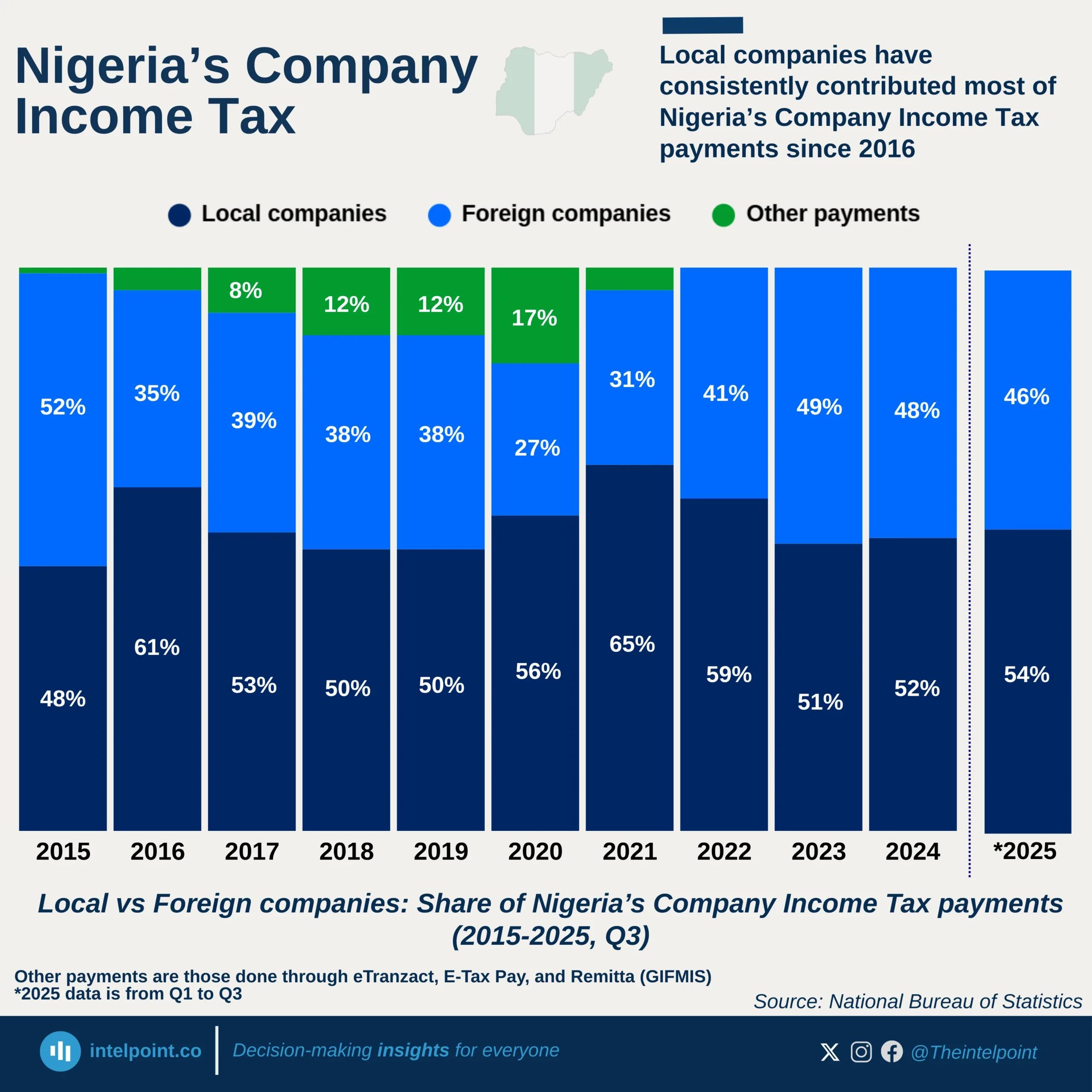
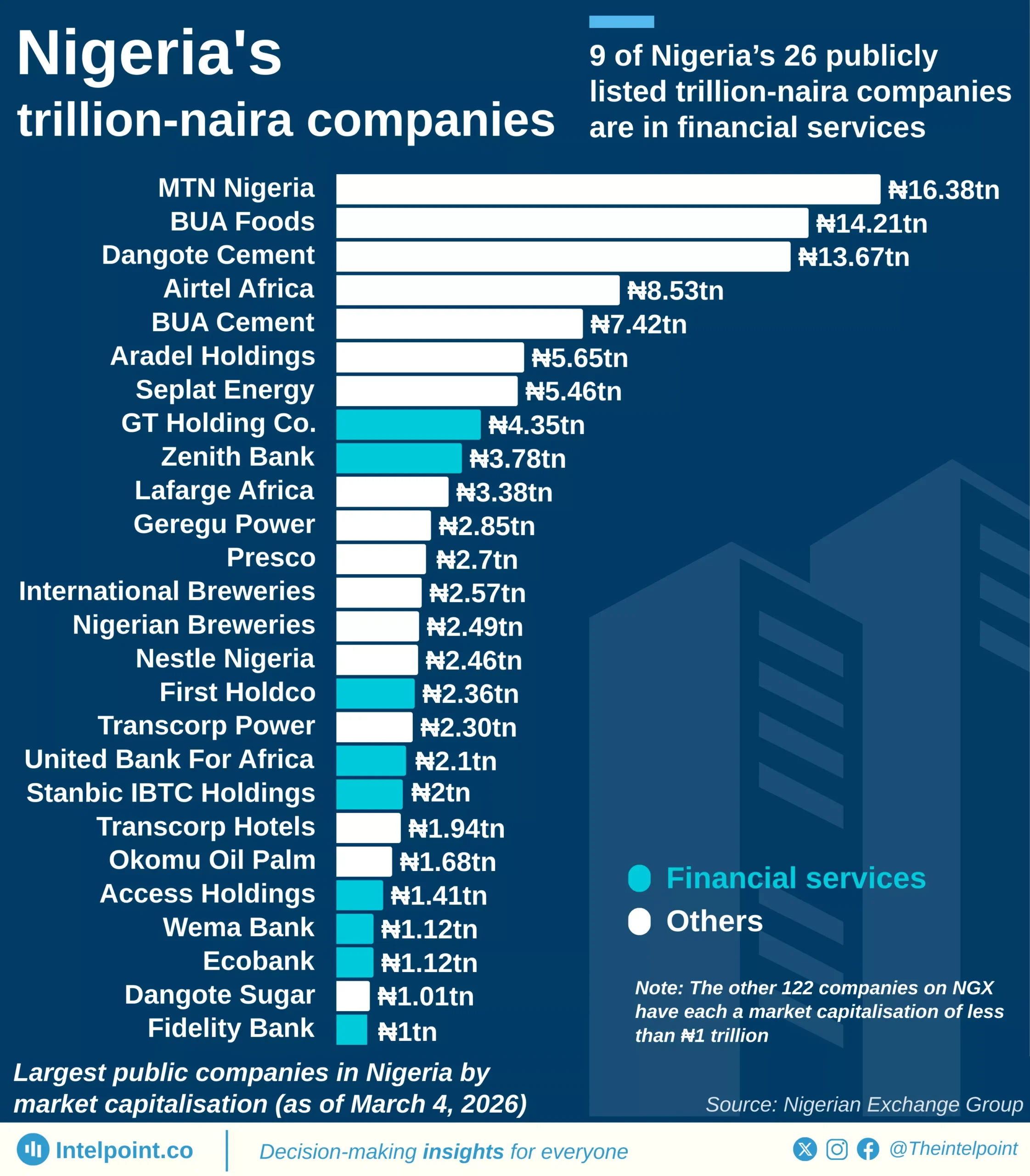
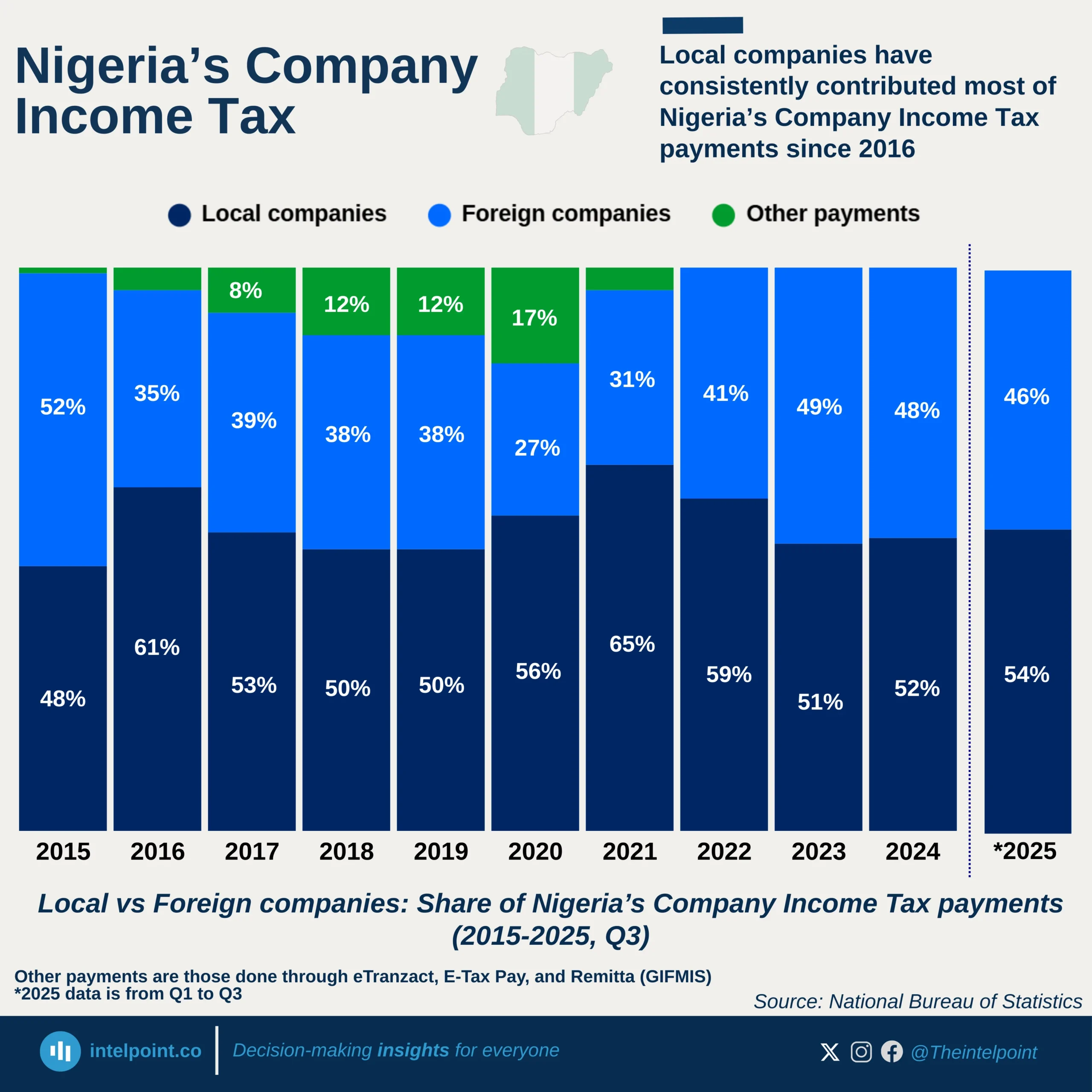
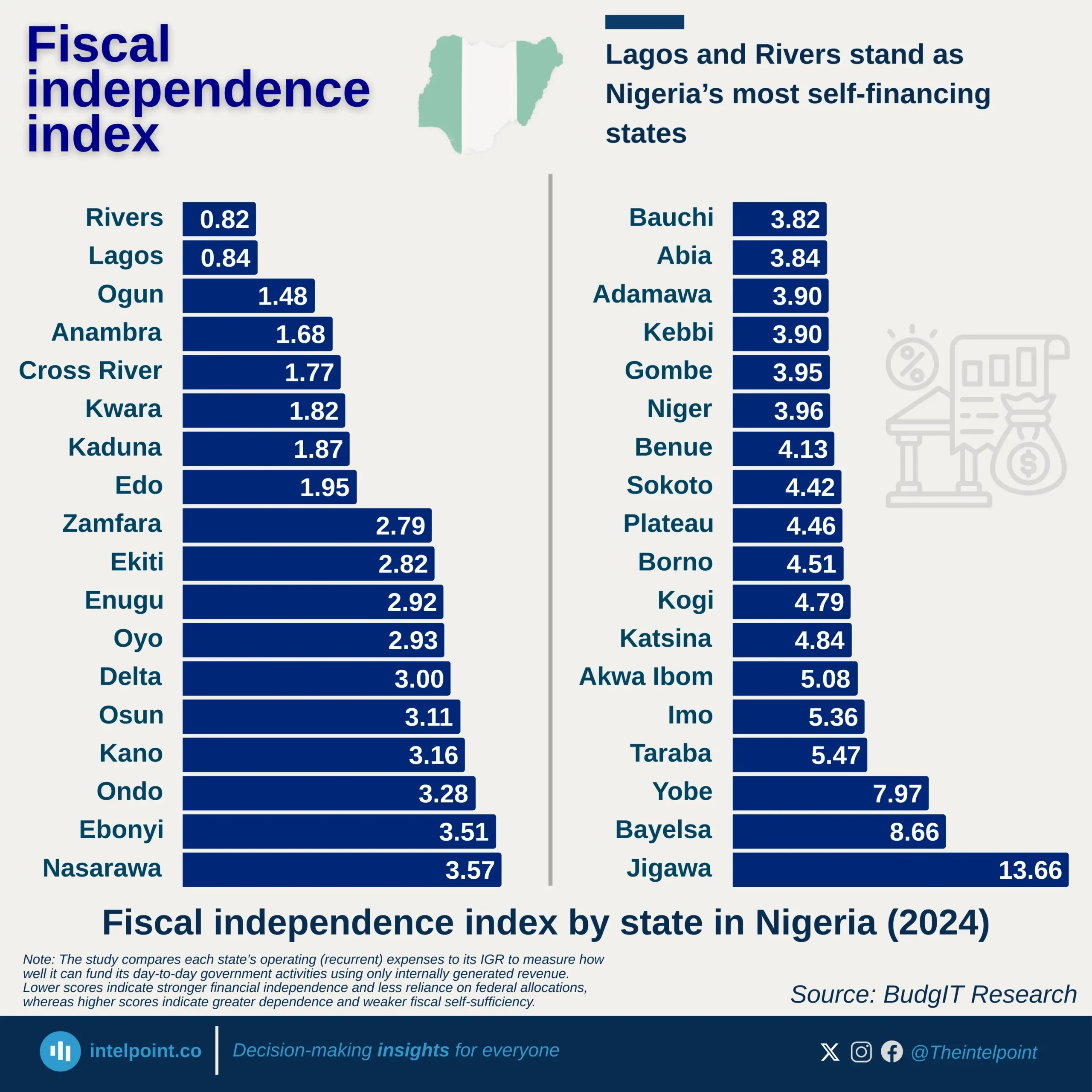
In 2024, the EU imported a total of 9.1 million barrels of crude oil per day, drawing heavily from a mix of Western allies and strategic global partners. The United States emerged as the dominant supplier, with 1.40M b/d, highlighting transatlantic energy ties. Norway and Kazakhstan solidified their roles as key regional contributors, combining for over 2.15M b/d and reinforcing Europe’s reliance on politically stable sources.
Nigeria, ranked 7th, supplied 0.54M b/d, affirming its strategic importance as a West African oil hub. Despite not leading, its consistent output places it ahead of major economies like Brazil and the UK. Beyond these top contributors, over 2.24M b/d came from other global sources, proving the EU’s ongoing commitment to supply chain diversity and energy security amidst global volatility.