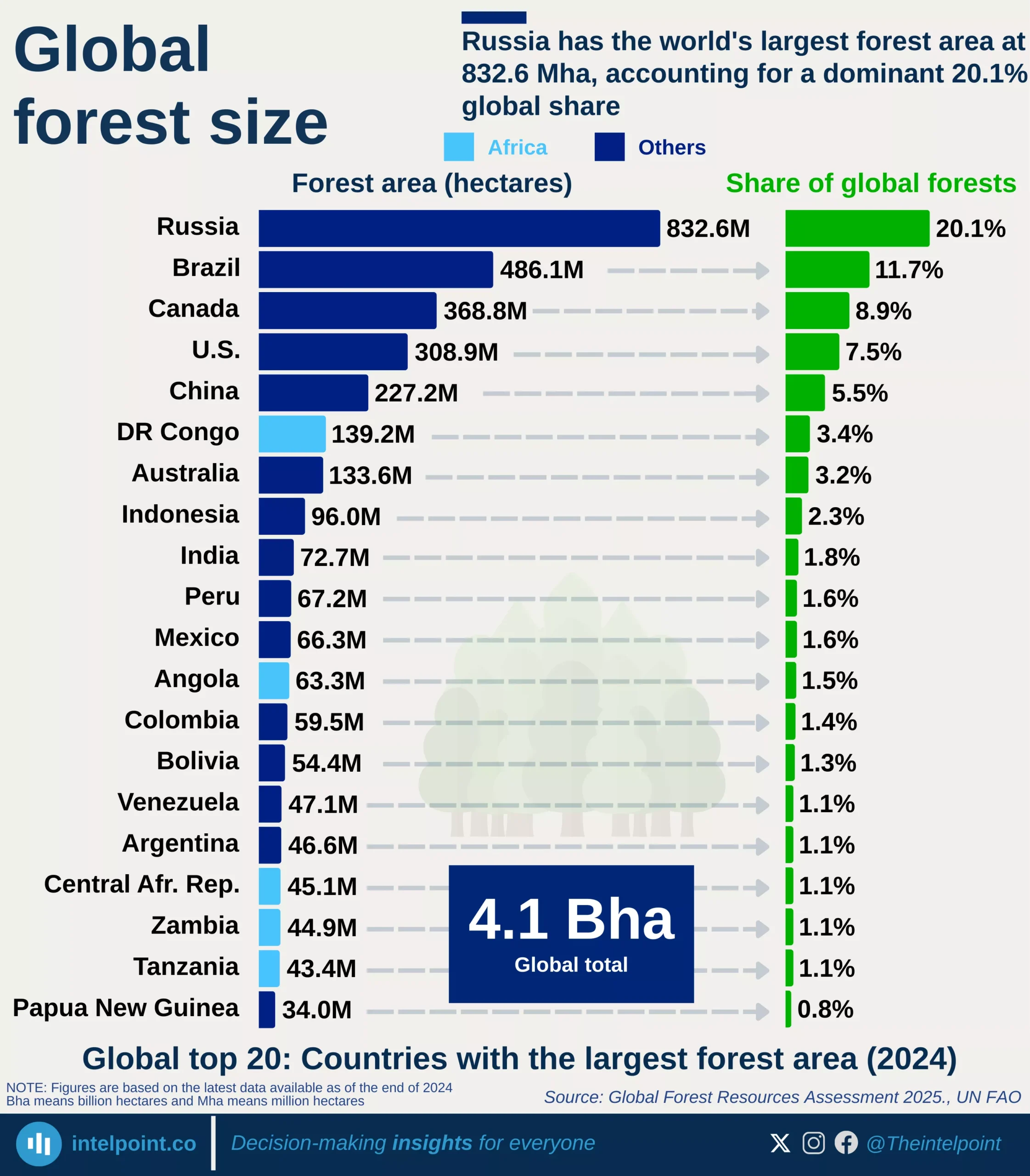
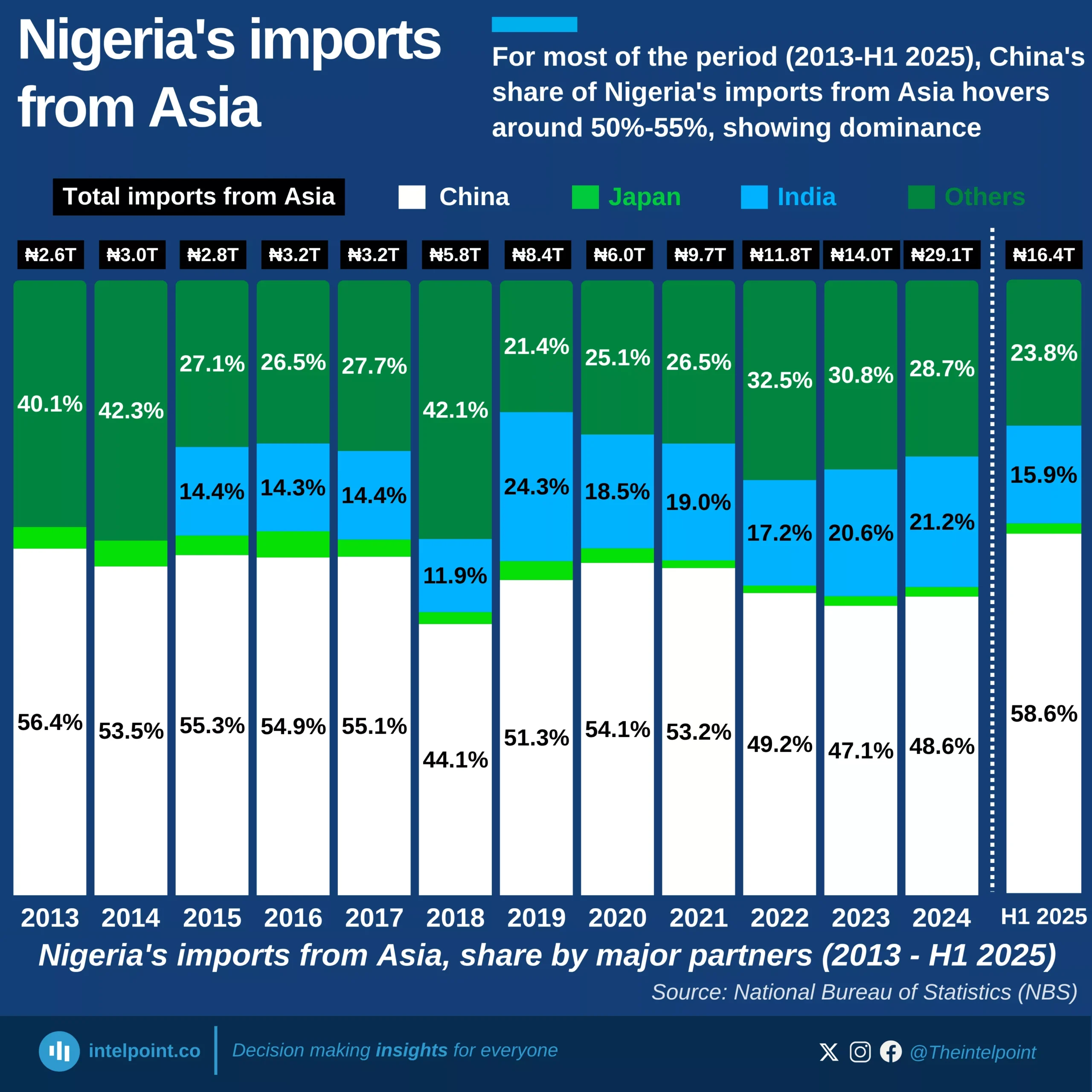
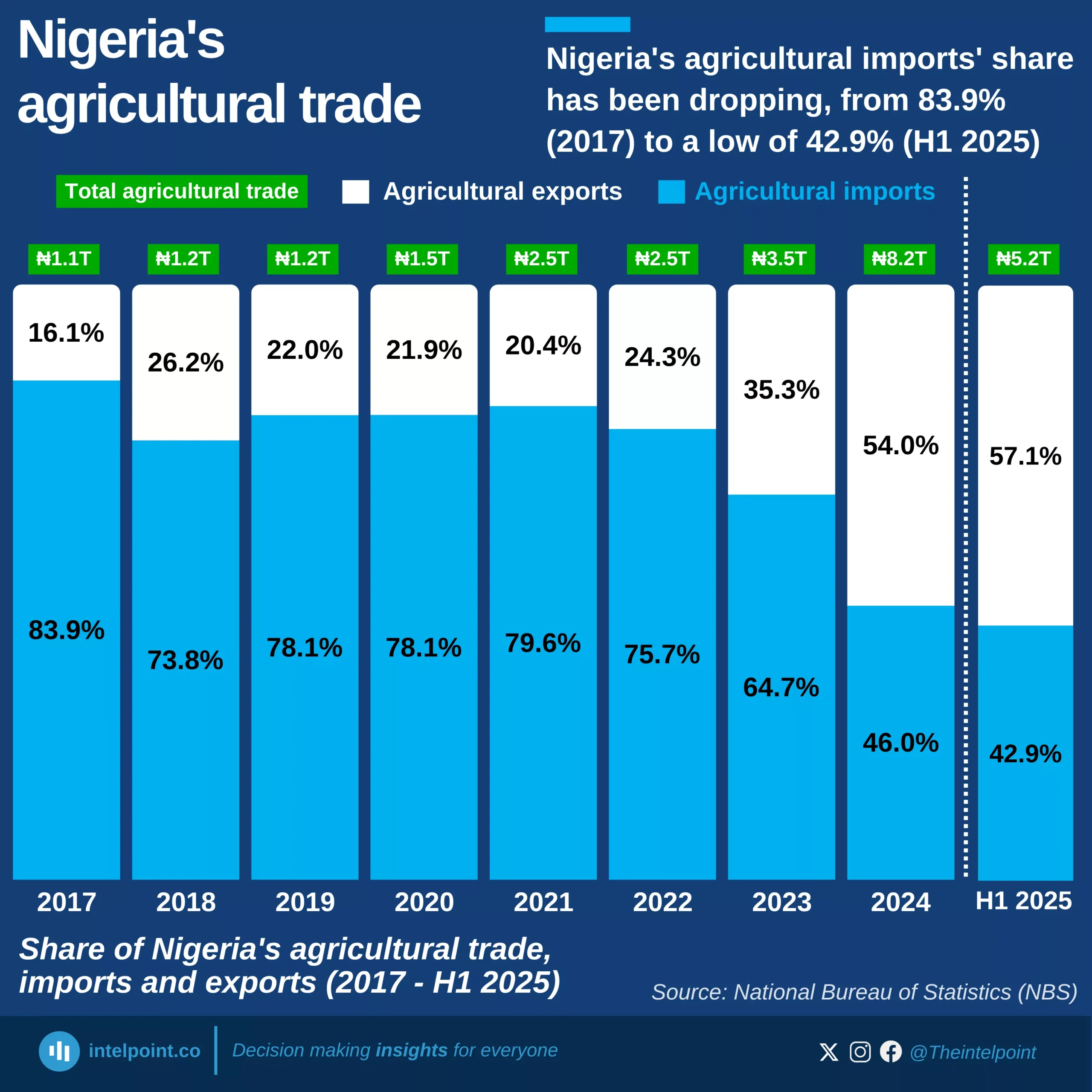
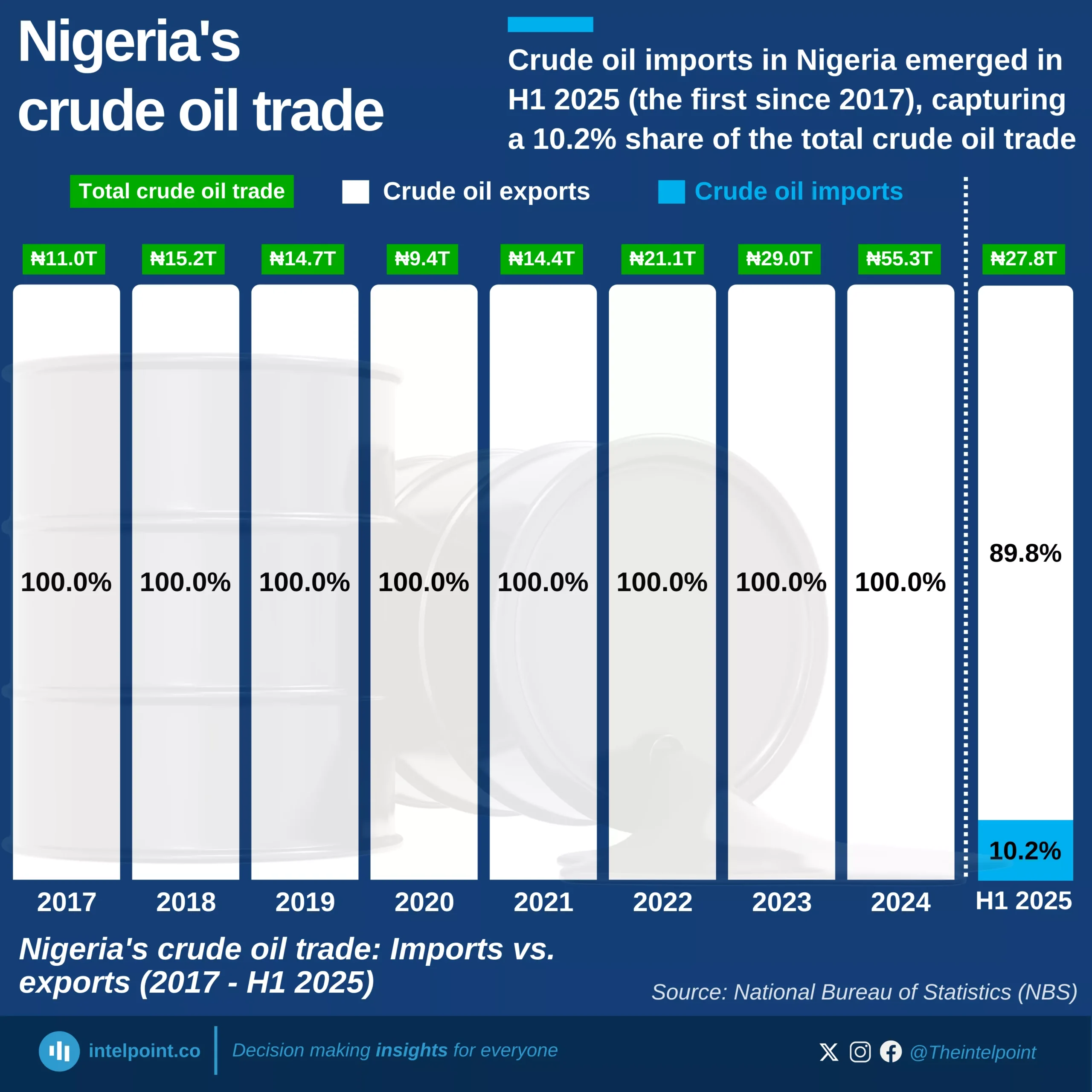
If you eat chocolate or anything made with cocoa-based fillings, there’s a good chance the raw beans passed through the Netherlands. Netherlands imported more cocoa beans than any other country in the world — 25.48 million tonnes across the 63-year span.
The US followed with 21.1 million tonnes, then Germany with 16.8 million. These three rarely dropped out of the top five in any given year. Malaysia climbed into the upper ranks starting in the 1980s, while the UK remained a steady buyer throughout. France, Belgium, and Italy also posted strong import volumes. The USSR, despite going inactive after 1991, still finished in the all-time top 10.
The numbers go beyond consumption. In the case of the Netherlands, it’s backed by one of the world’s largest cocoa grinding and processing industries. Facilities in Amsterdam and Zaandam have made the country a key hub for turning raw cocoa into butter, powder, and other ingredients used by global food brands, as documented by the International Cocoa Organization and other trade reports.
This long-term growth mirrors a global trend: total cocoa bean imports quadrupled between 1961 and 2023, rising from just over 1 million tonnes to nearly 4 million.