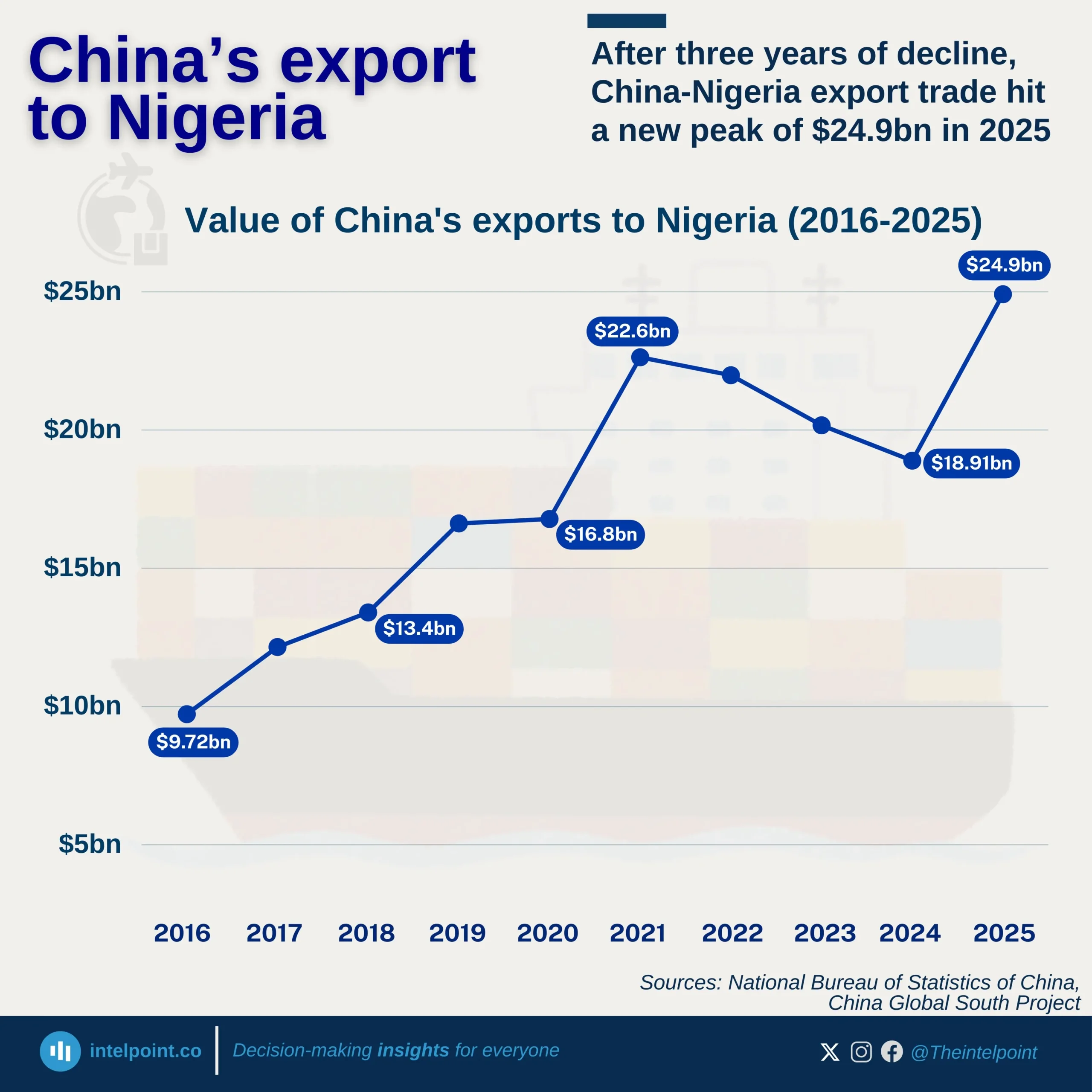
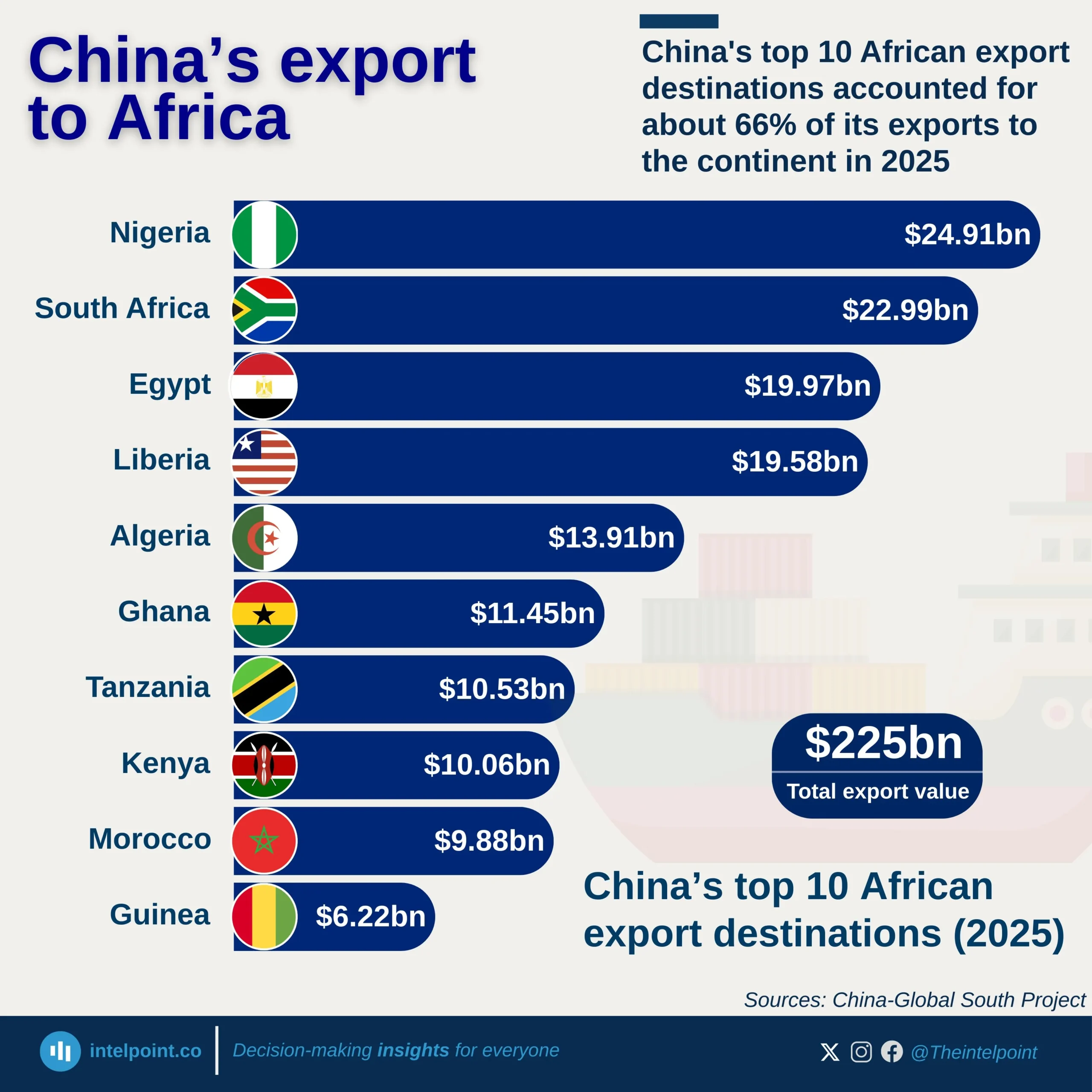
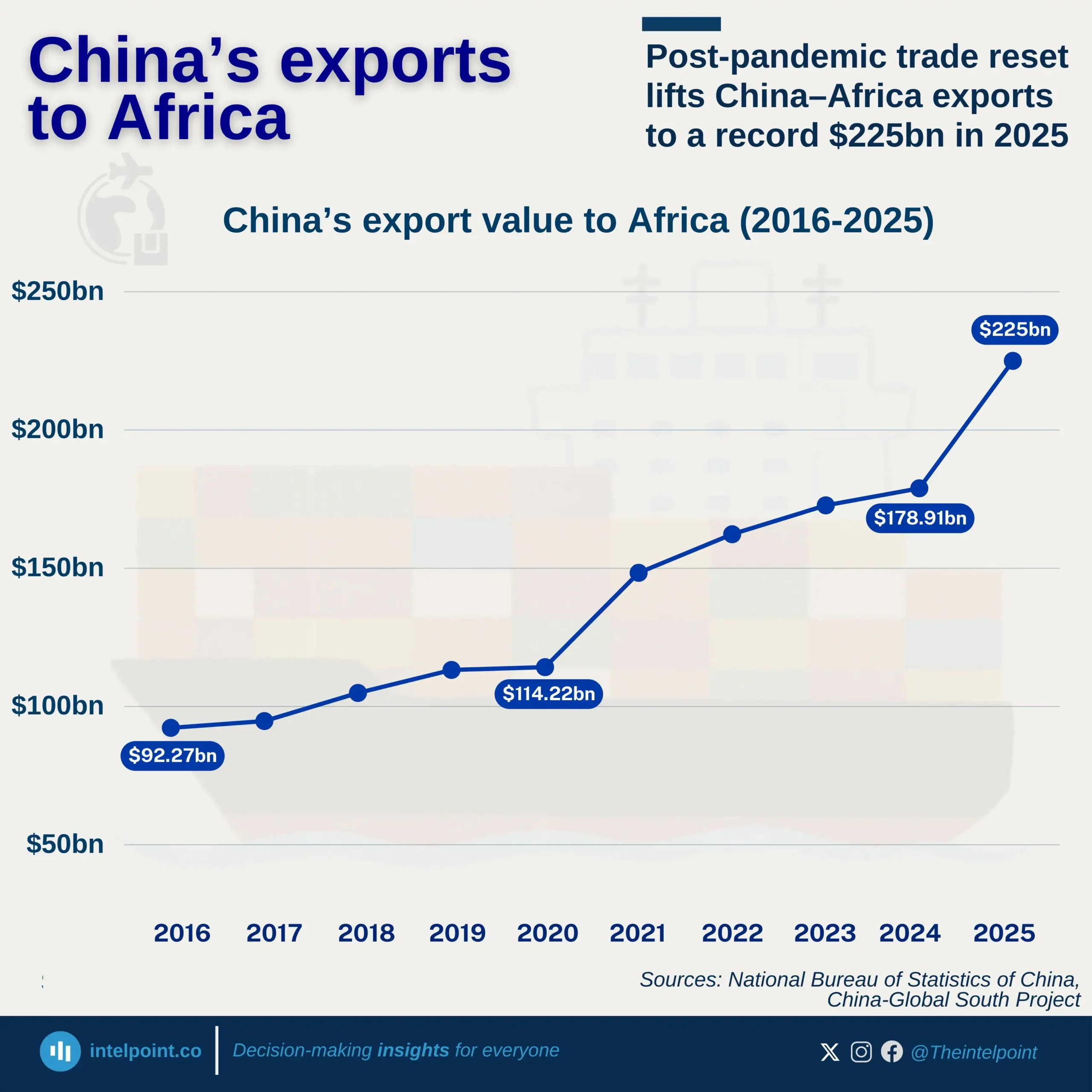
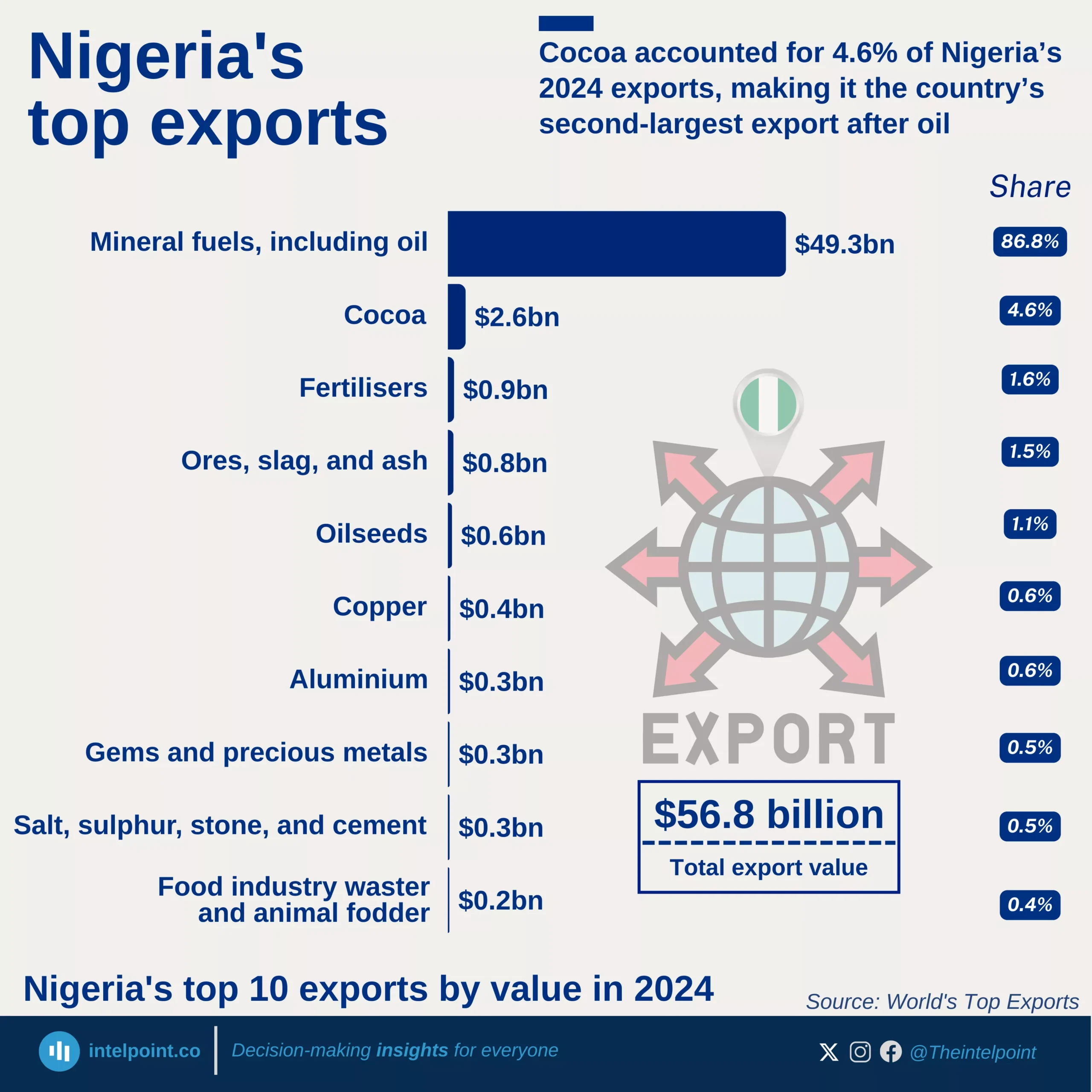
From the World Bank data, Djibouti’s inflation rate has experienced obvious fluctuations over the past decade, with peaks and troughs. The highest inflation rate during this period occurred in 2022, reaching 5.18%. Conversely, 2015 saw the lowest inflation rate at -0.85%, highlighting a brief period of deflation. The years 2016, 2019, and 2022 were particularly notable for high inflation rates. Despite these fluctuations, other years, including 2014, 2017, 2018, and 2023, had relatively stable inflation, with modest increases or decreases. In 2023, the inflation rate notably dropped to 1.50%, a significant decrease from the 2022 peak.
In summary, the data illustrates that while Djibouti has faced periods of inflationary pressure, particularly in 2019 and 2022, the country has also seen years of lower inflation, contributing to an overall mixed but progressively stable inflation trend in recent years.