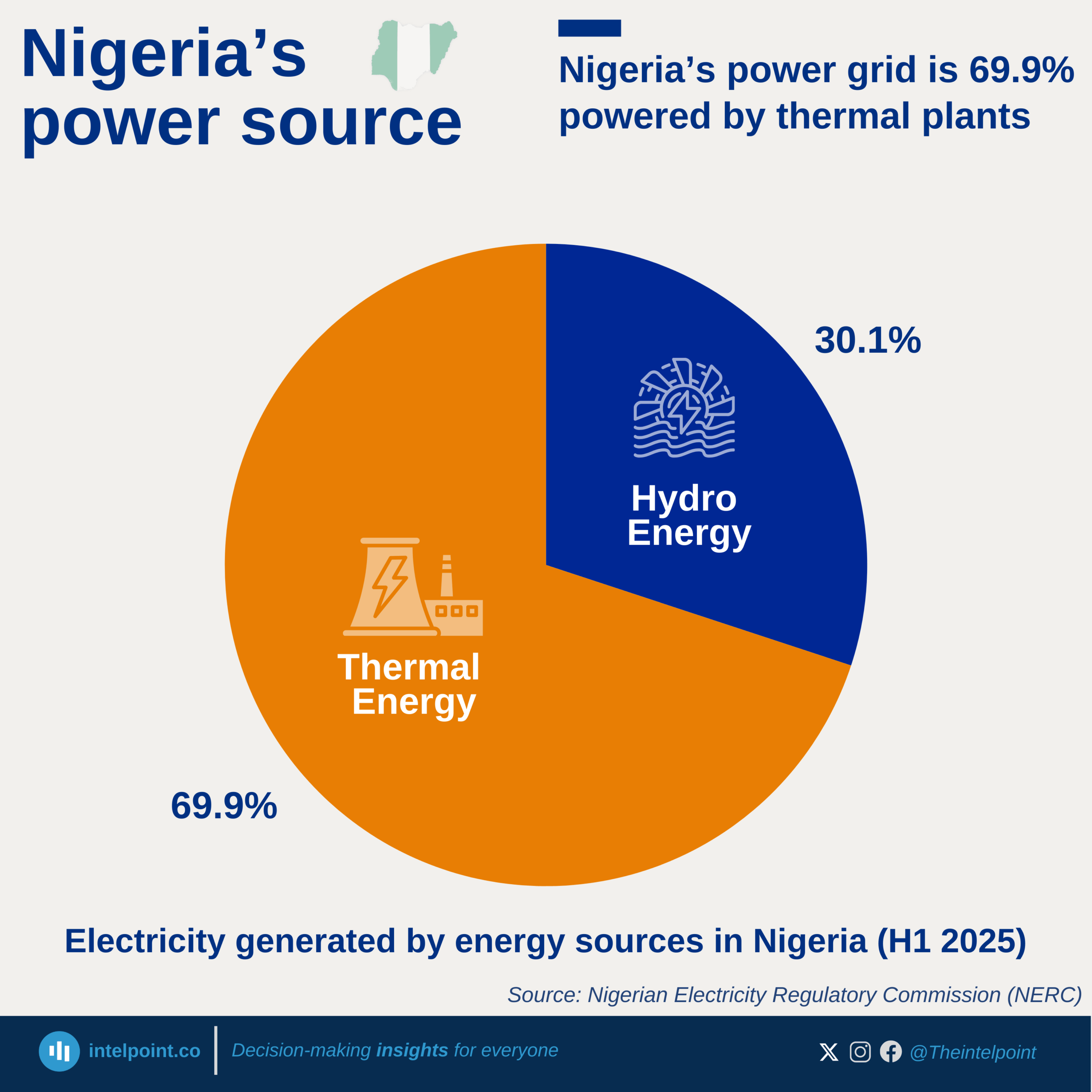
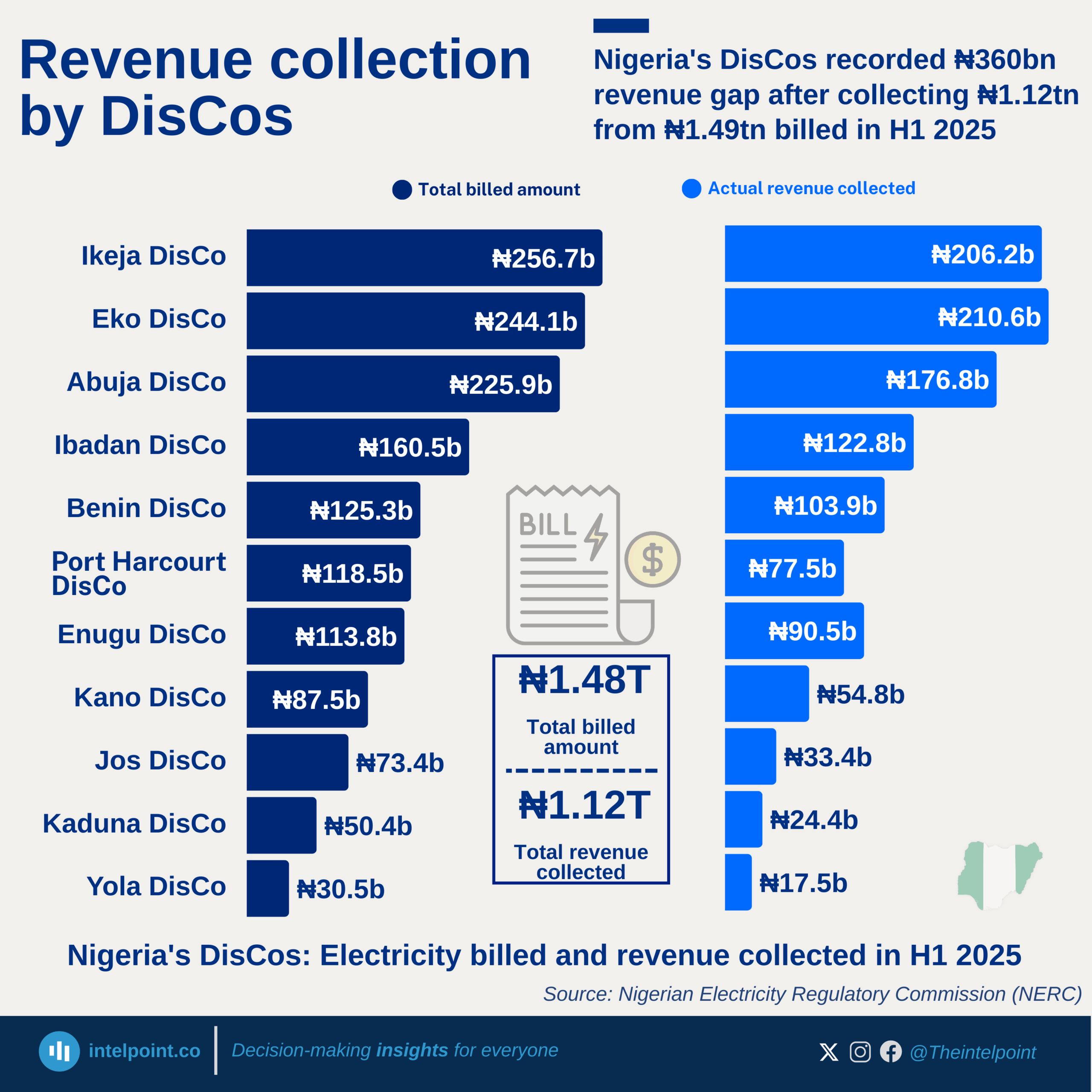
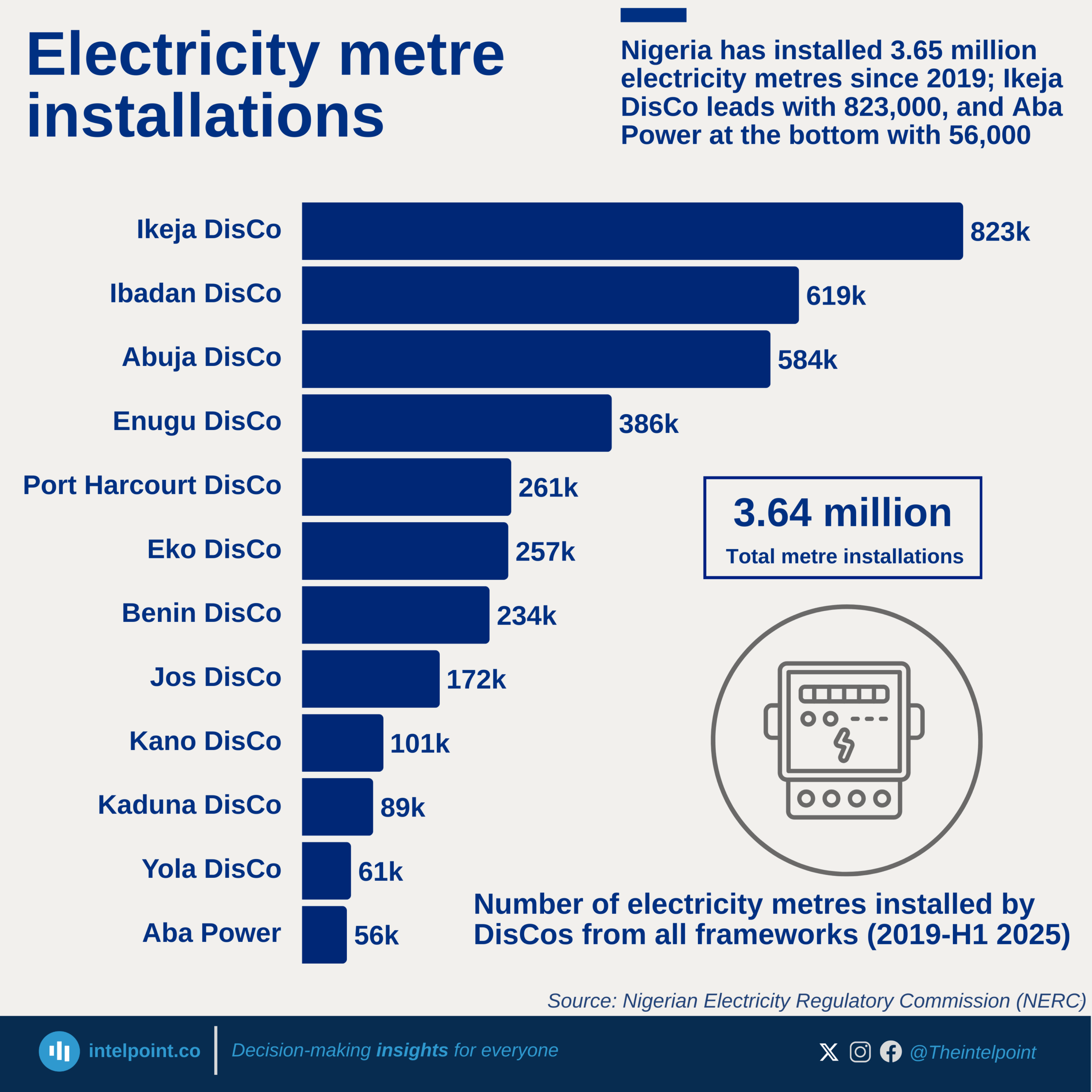
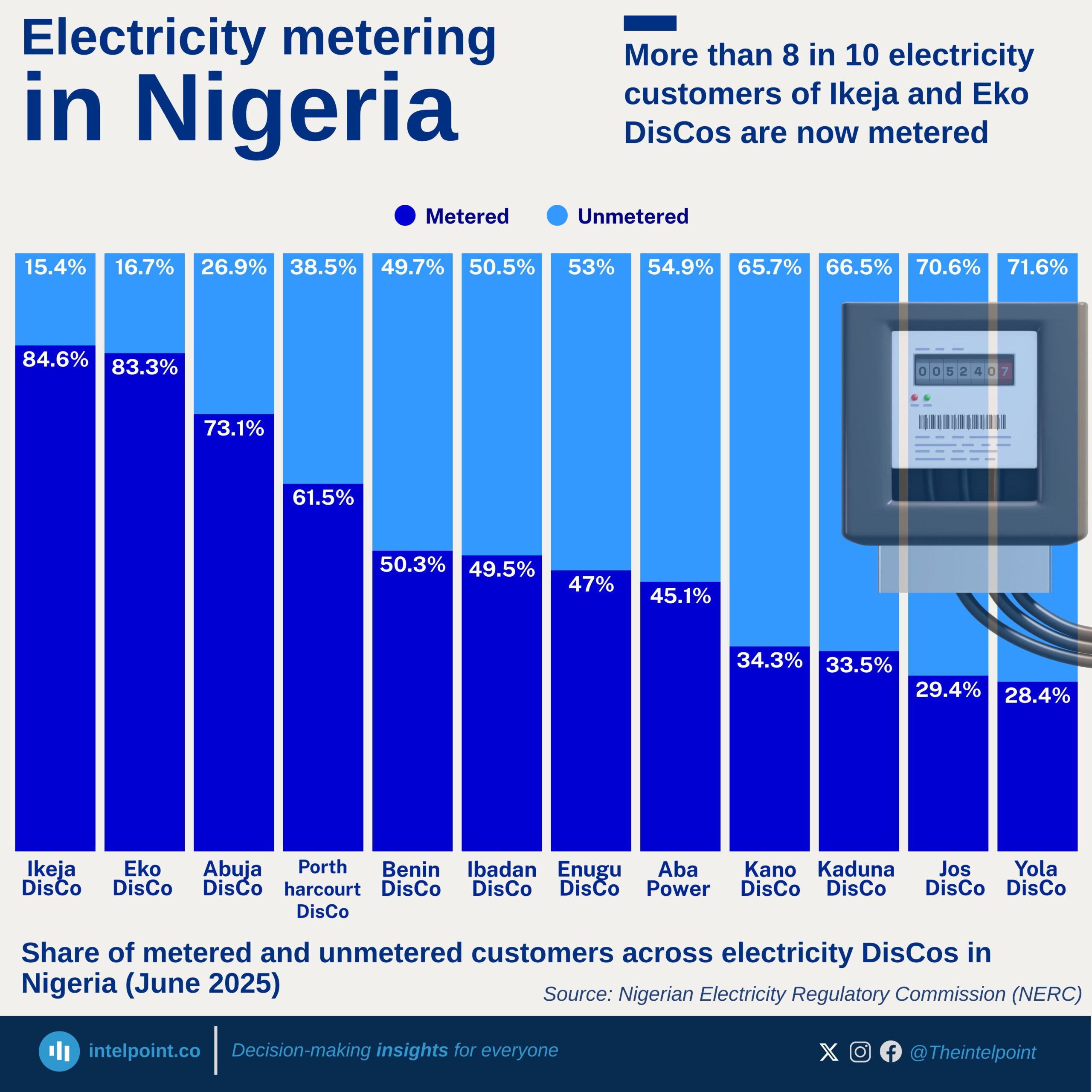
In February 2025, the North East recorded the highest year-on-year increase in diesel prices at 36.26%, followed closely by the North Central at 33.71%. This steep rise in energy costs in the northern regions contrasts sharply with the southern zones, where price changes were far more modest, dipping as low as 6.97% in the South East. The contrast highlights an uneven energy burden across Nigeria that could have ripple effects on transportation, business operations, and the overall cost of living in different parts of the country.