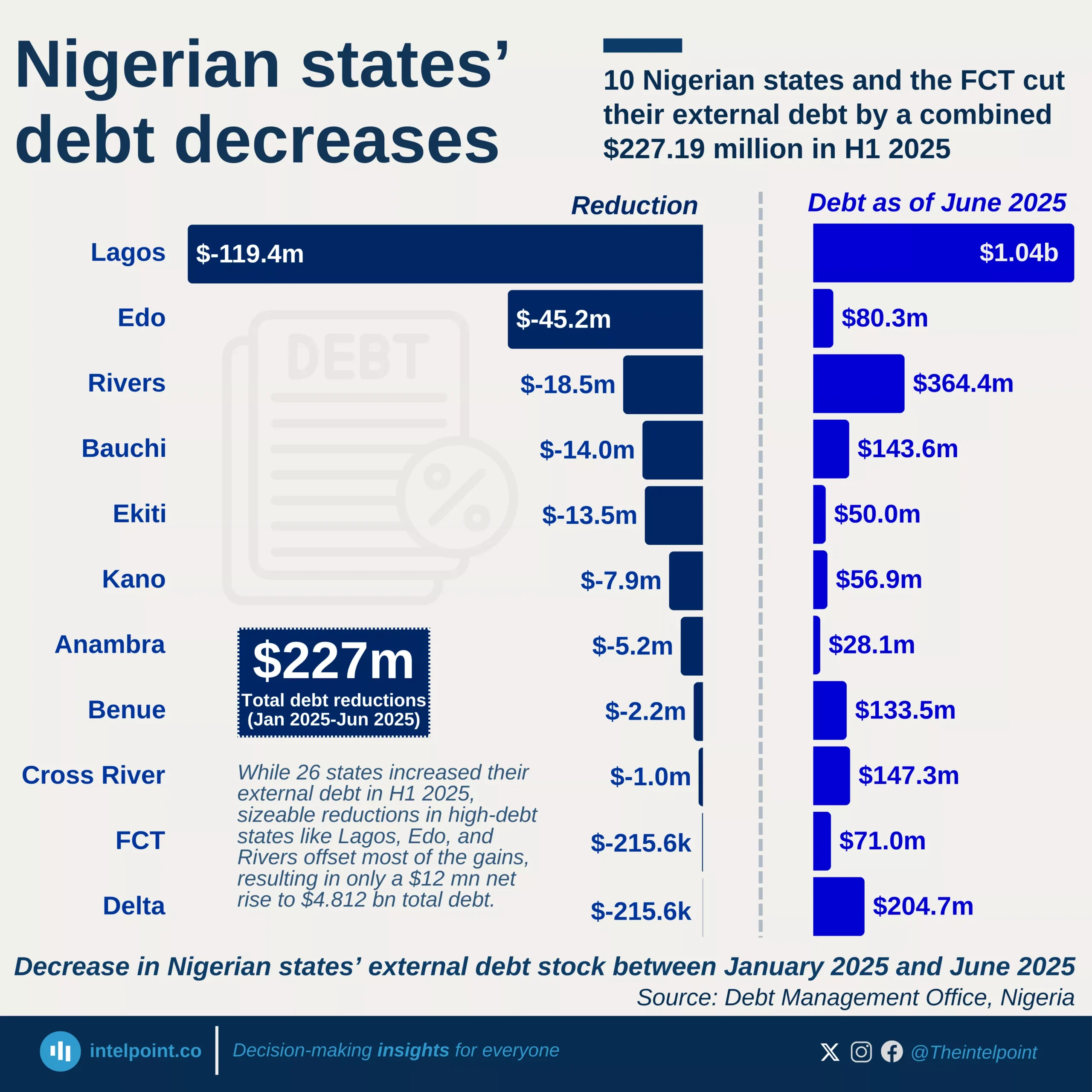
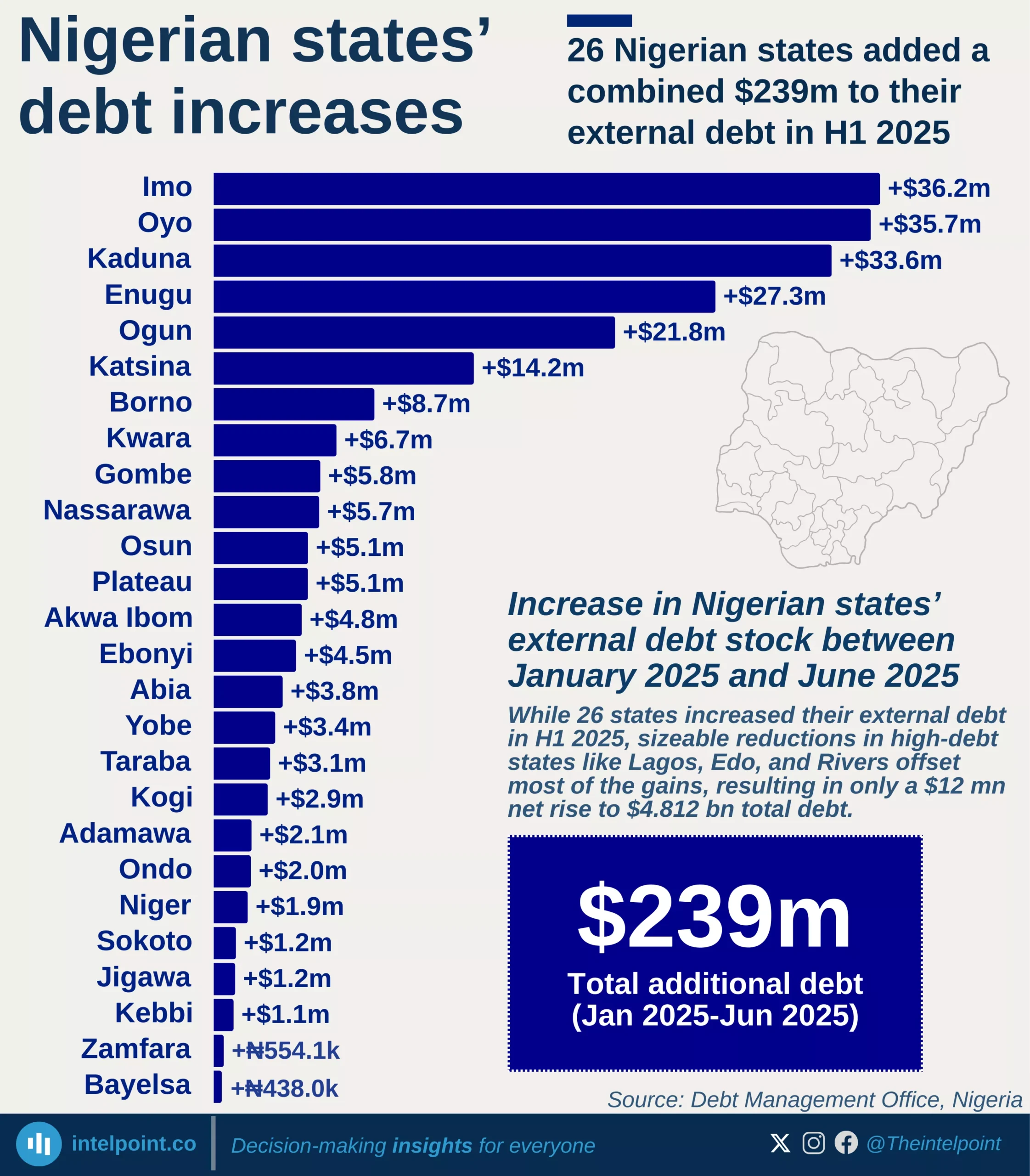
As of June 2025, Nigeria’s total public debt climbed to an estimated ₦152.4 trillion, underscoring the persistent fiscal challenges facing Africa’s largest economy. The domestic debt stock, at ₦80.5 trillion, now accounts for just over half of total borrowings, a sign of the federal government’s increasing shift towards local financing in response to exchange rate volatility and tighter global credit conditions.
Meanwhile, external debt, valued at ₦71.8 trillion, continues to represent a significant portion of Nigeria’s obligations. This includes loans from multilateral institutions, bilateral creditors, and commercial instruments such as Eurobonds. The balance reflects Nigeria’s efforts to blend concessional financing with market-based borrowing to fund infrastructure and budgetary gaps.
The steady rise in both domestic and external debt highlights the government’s struggle to balance fiscal sustainability with developmental needs. As debt levels approach record highs, analysts warn that maintaining macroeconomic stability will depend on stronger revenue mobilisation, prudent debt management, and structural reforms to boost productivity and exports.