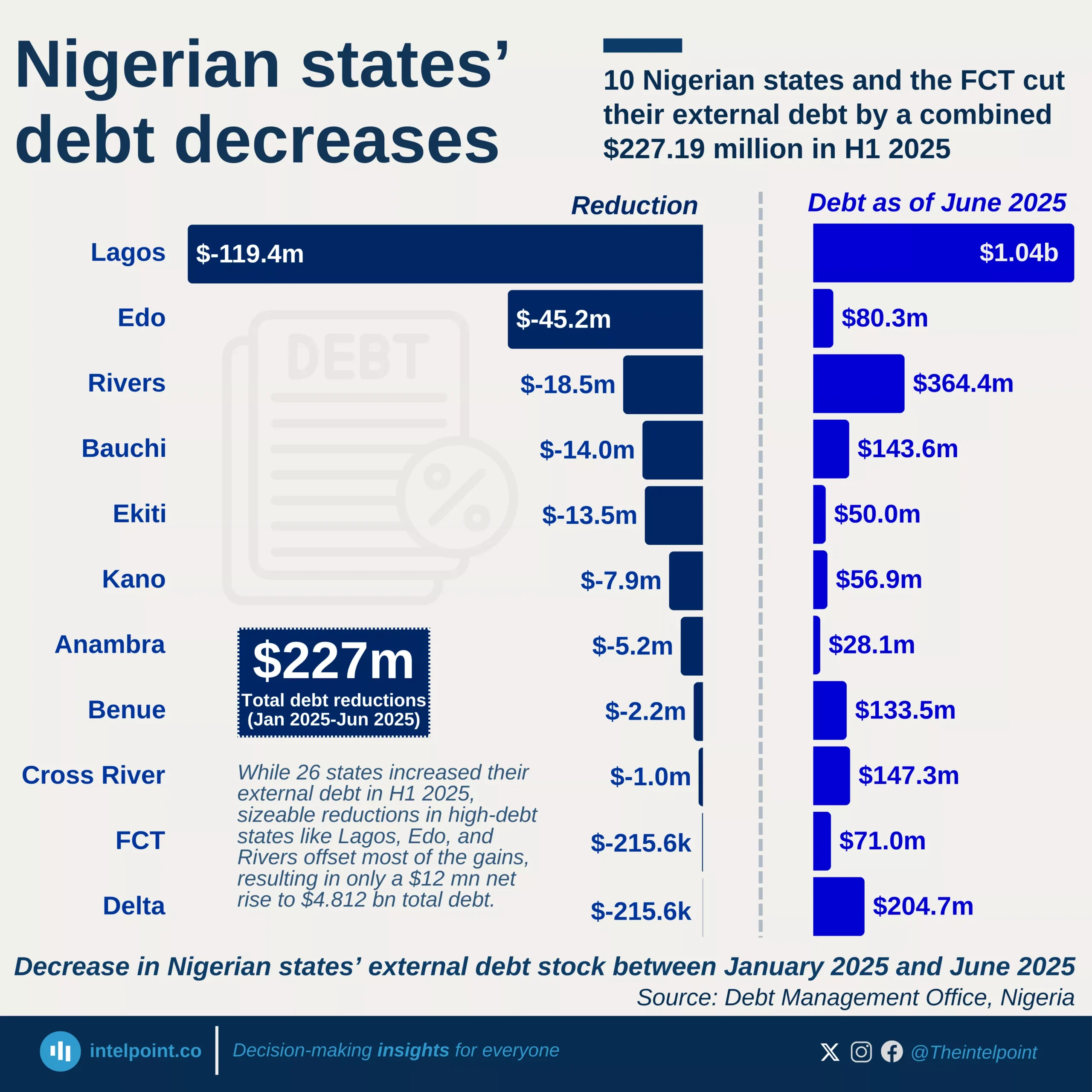
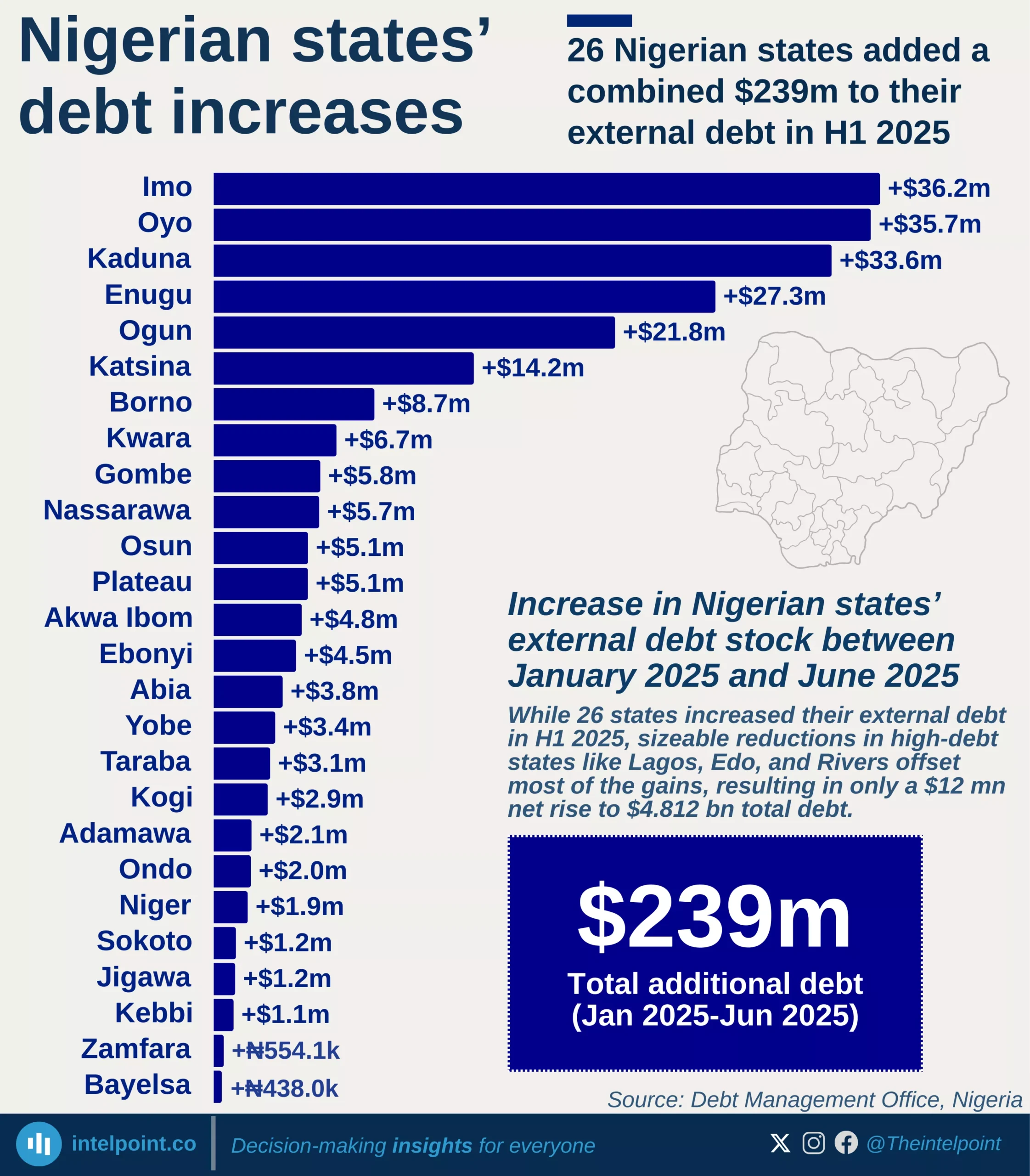
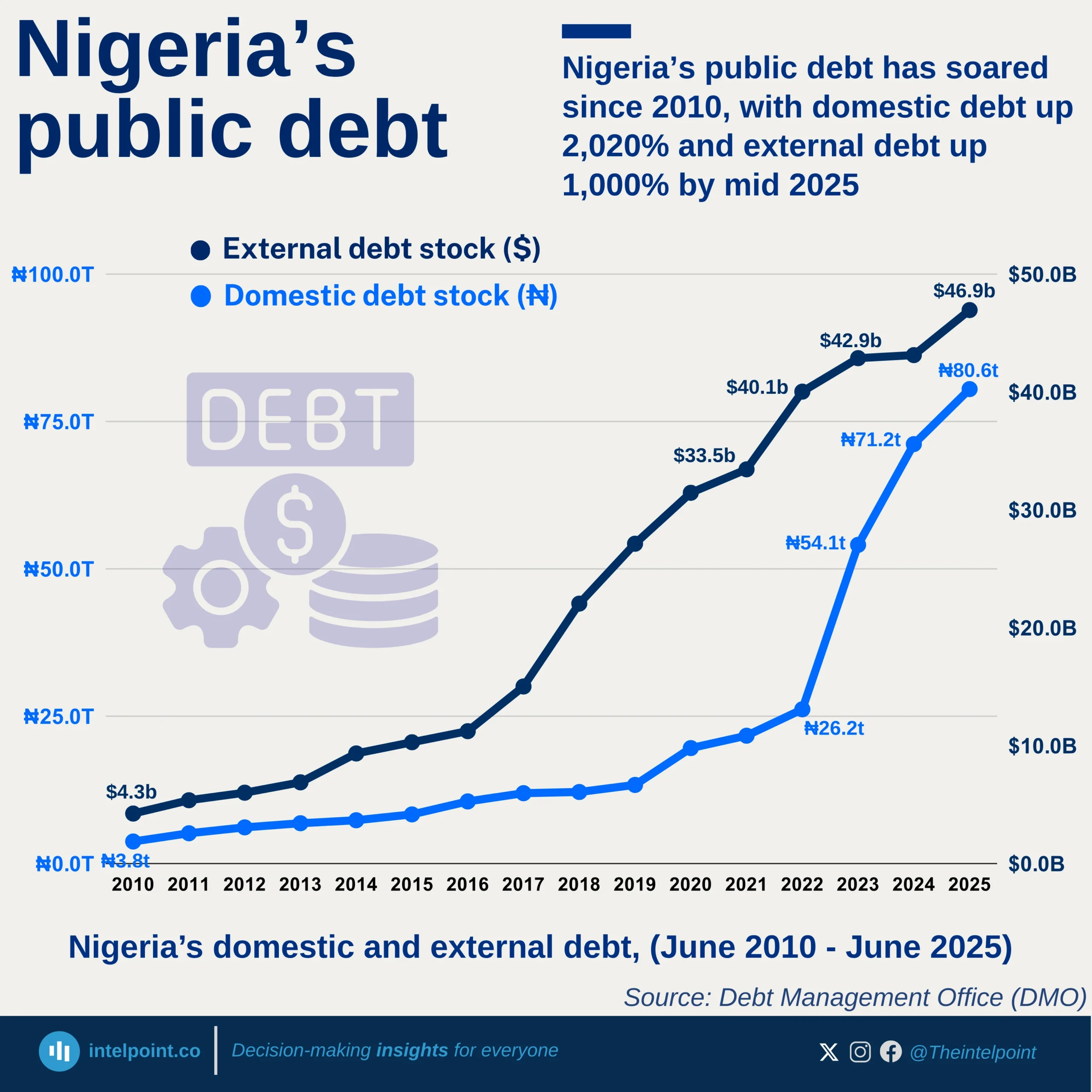
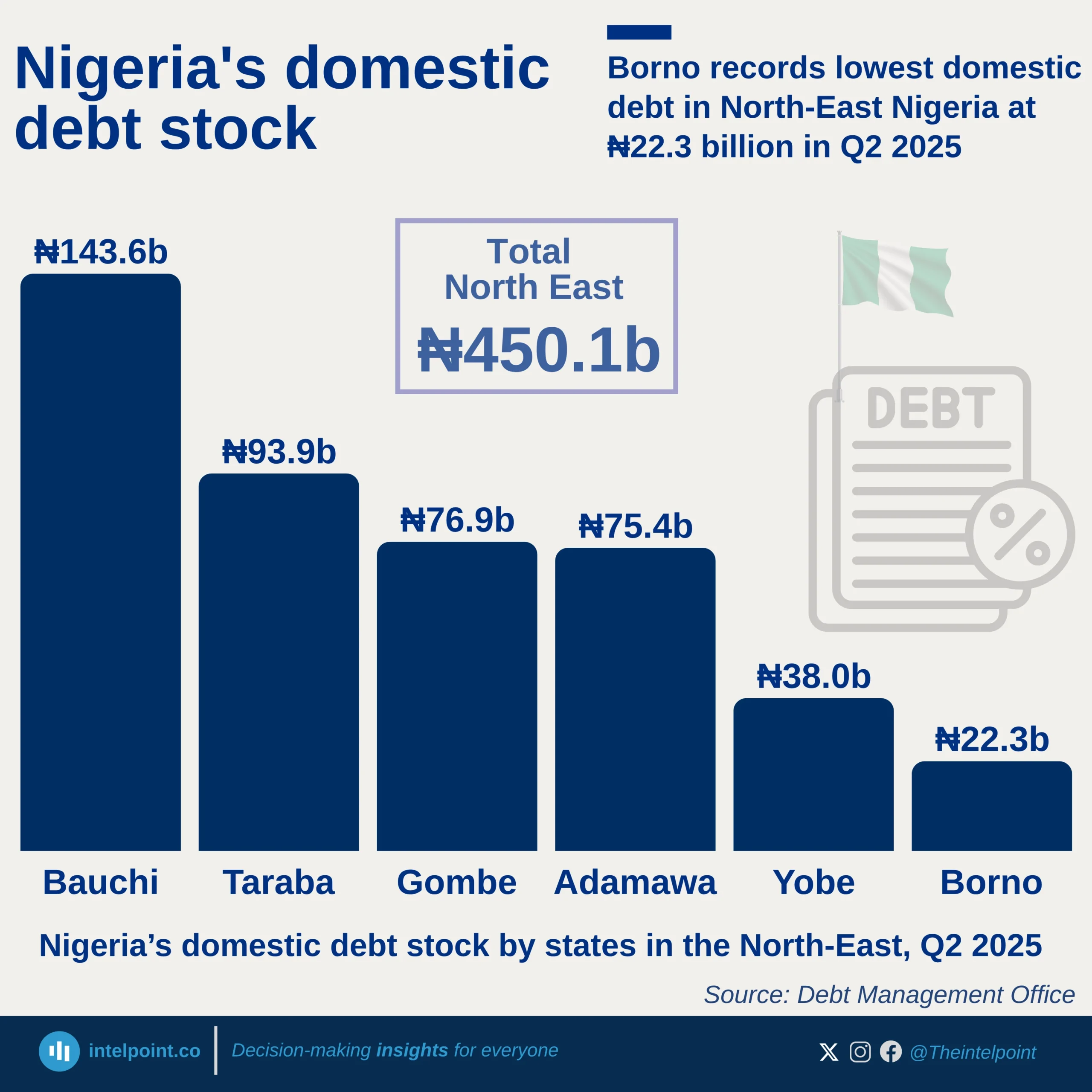
The cost of borrowing in Africa has reached alarming levels, with 27.5% of government revenue now going towards interest payments, a sharp rise from 6.8% in 2008. This means that for every $1 a government earns, nearly 28 cents are spent on servicing debt alone, leaving little room for infrastructure, healthcare, or education investments. At the same time, the interest burden as a percentage of GDP has also increased, jumping from 5.4% in 2008 to 8.2% in 2024. Governments are now paying more for the money they borrow, putting fiscal sustainability at risk.