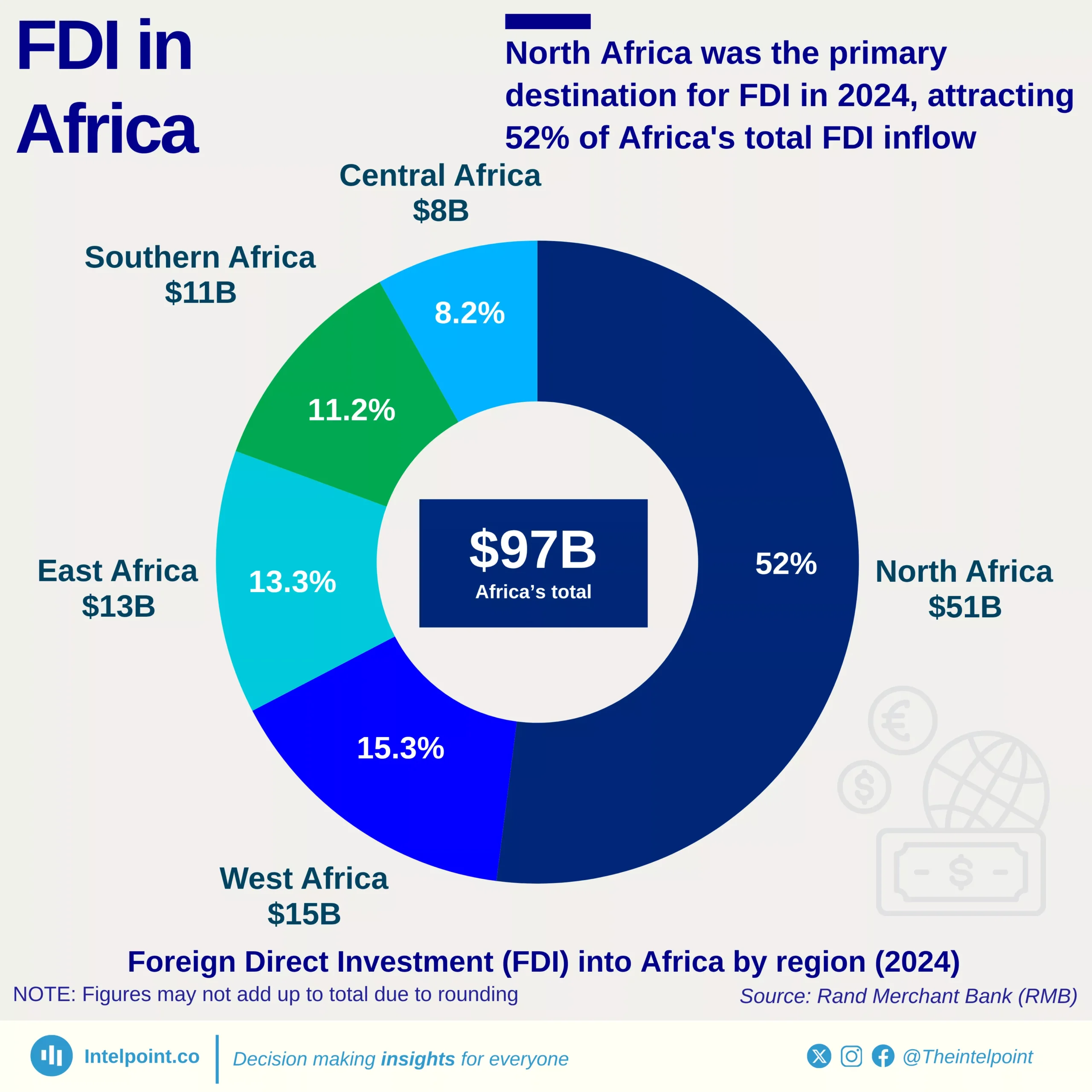
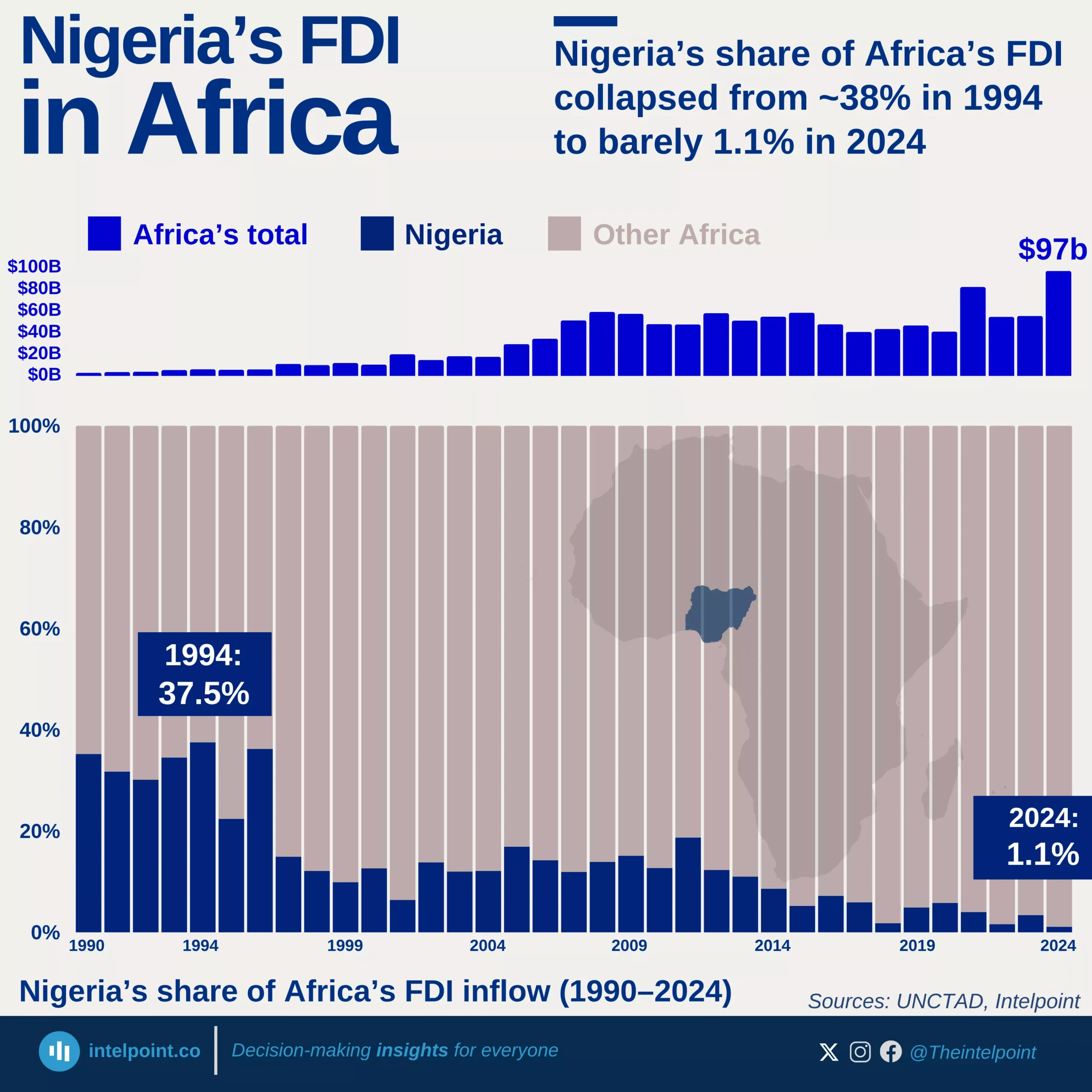
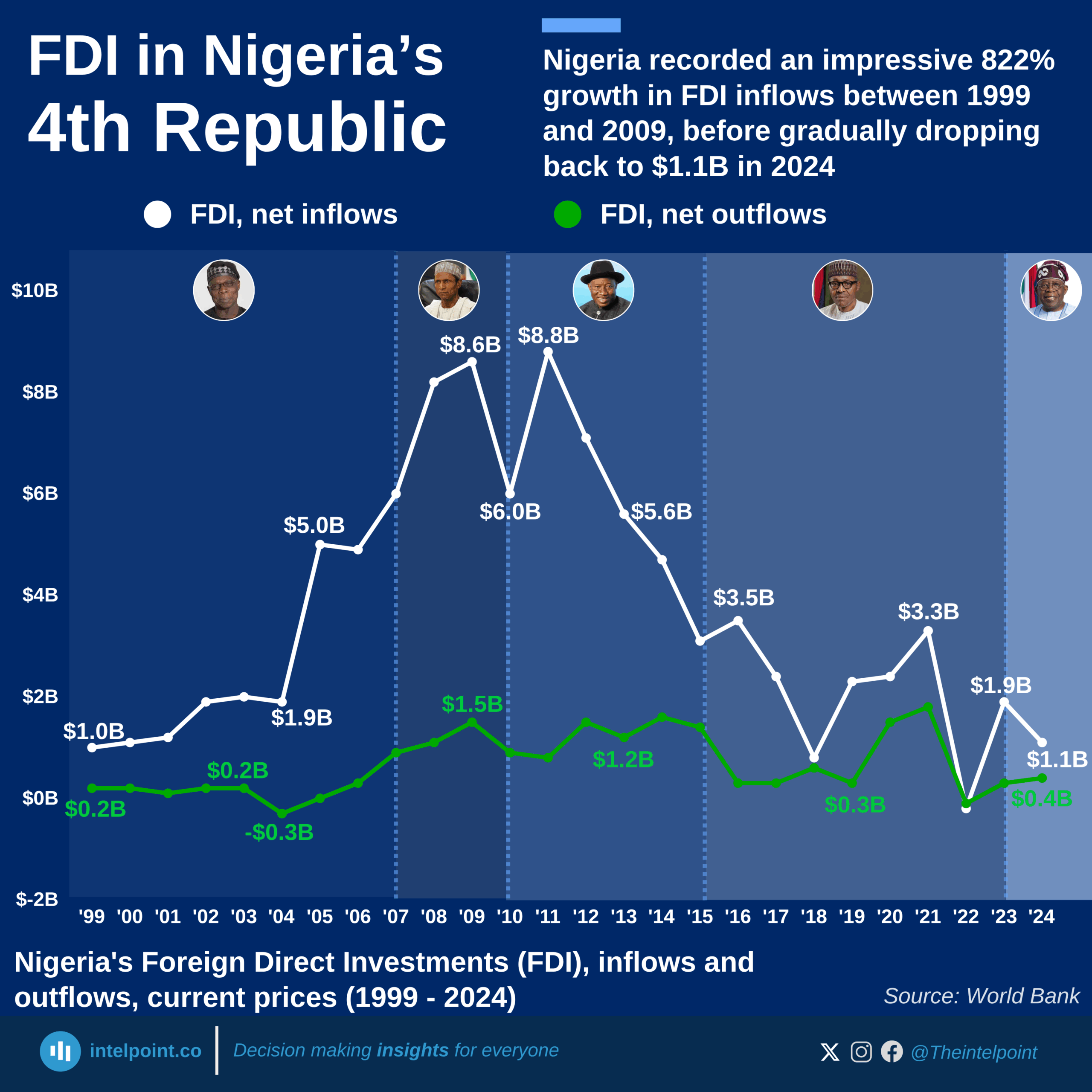
Over the last 35 years, Ghana’s foreign direct investment (FDI) journey has been dramatic. From a baseline of just $0.01 billion in 1990, inflows began to pick up in the early 2000s and surged significantly after 2006. Between 2008 and 2014, FDI remained above $2.5 billion annually, signalling investor optimism as Ghana became one of Africa’s fastest-growing economies and an emerging oil producer. The peak came in 2019, when Ghana drew $3.88 billion, its highest-ever annual inflow.
However, the global pandemic disrupted this momentum. Inflows fell to $1.88 billion in 2020, and have not crossed the $2 billion mark since. The most recent figures show $1.67 billion in 2024, pointing to a gradual recovery but still well below pre-pandemic highs.