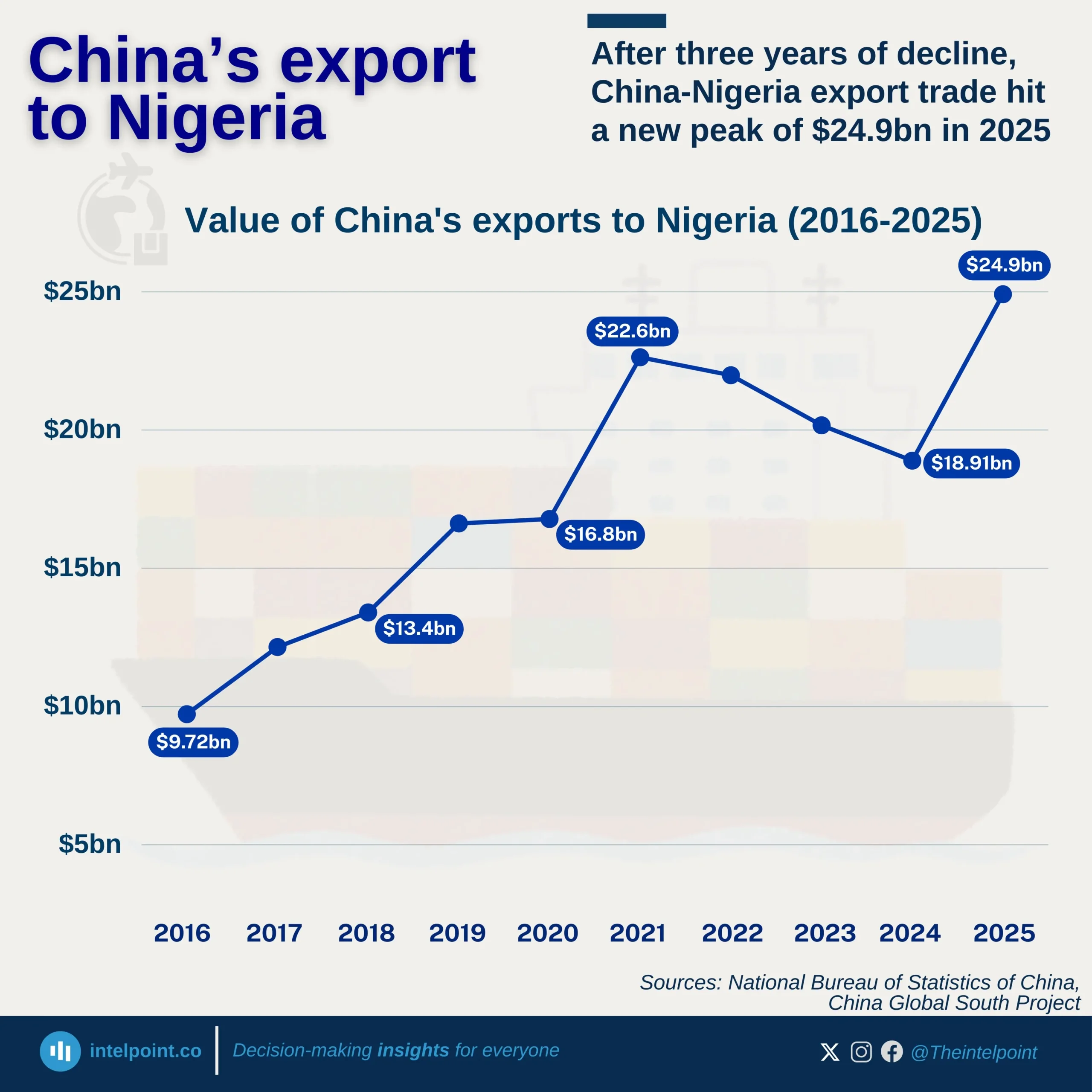
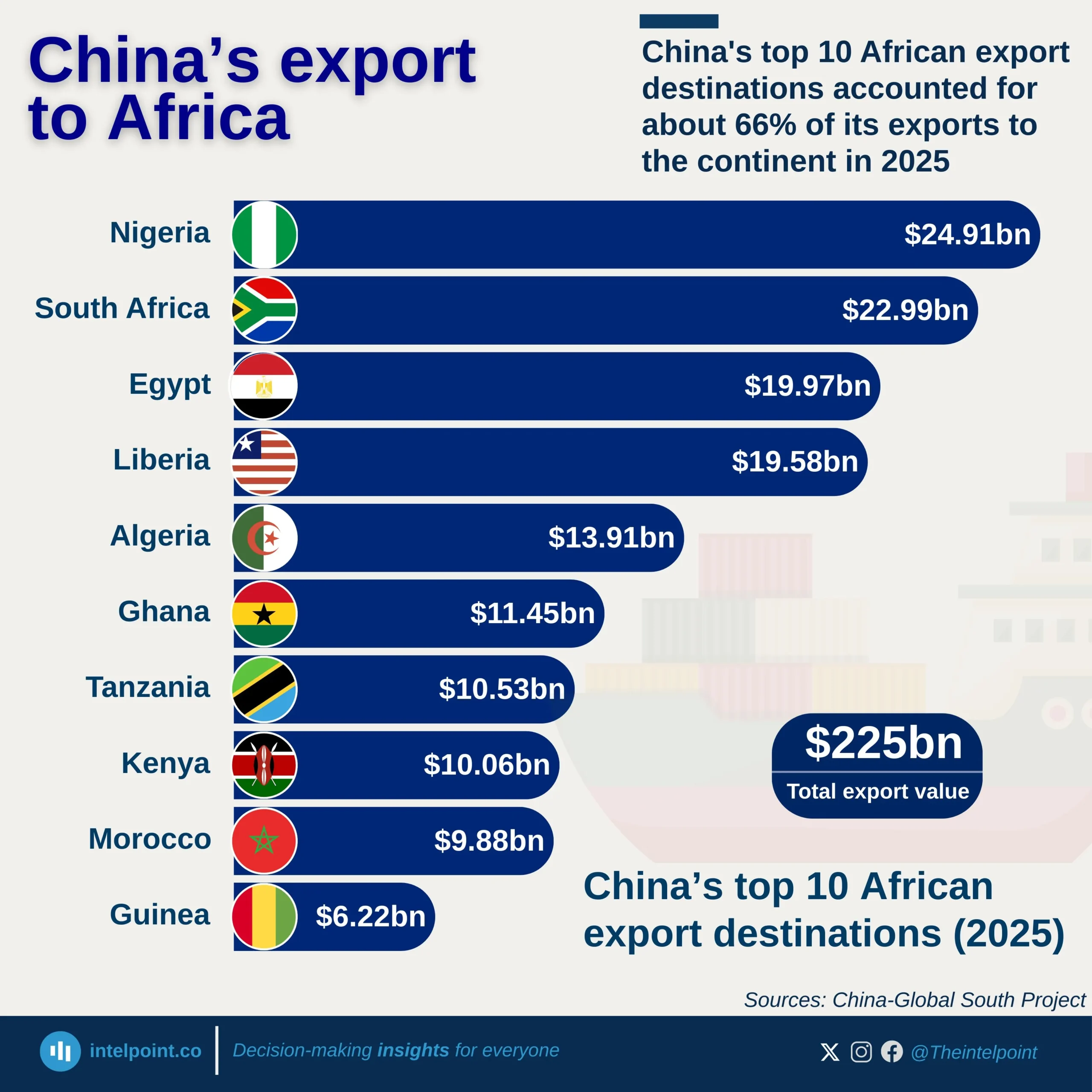
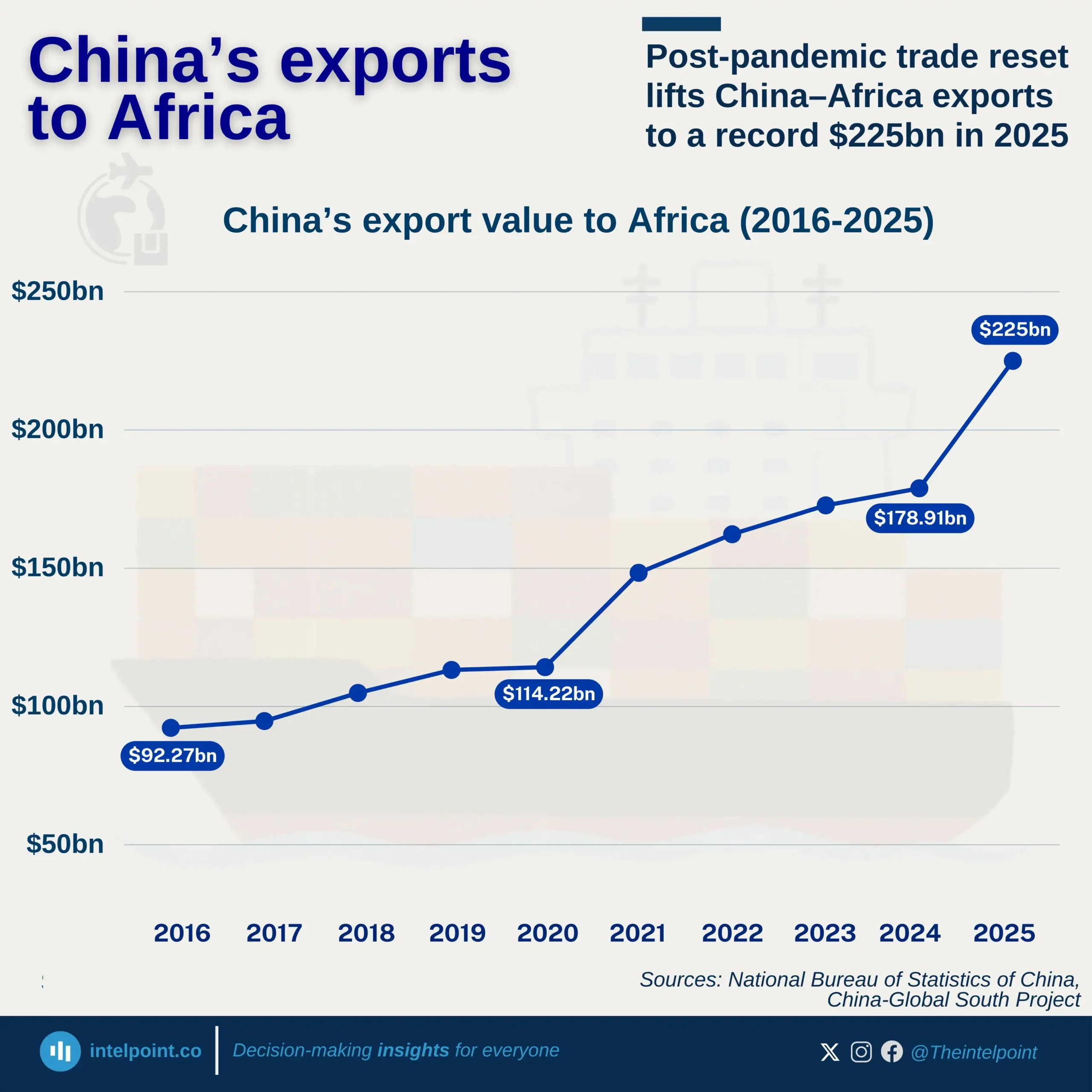
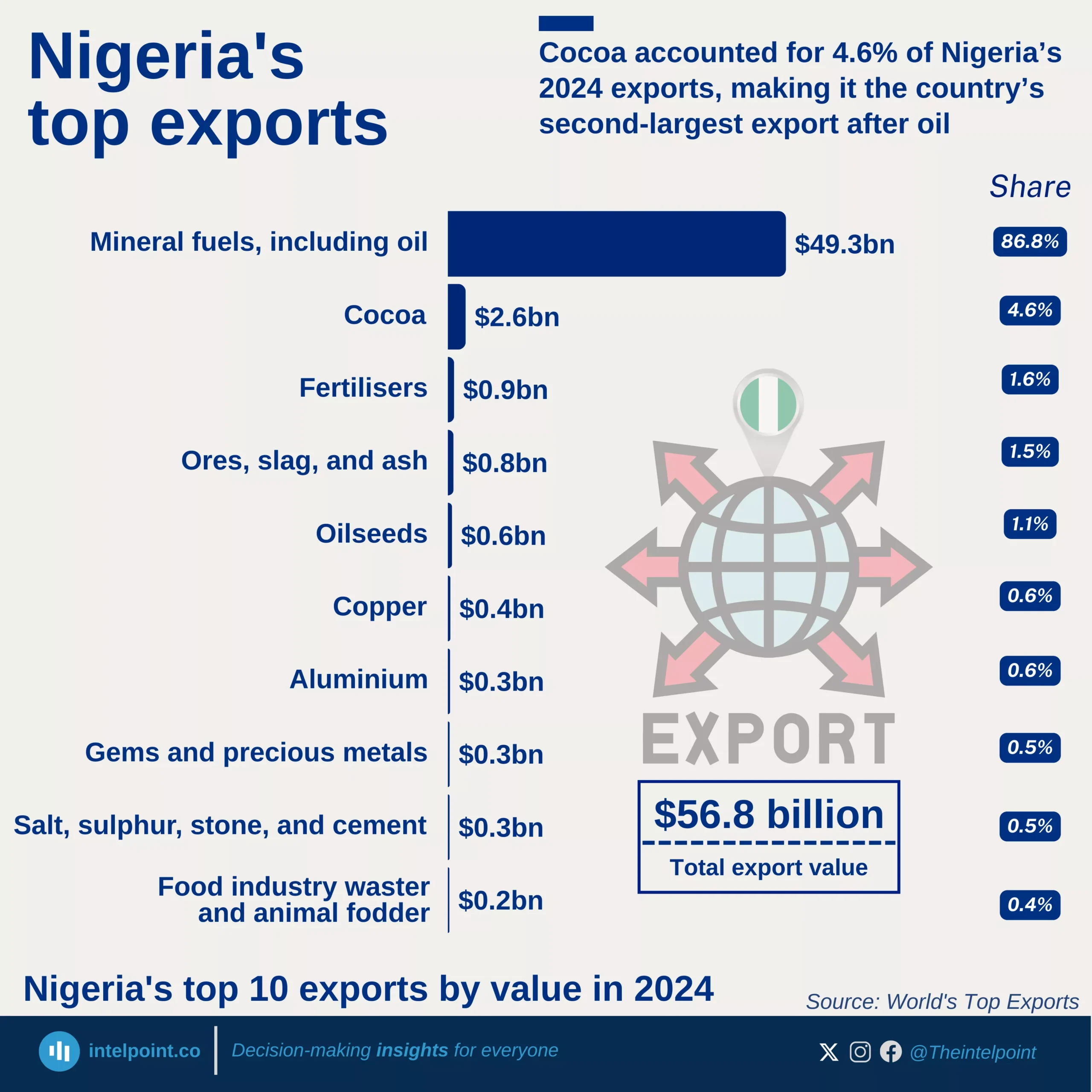
Key Takeaways:
In 2023, mineral fuels, oils, and distillation products were China’s largest imports from Nigeria, valued at $1.41 billion. This was followed by imports of ores, slag, and ash, which amounted to $399.09 million, and salt, sulphur, earth, stone, plaster, lime, and cement, valued at $305.91 million. Copper imports totaled $142.07 million, reflecting China's demand for industrial inputs.
Nigeria also exported a range of agricultural and animal products to China, including oil seeds ($50.73 million), raw hides and skins ($7.85 million), and coffee, tea, maté, and spices ($7.39 million).