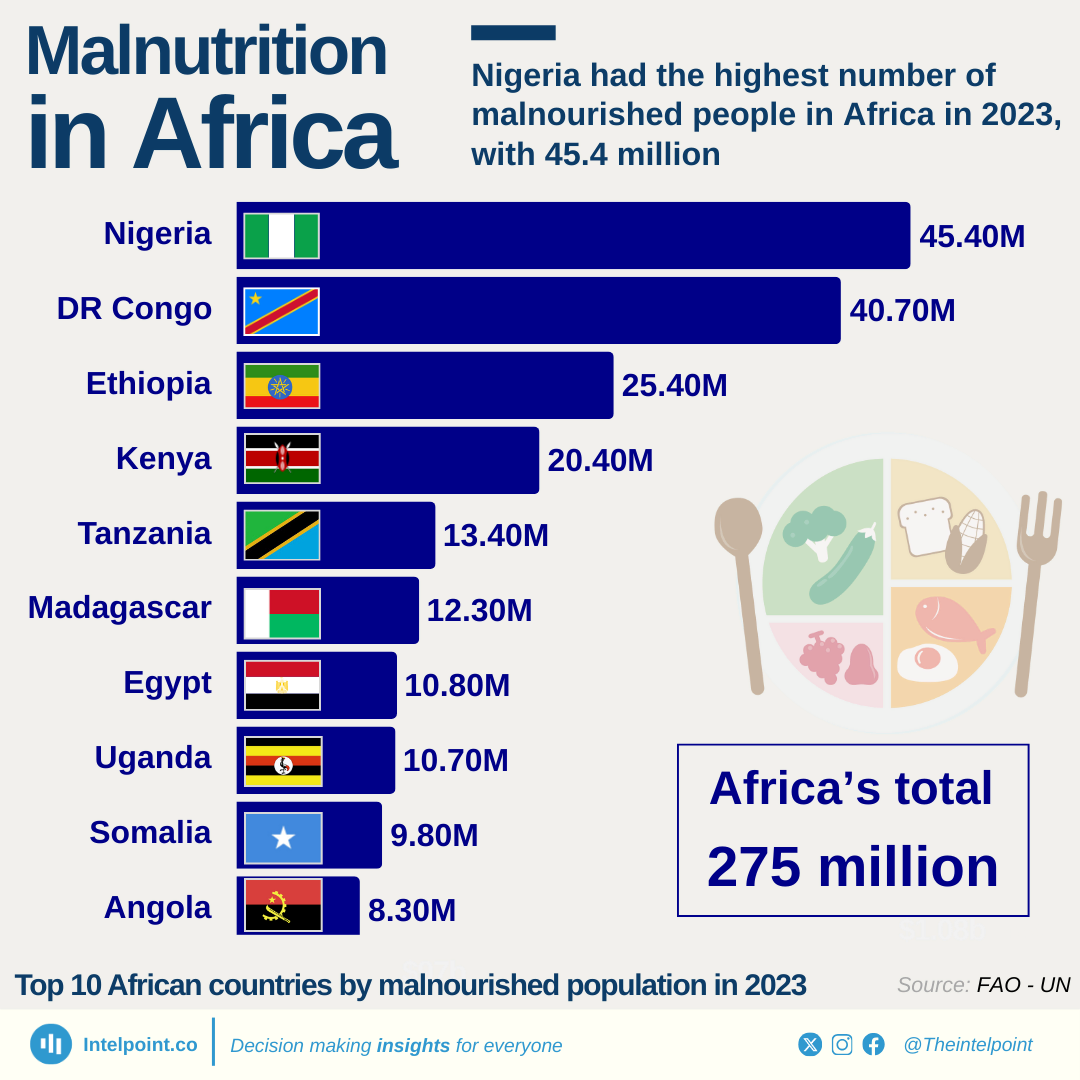
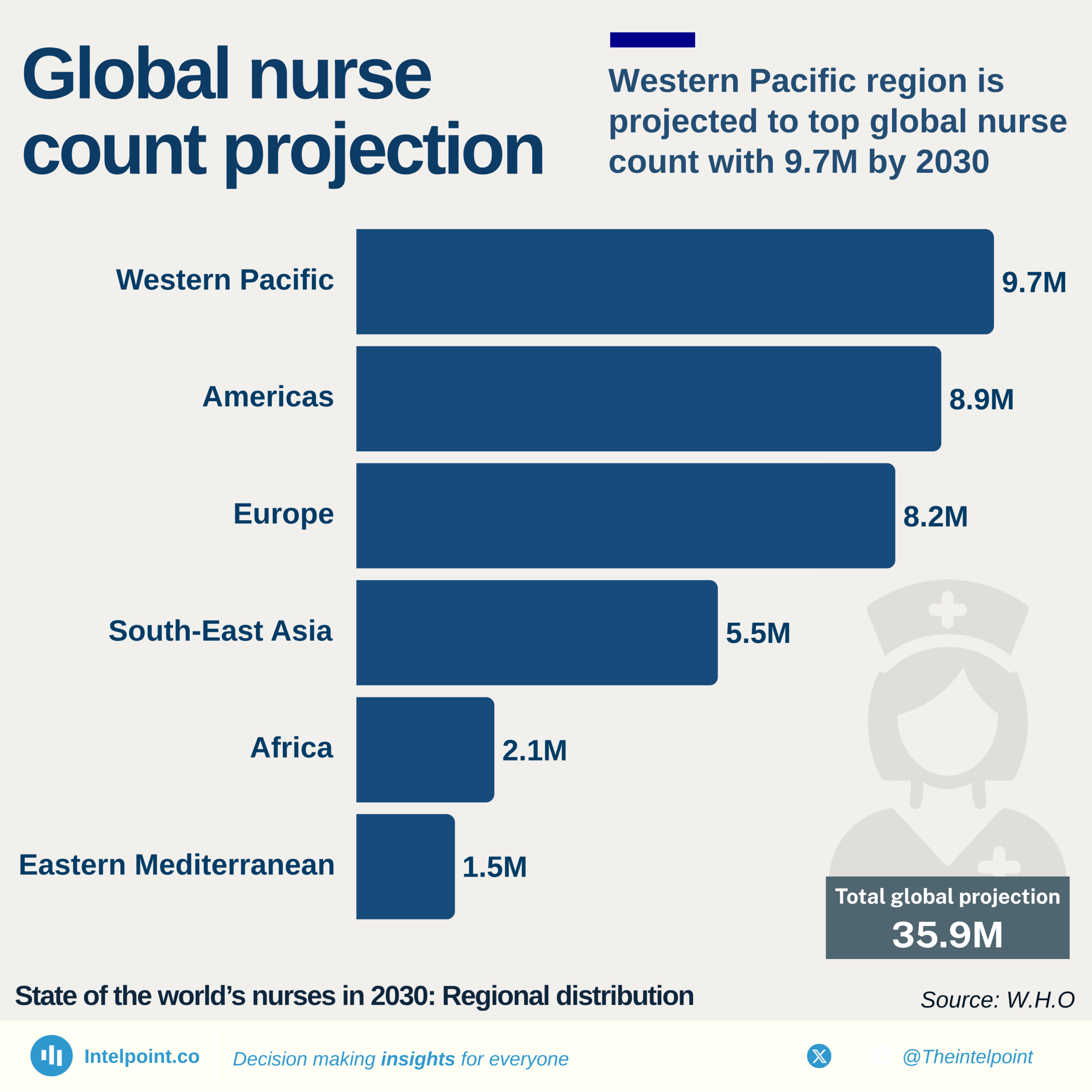
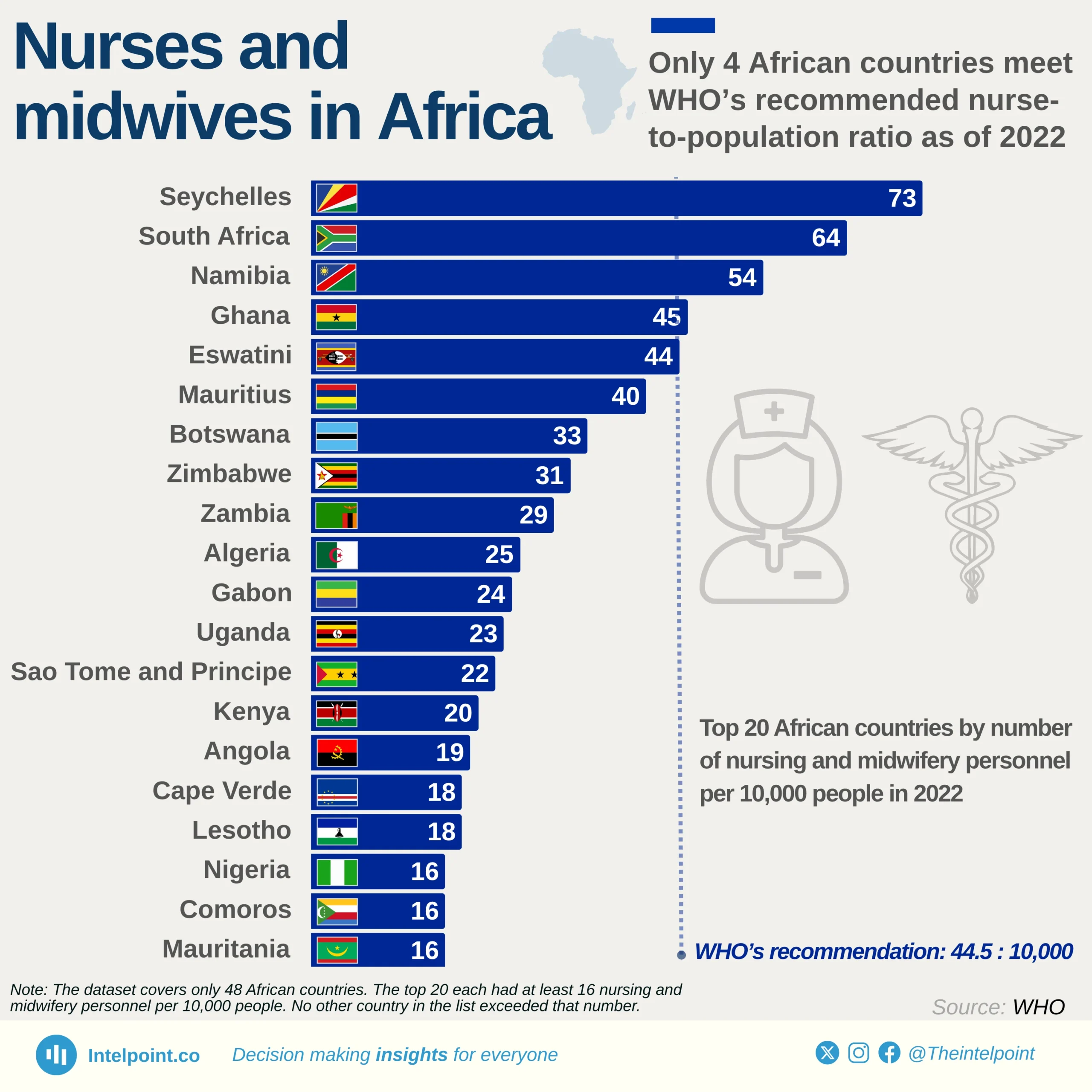
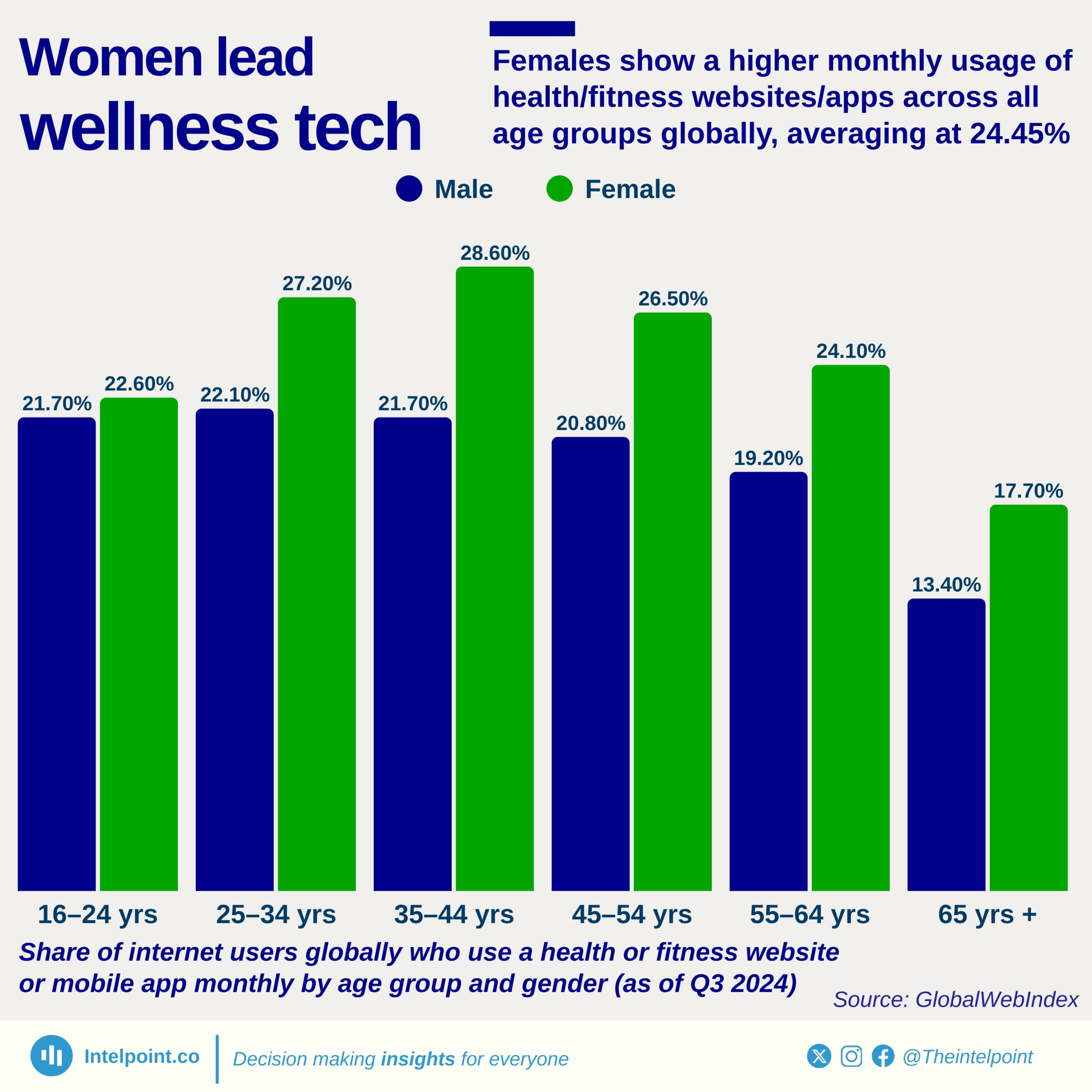
Birth asphyxia is a condition where a baby does not receive sufficient oxygen before, during, and after birth. It is a leading cause of early neonatal mortality and was selected as an indicator in the assessment of the management of maternal and neonatal complications in Nigeria.
The percentage of health facilities surveyed that provide appropriate treatment for birth asphyxia varies from as low as 19.4% in the North West to as high as 50.3% in the South-South. With no zone exceeding 50%, significant gaps remain in reducing infant mortality in Nigeria.