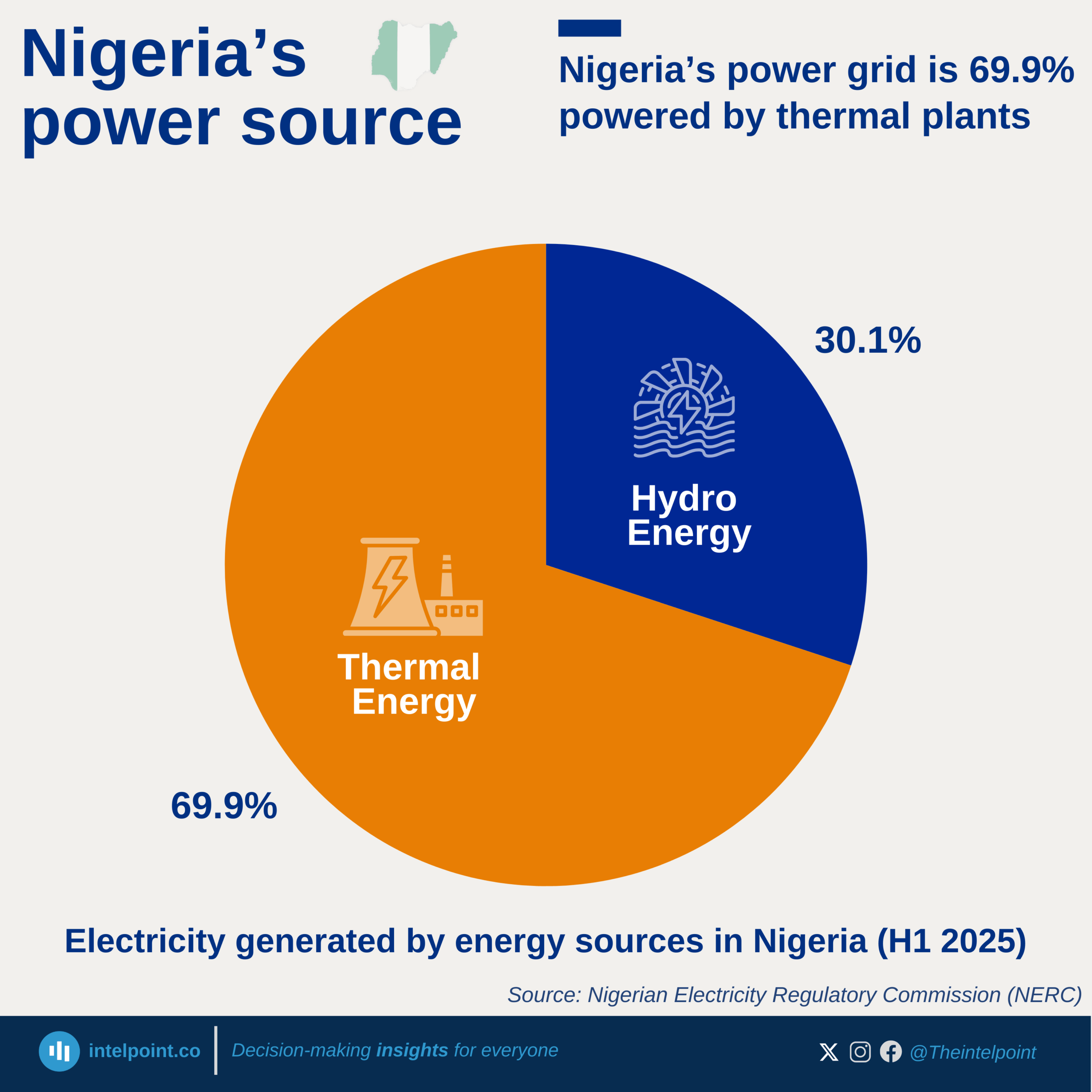
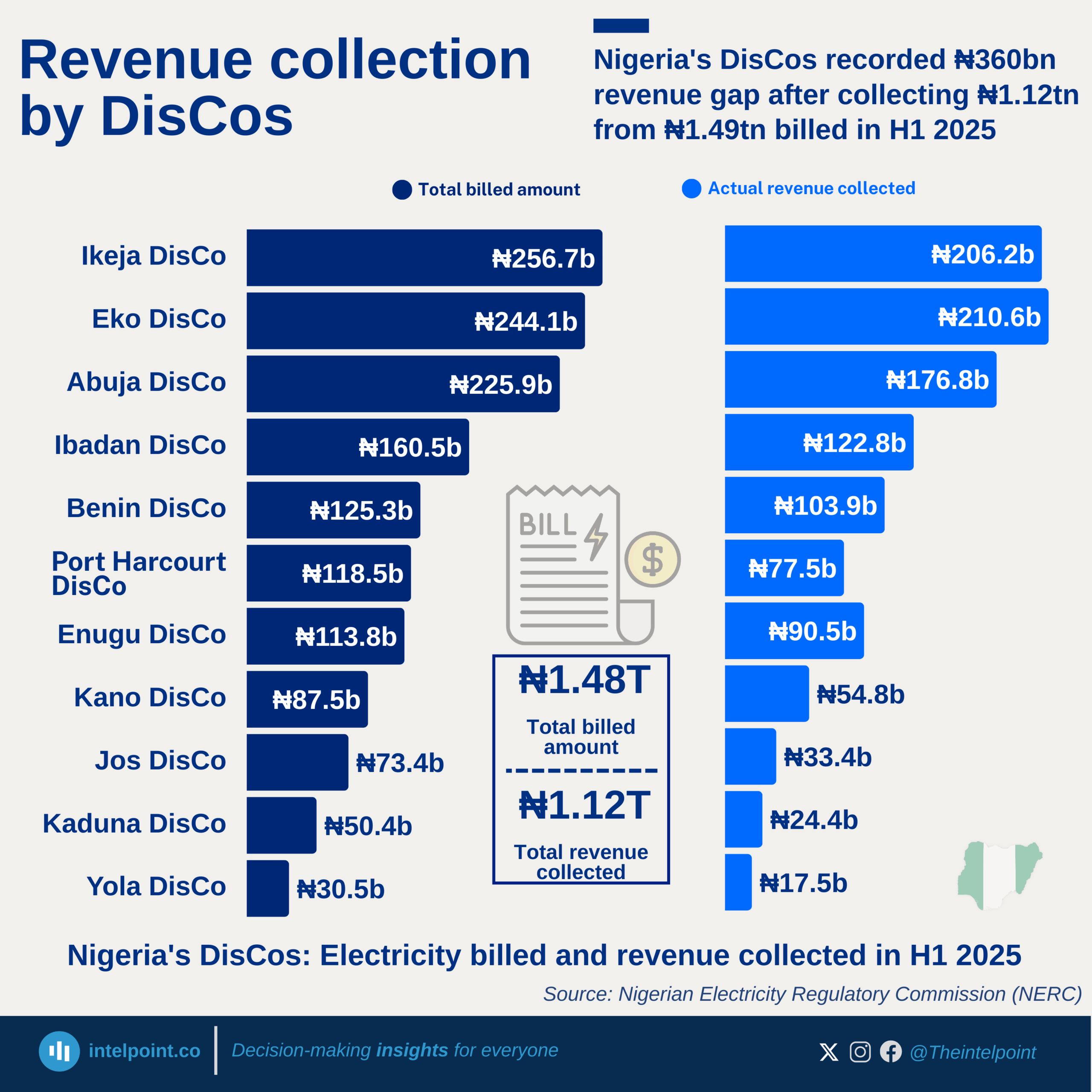
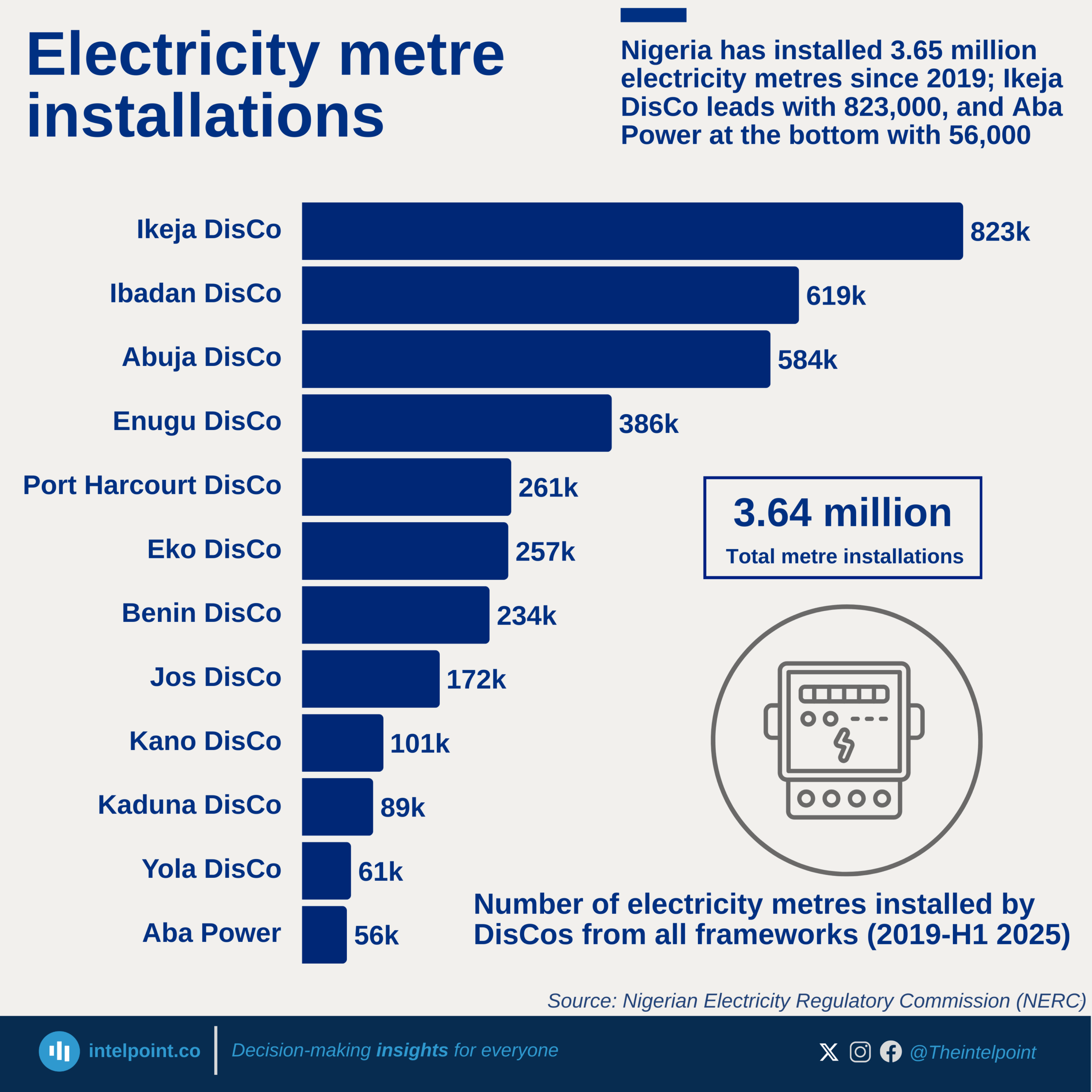
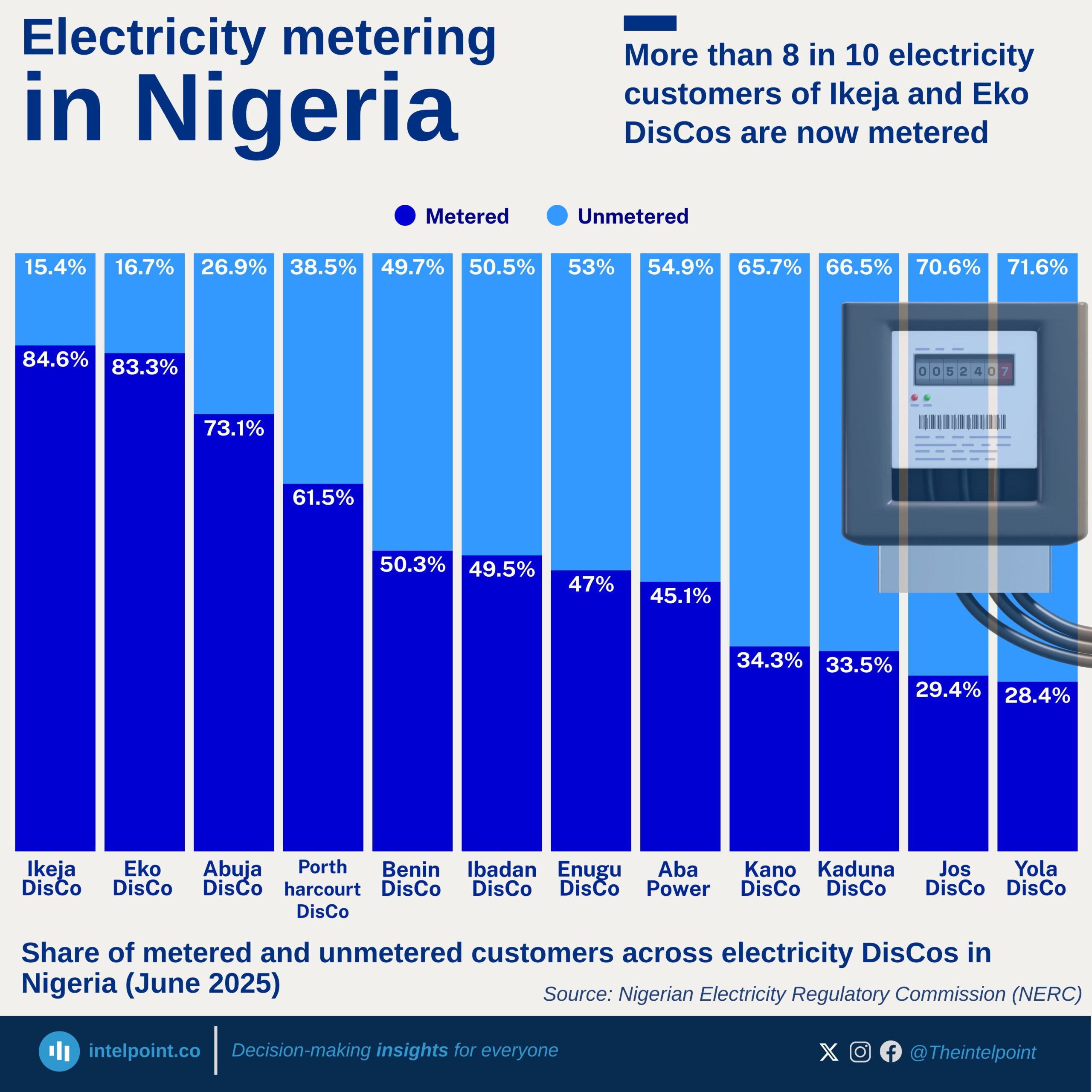
Black liquor is the by-product from the kraft process when digesting pulpwood into paper pulp. It is a source of biofuel derived from organic, renewable biomass sources and a very important form of energy.
In 2023, the United States of America led the production of black liquor with 696.0PJ (petajoules) produced, making up 38.9% of the total quantity produced globally. Sweden, Canada, Finland and Japan produced 185.1PJ (10.4%), 157.9PJ (8.8%), 142.5PJ (8.0%), and 133.0PJ (7.4%), respectively.
South Africa is the only African country producing black liquor, with 16.4PJ produced, making up 1% of the global total. Comparing the growth of the pulp and paper industry in Africa with the fact that Africa produced only 1% of black liquor in 2023, it was revealed that there is a huge gap in the recycling of by-products, commonly called waste products, in Africa.