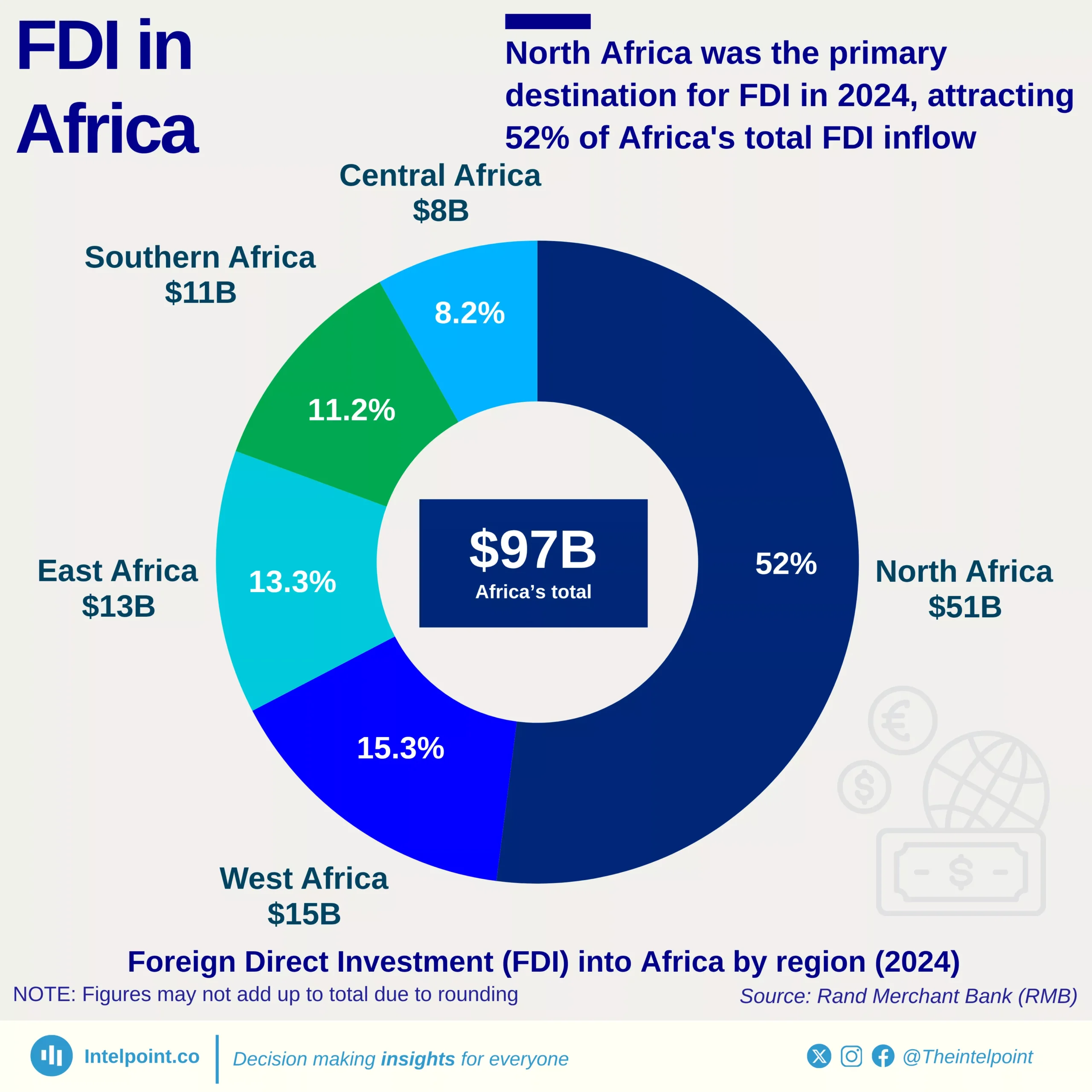
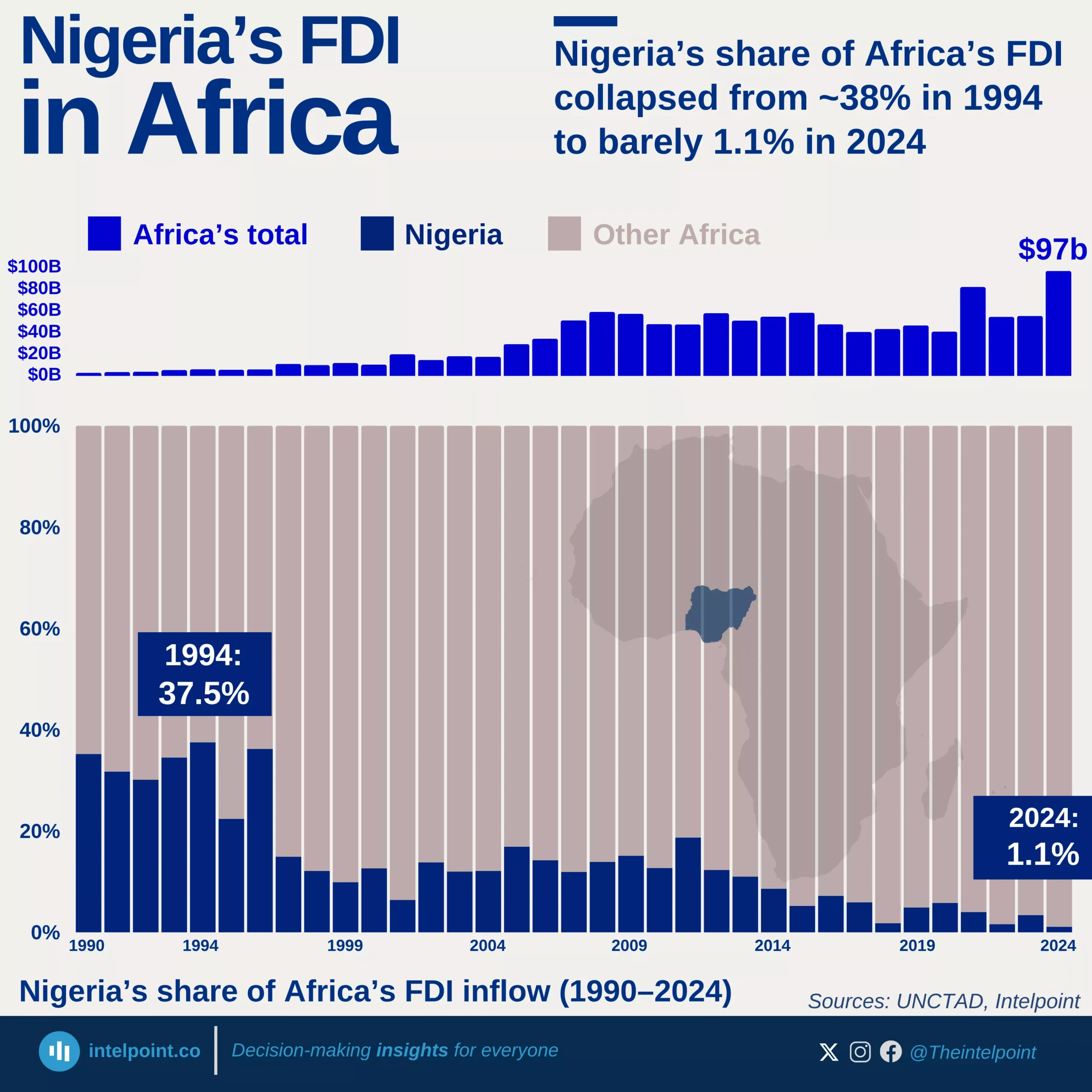
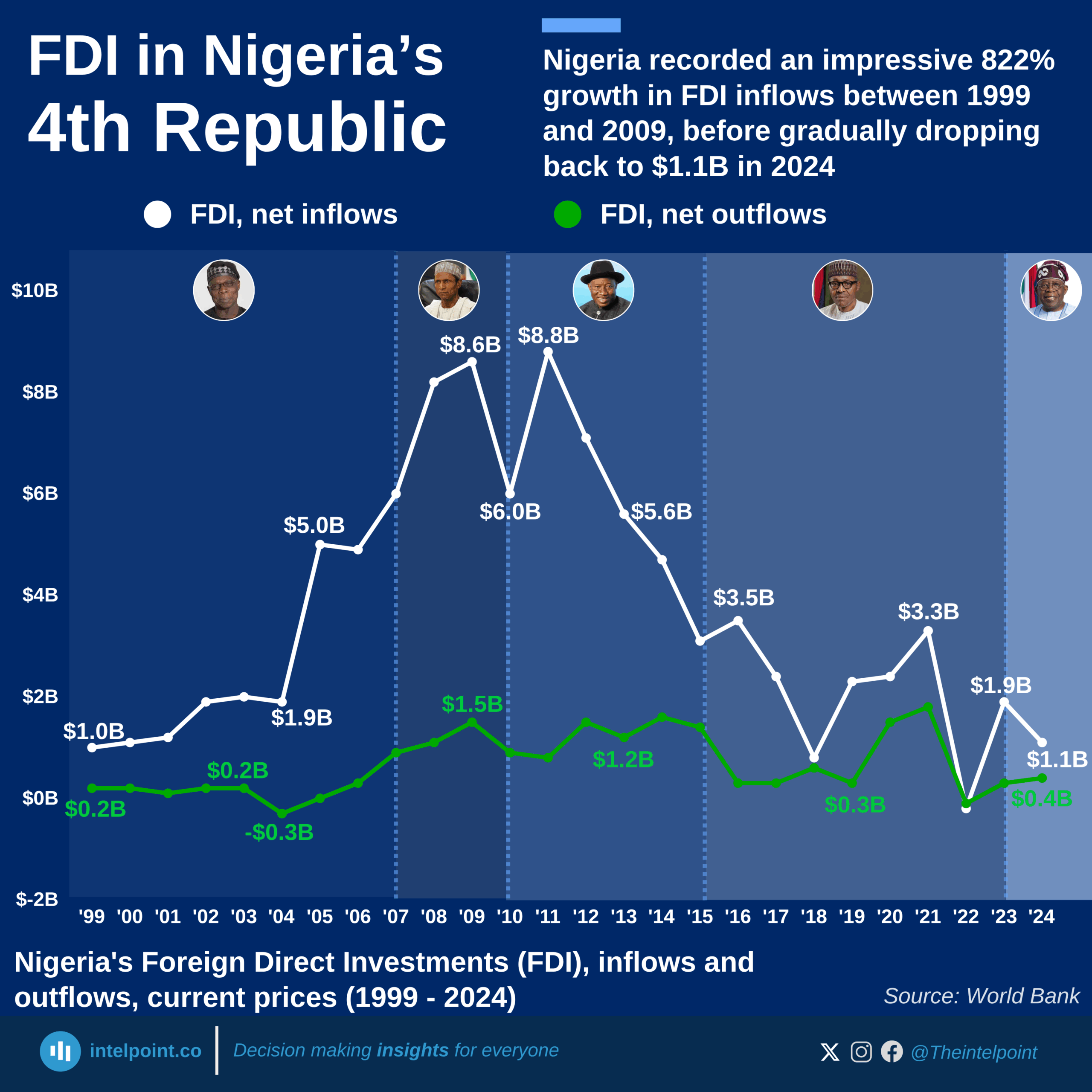
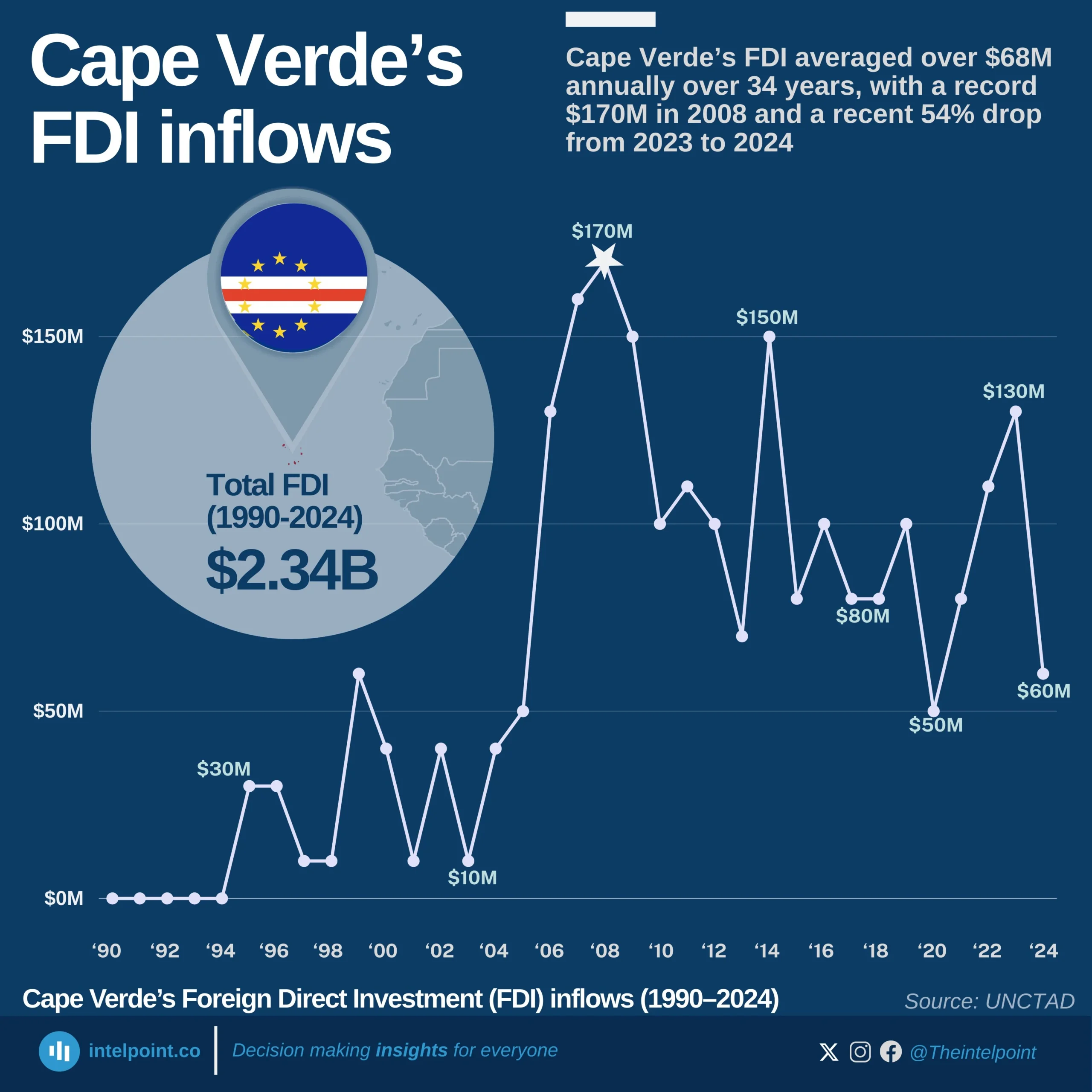
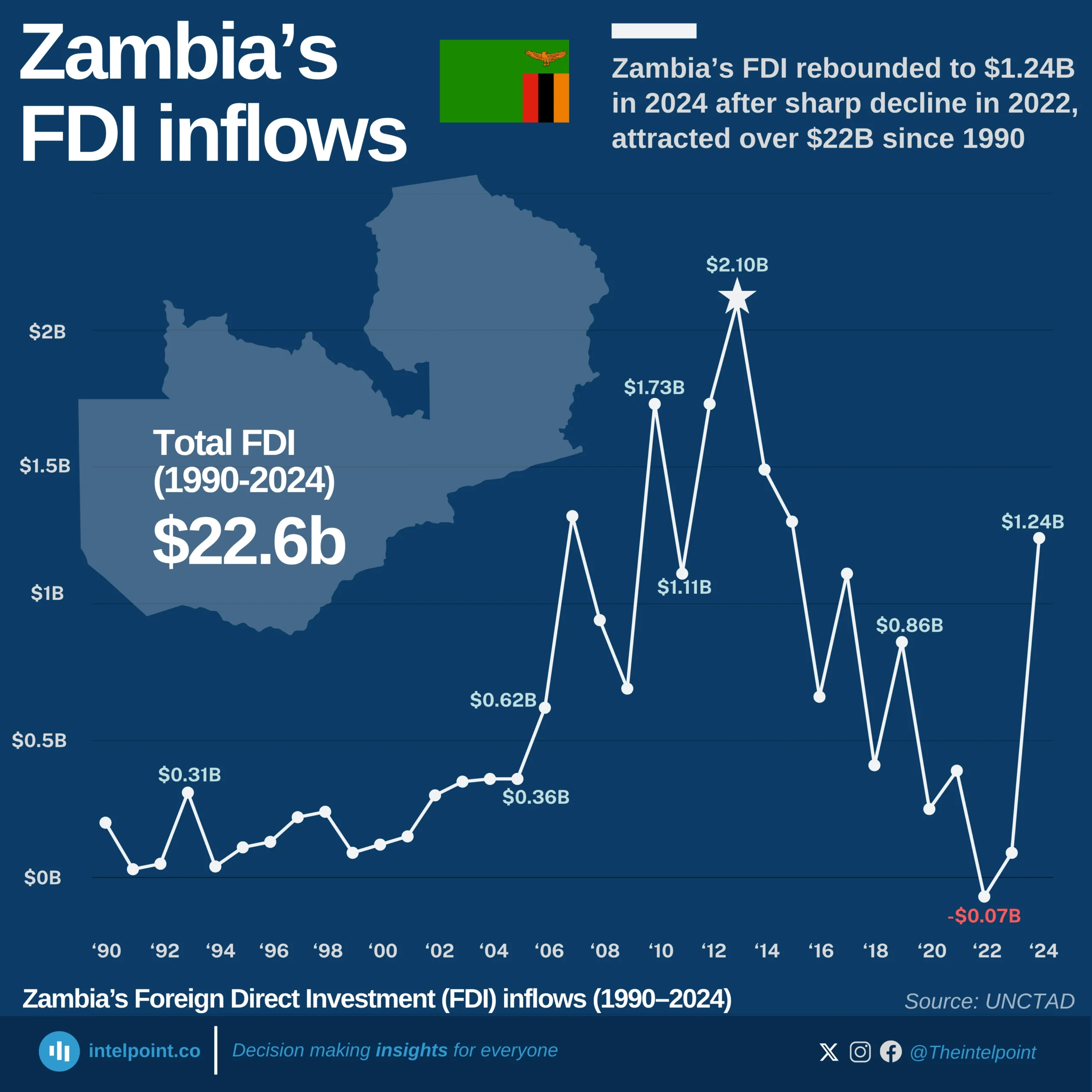
Between 1990 and 2024, Egypt’s FDI trajectory reflected decades of economic shifts, policy reforms, and political events. After steady gains in the 1990s and early 2000s, inflows surged to $11.6 billion in 2007, only to crash to –$0.48 billion in 2011 amid the Arab Spring, when capital flight outpaced new investments. Recovery followed gradually, with annual FDI stabilising between $5 billion and $8 billion for much of the next decade.
The turning point came in 2024, when Egypt attracted a record-breaking $46.6 billion in FDI—its highest ever. This massive jump was largely driven by the $35 billion Ras El Hekma deal with Abu Dhabi’s sovereign wealth fund (ADQ), signalling renewed investor confidence. The 2024 figure is nearly 10 times Egypt’s long-term annual average and cements the country’s position as one of the most dynamic FDI destinations globally.