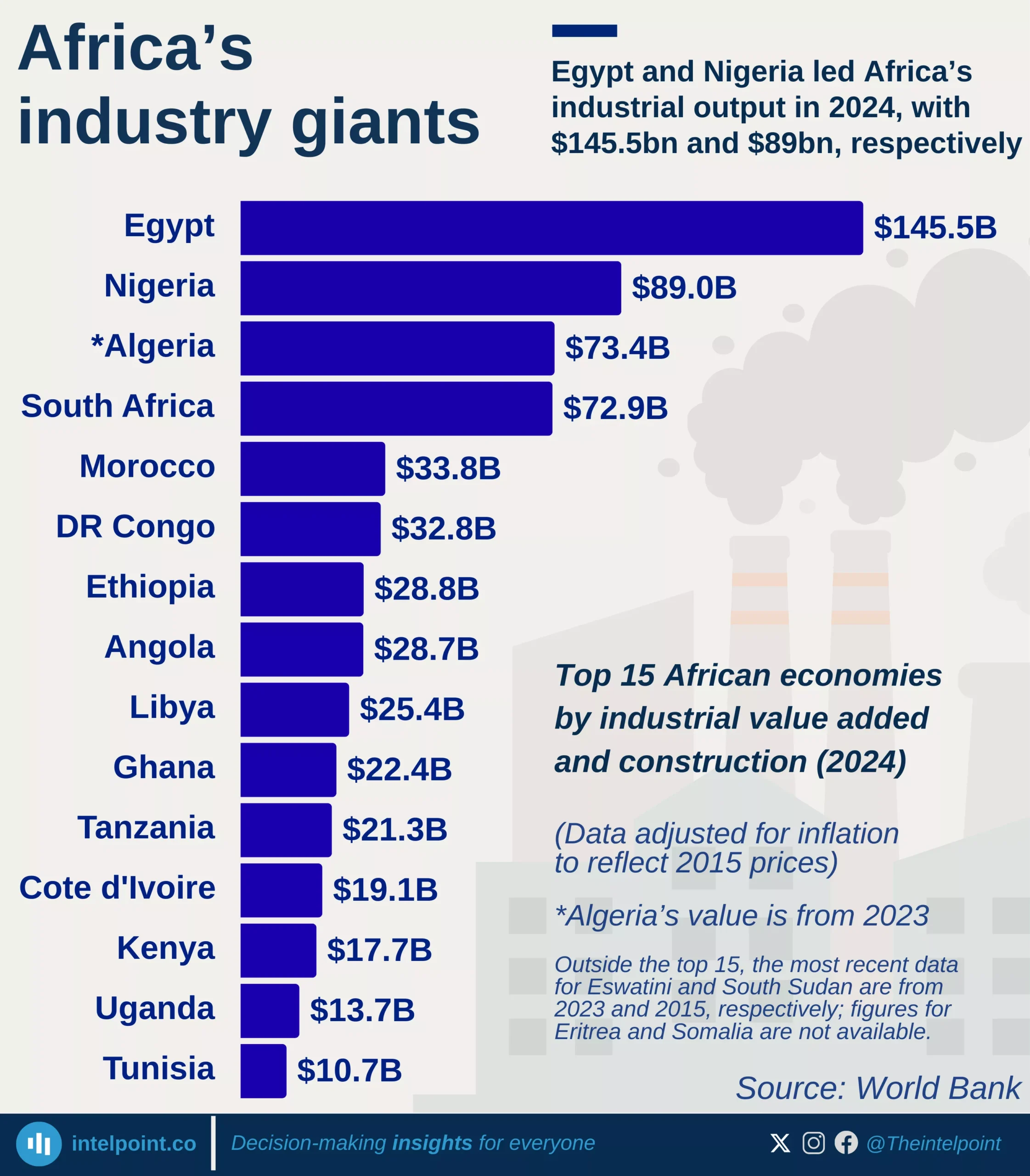
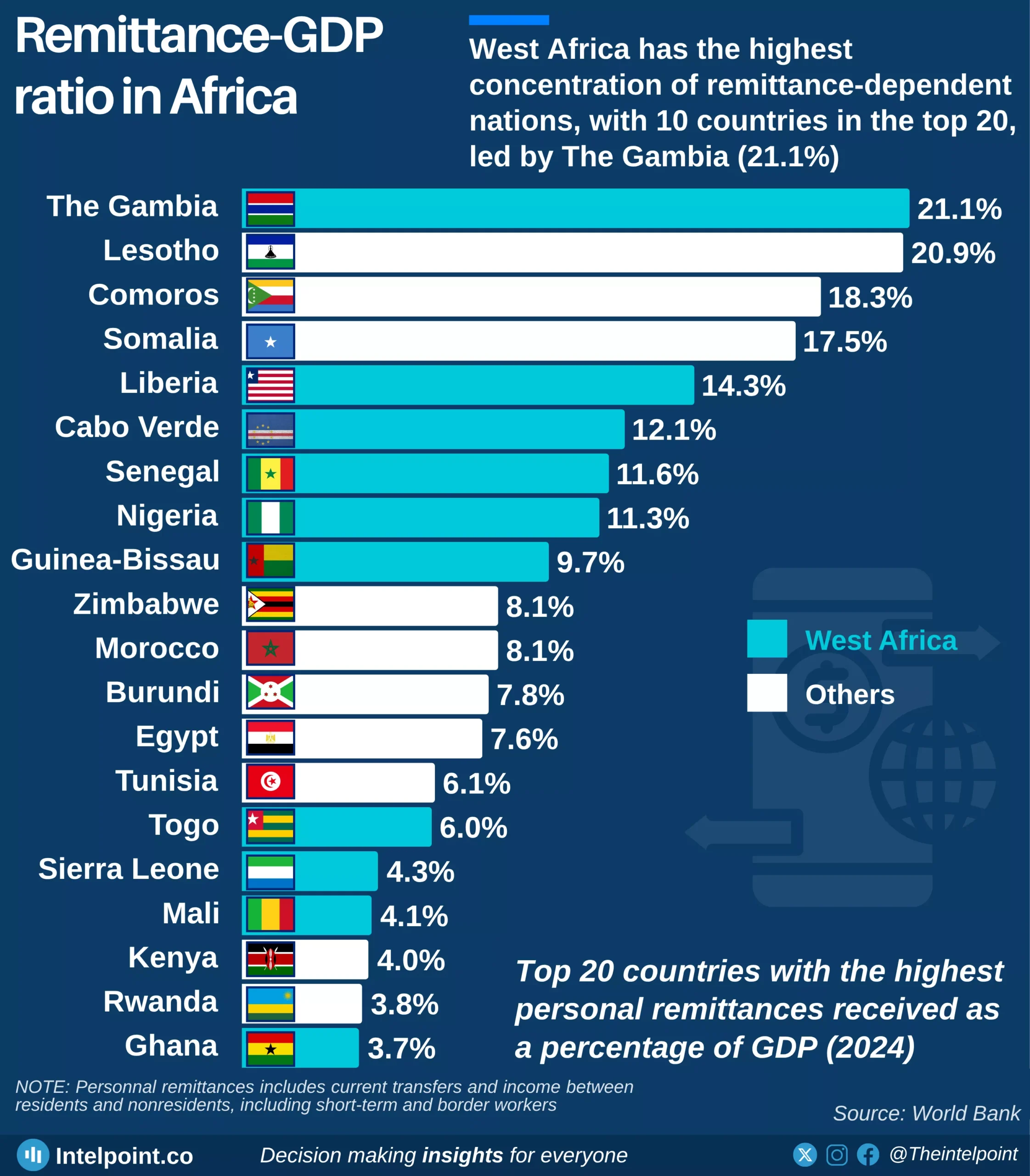
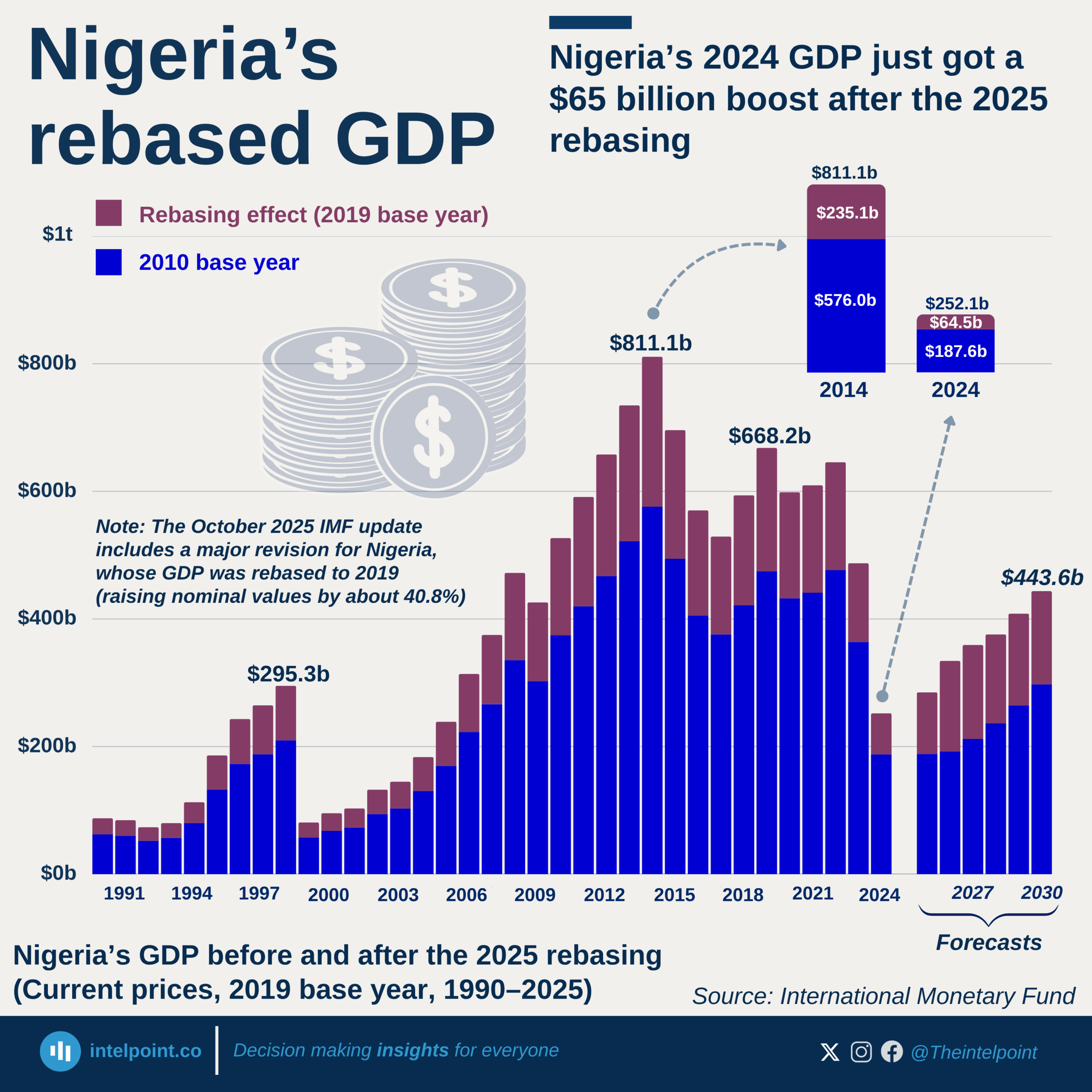
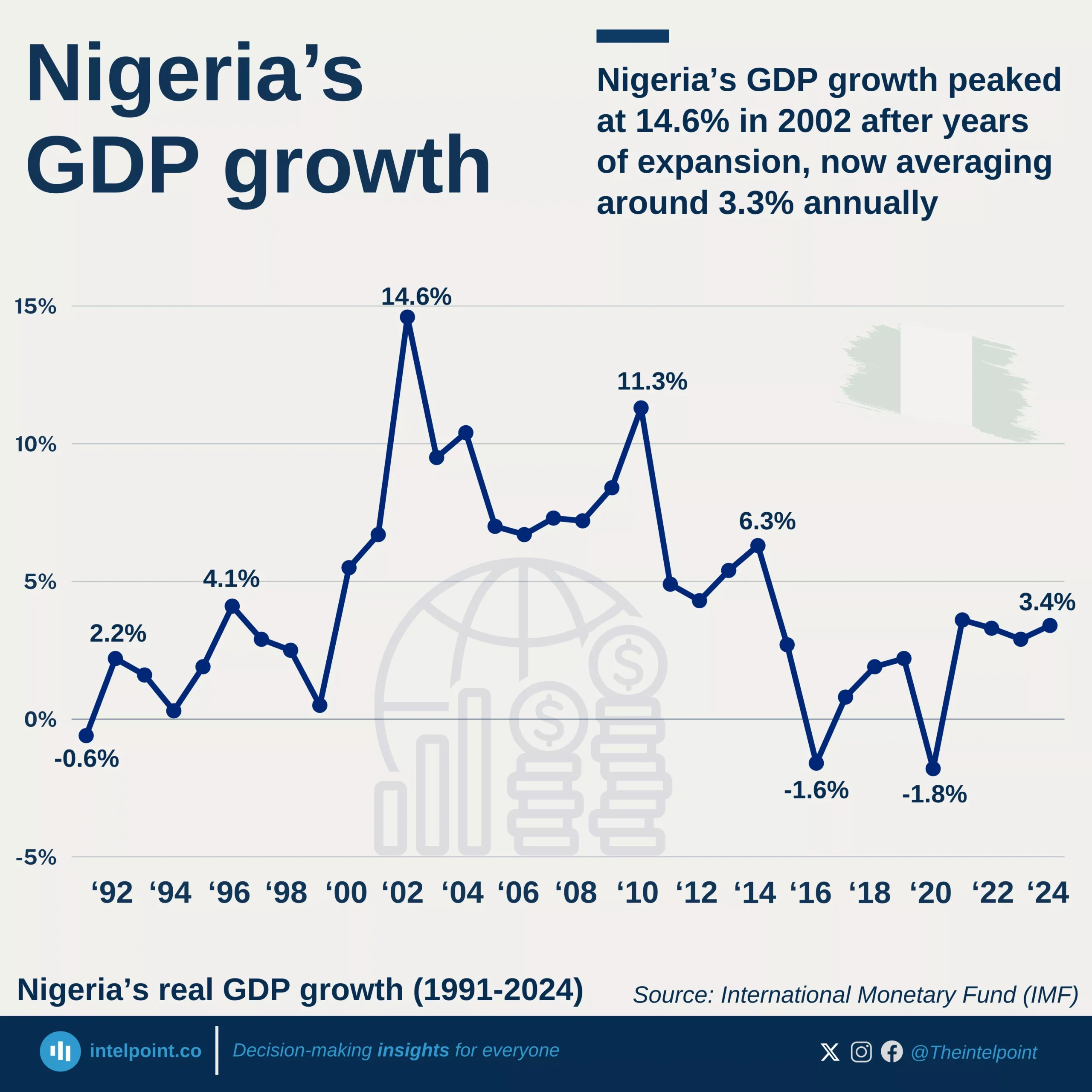
In Q1 2024, Nigeria's financial institutions accounted for 6.40% of GDP, nearly double their 2022 contribution of 3.60% and significantly up from 4.60% in 2023. This highlights the increasing role of financial institutions in driving economic growth and stability.
From 2016 to 2019, the sector’s share of GDP remained relatively stagnant, hovering around 2.60% to 2.70%. The turning point came in 2020, when the figure climbed to 3.00%, coinciding with major digital banking adoption, financial inclusion policies, and the rise of fintech startups. Since then, the sector has grown consistently, reflecting deeper financial penetration and economic formalisation.