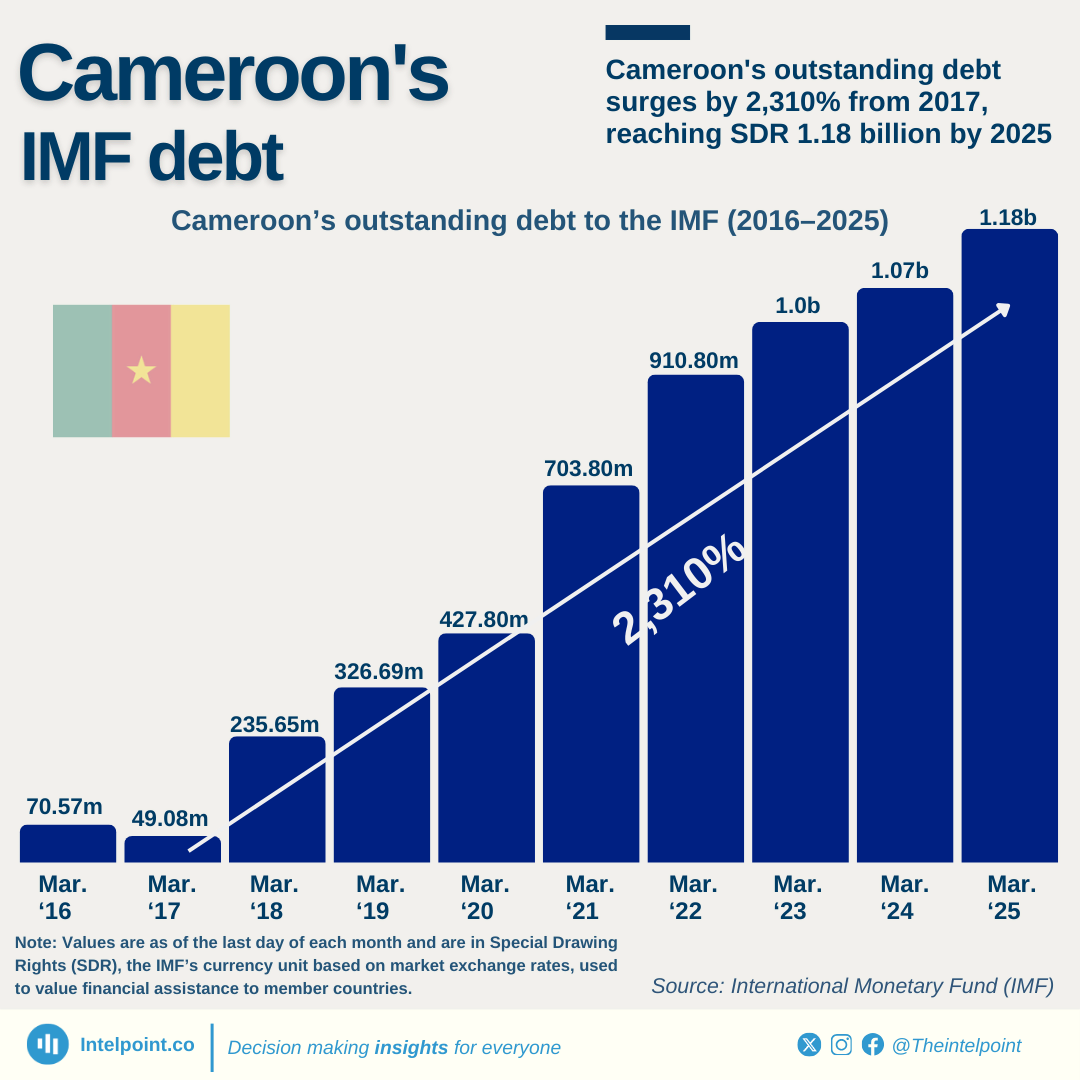
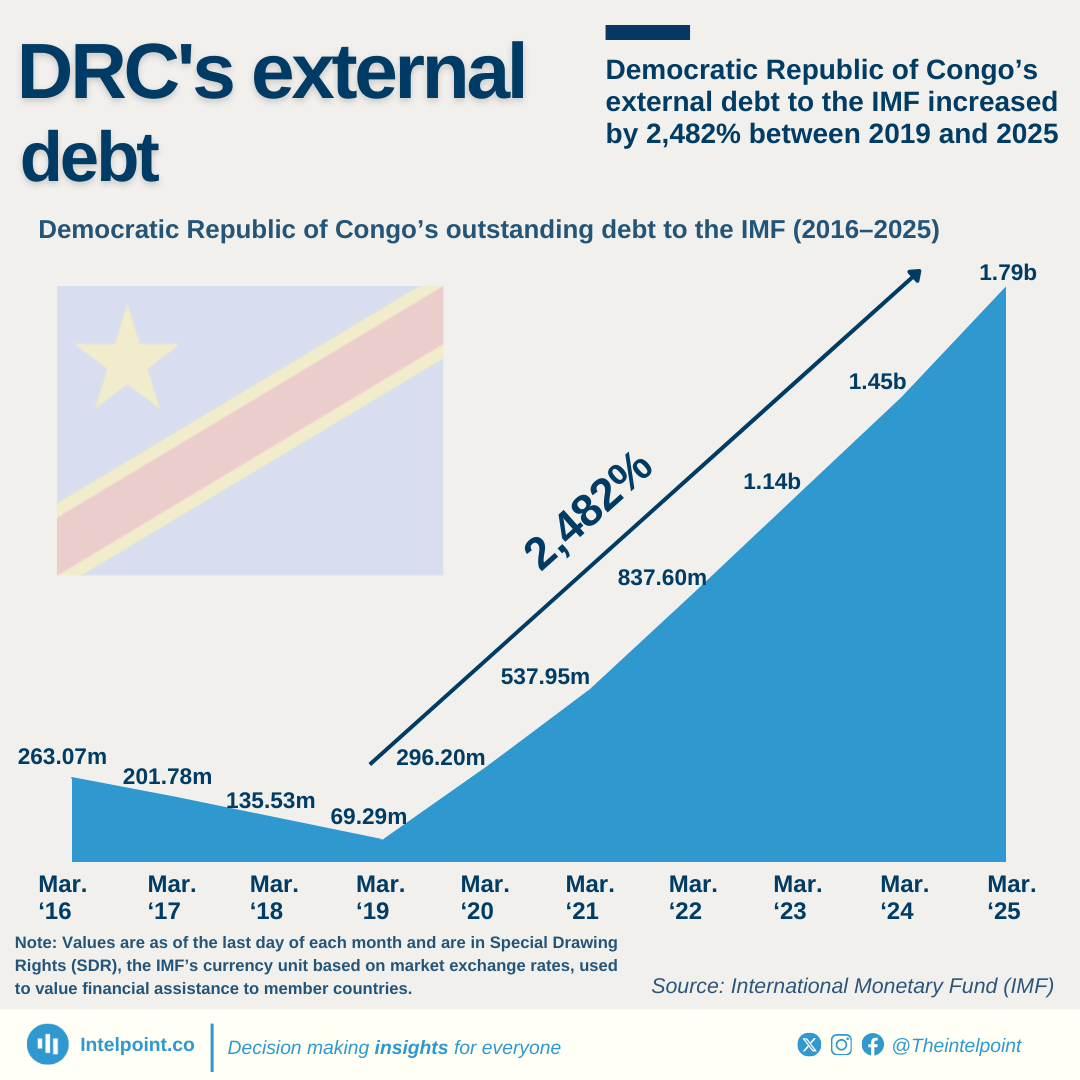
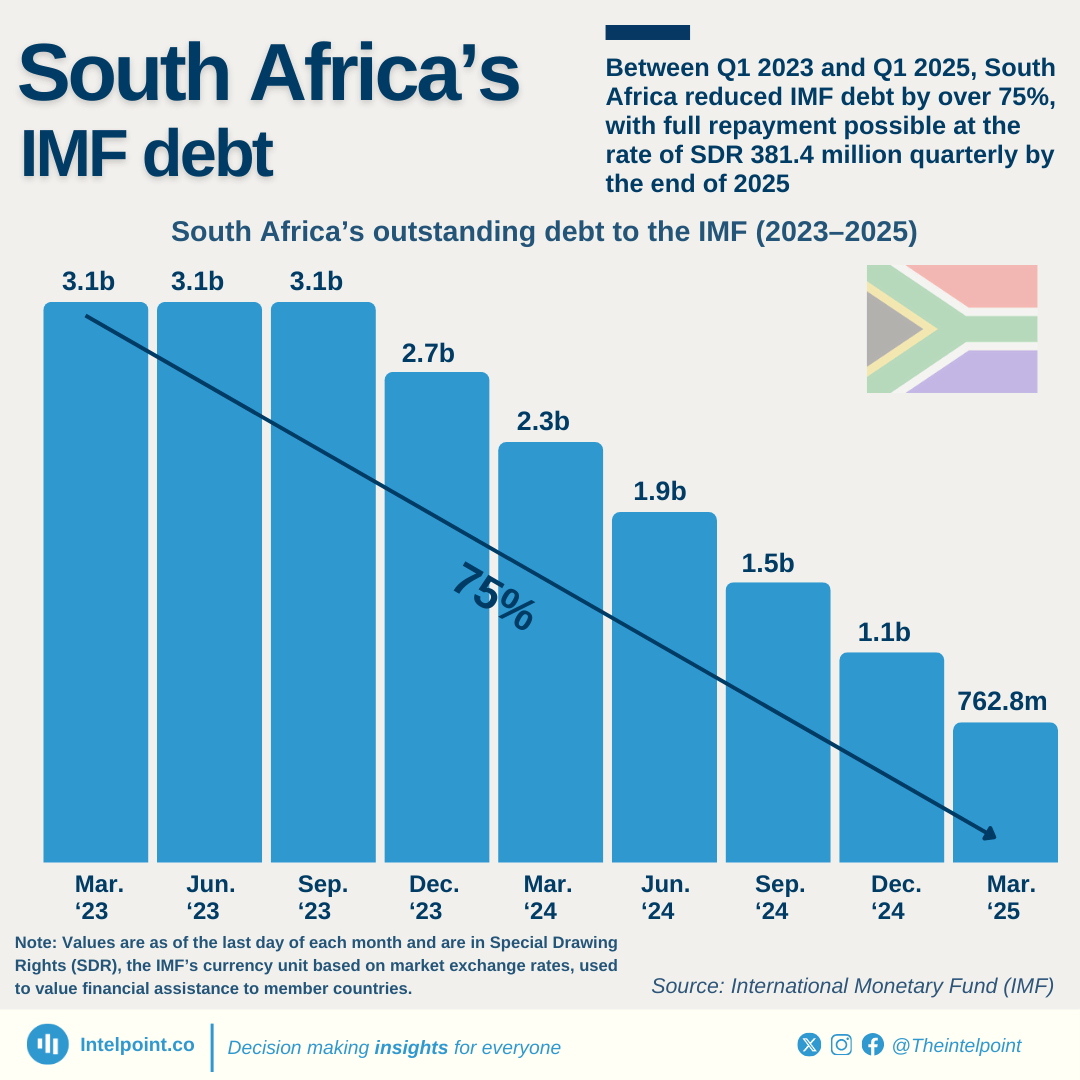
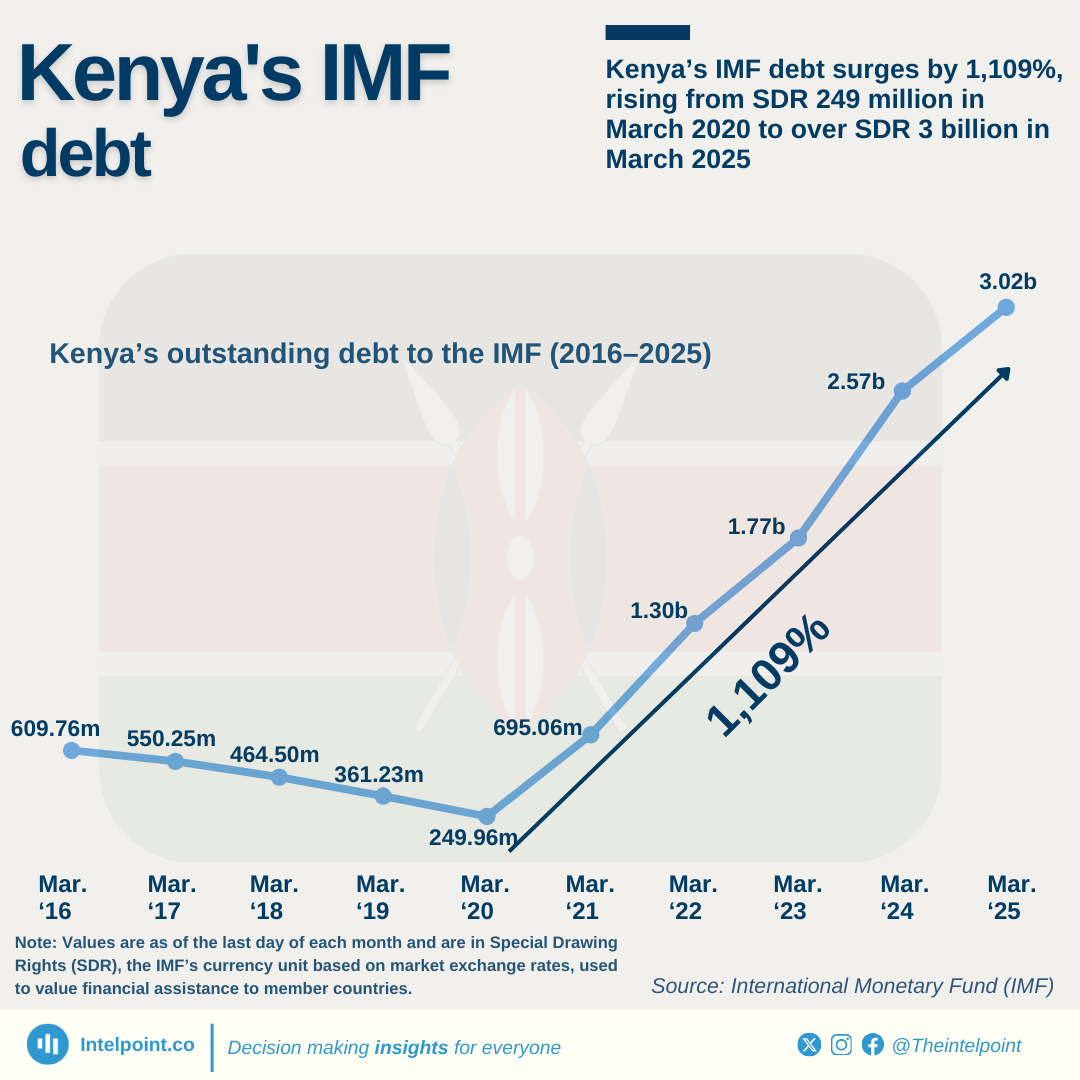
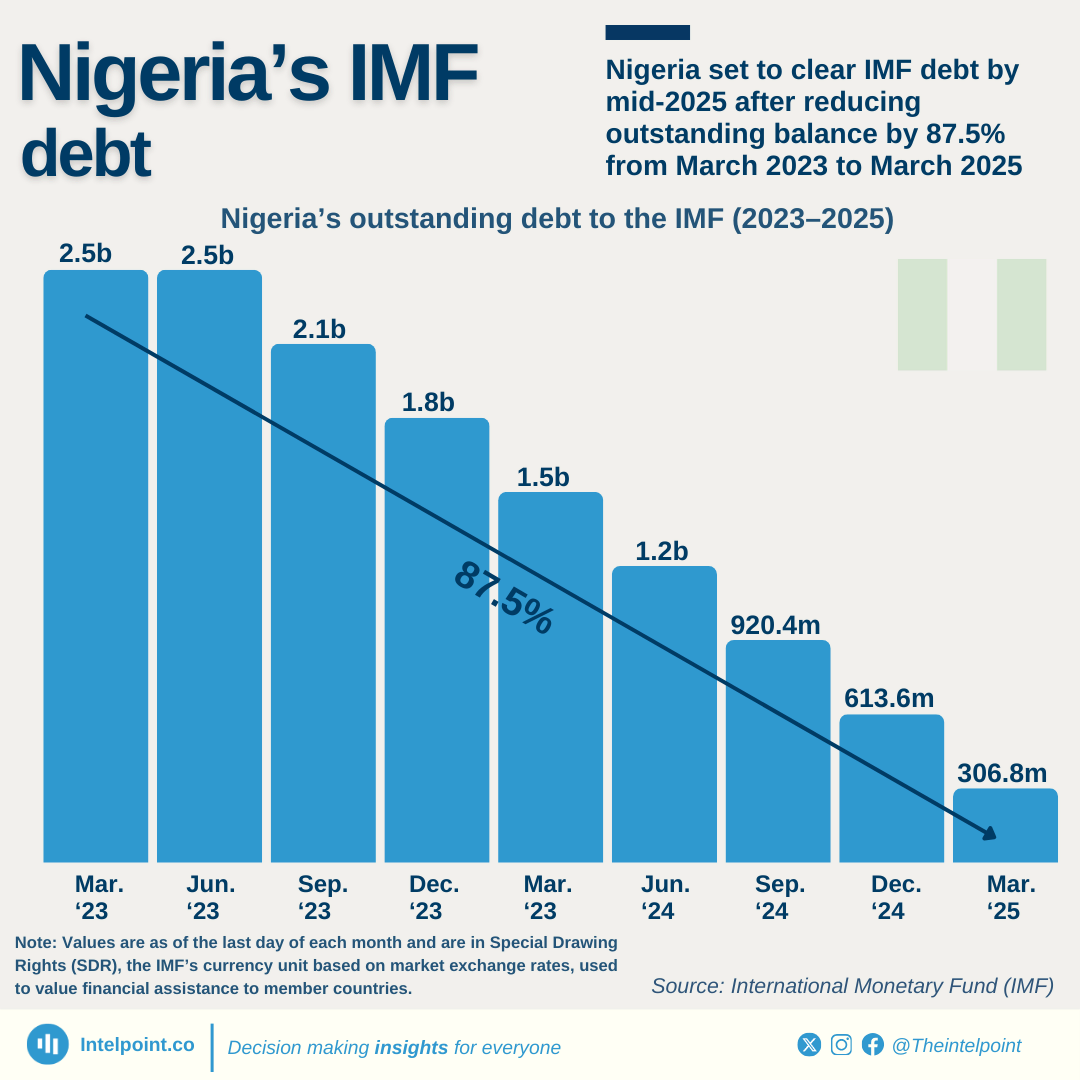
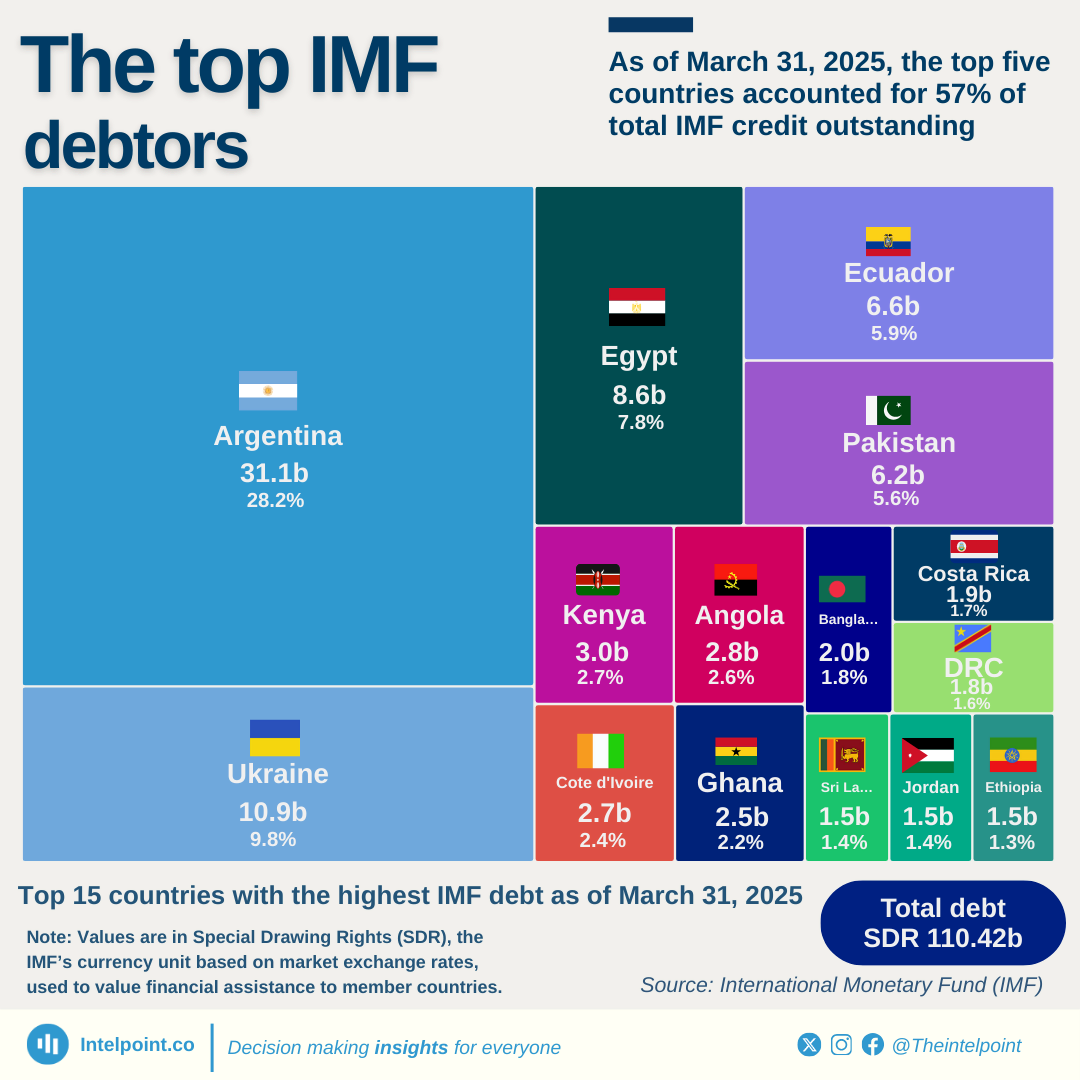
Nigeria’s public debt decreased in dollar terms between June 2023 and June 2024. However, when converted to naira, it jumped to ₦134.3 trillion, largely due to currency devaluation. This sharp increase in debt could lead to tighter budgets, potentially affecting public services and everyday costs for Nigerians.