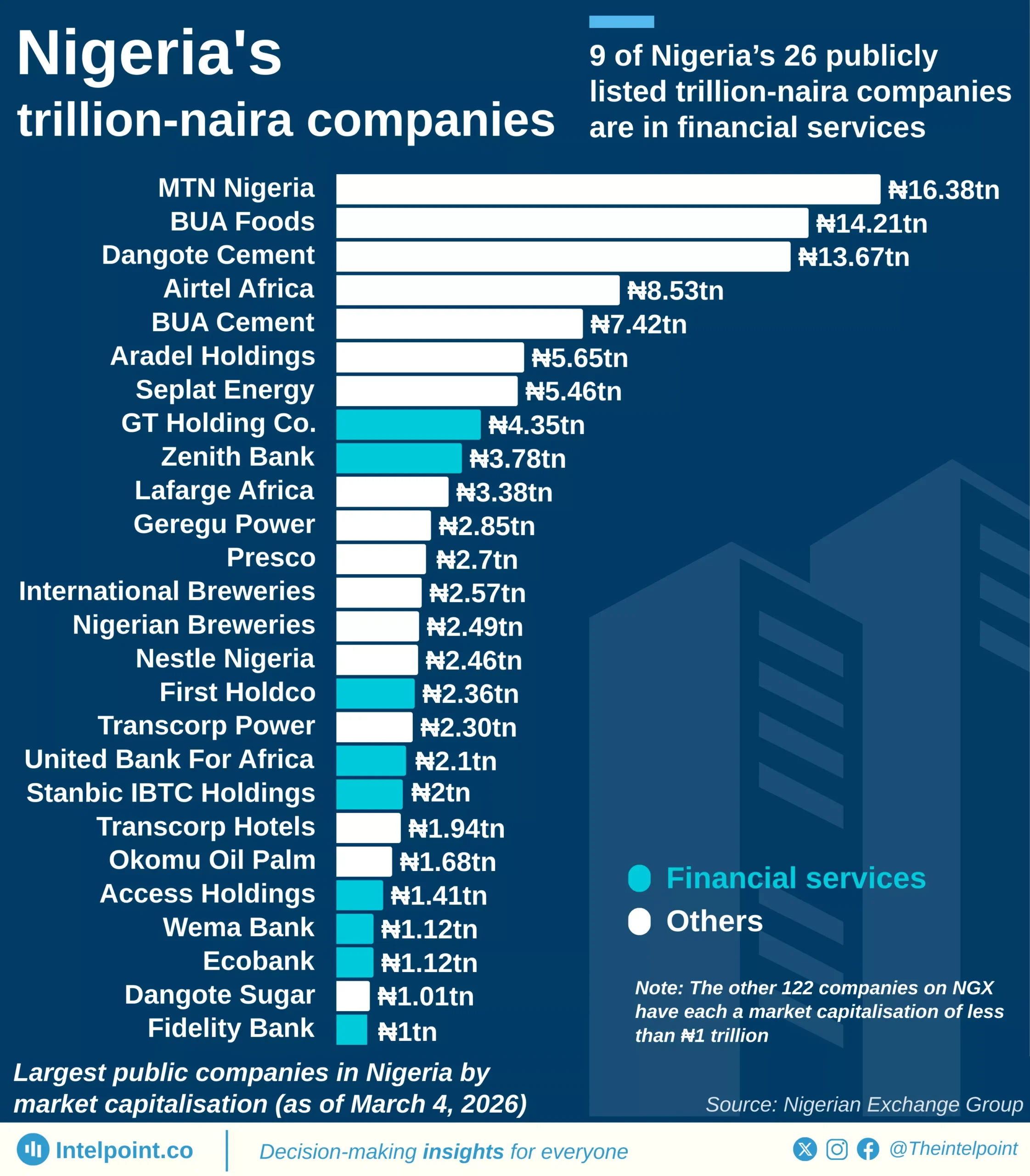
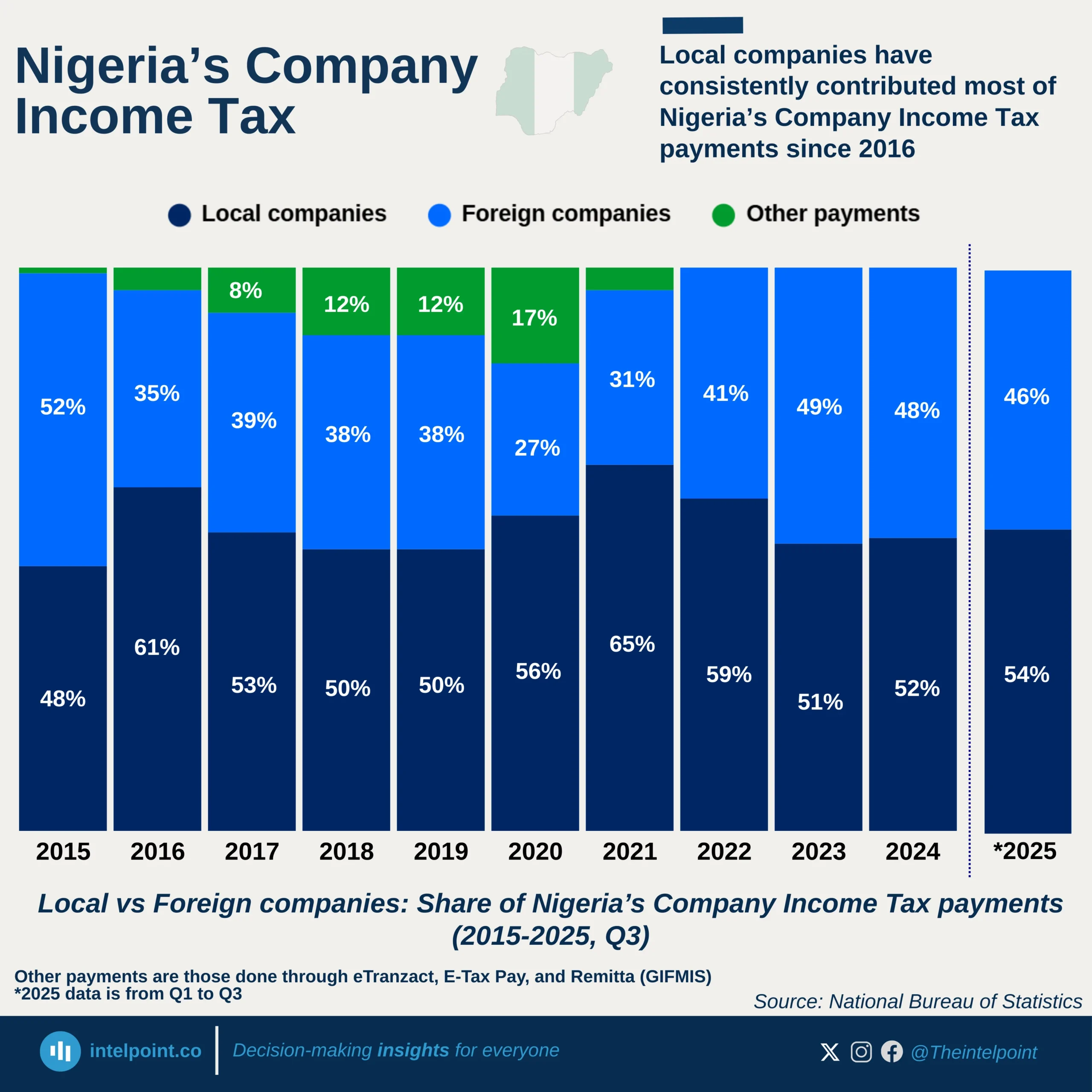
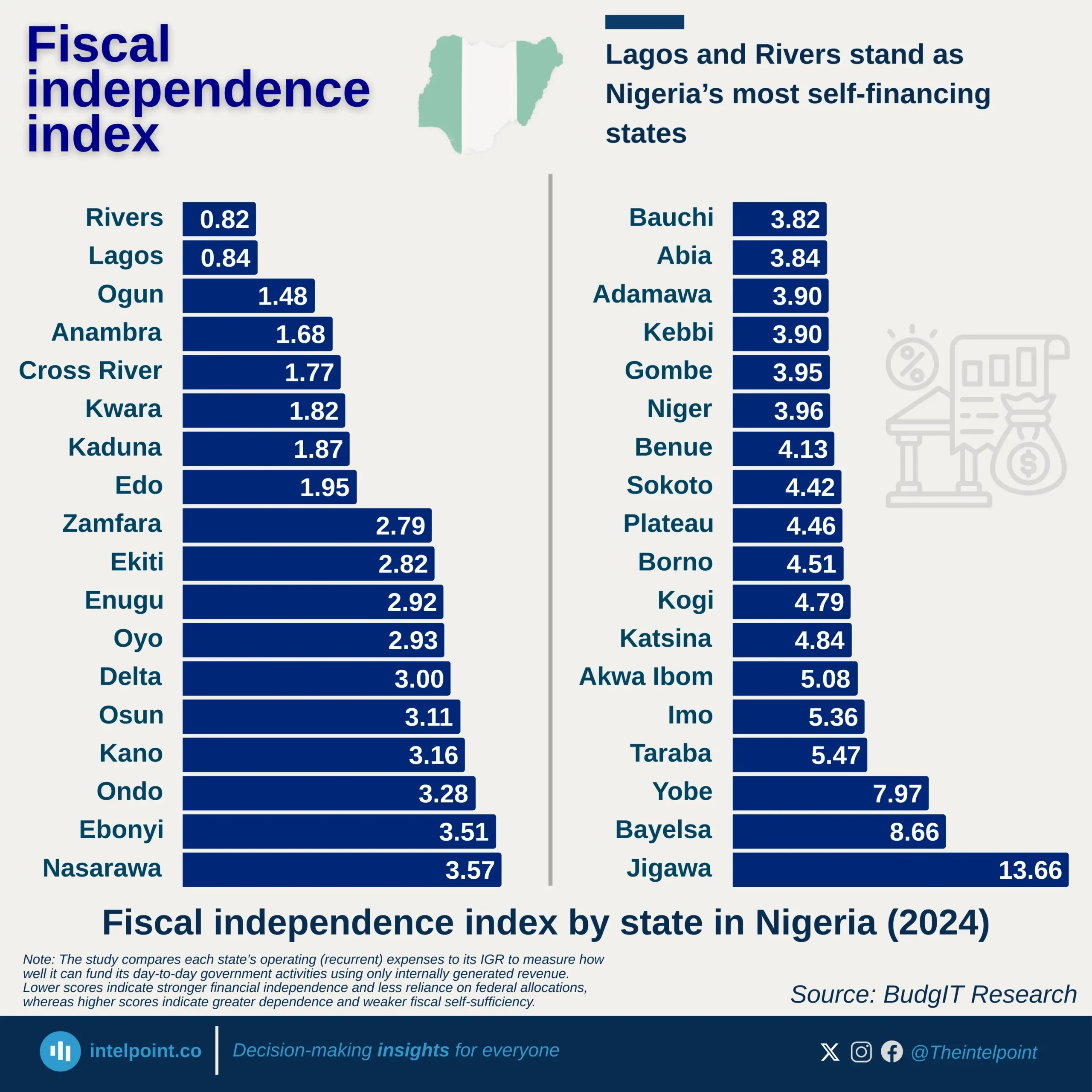
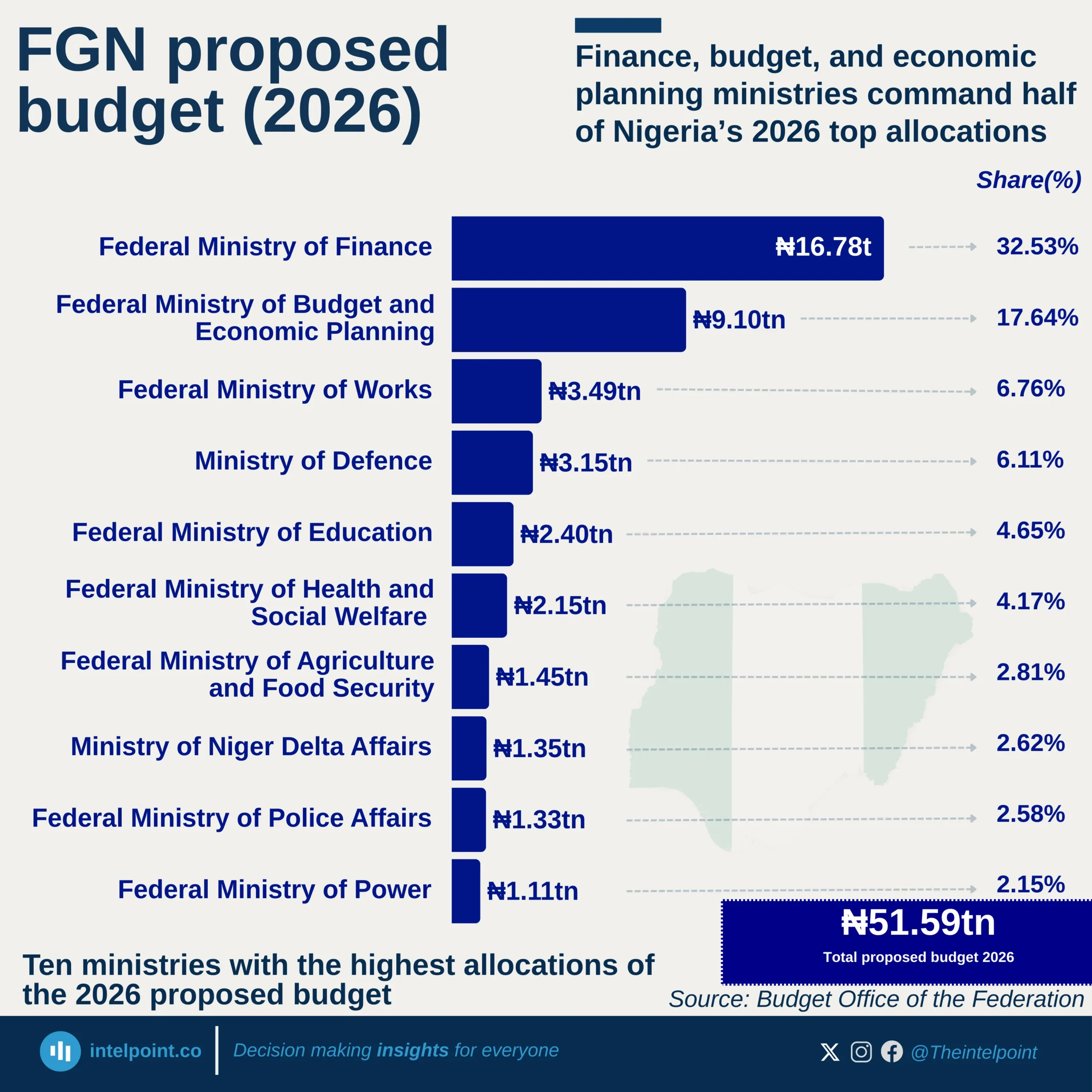
The shadow economy, also called the informal or underground economy, encompasses legal economic activities that remain unregistered, untaxed, and outside official statistics. These include informal trade, unlicensed businesses, and cash-based services, and in many African countries, they form a critical part of livelihoods.
According to estimates from Ernst & Young, Sierra Leone has the largest shadow economy in Africa, at 64.5% of GDP, followed by Niger (56.3%) and Ethiopia (50.2%), where more than half of all economic activity is informal. The report notes that these high percentages are driven by various factors, including the effectiveness of government institutions, the legal framework, and the tax burden.
Even Nigeria, Africa’s fourth largest economy, is estimated to have 30.0% of its GDP occurring off the books. At the lower end of the provided list, Togo (28.1%) still shows significant informality. While such economies can foster resilience and entrepreneurship in regions with limited formal employment, they also represent lost tax revenue, weaker regulation, and economic blind spots. The report's findings highlight a strong link between lower-income economies and larger shadow economies.