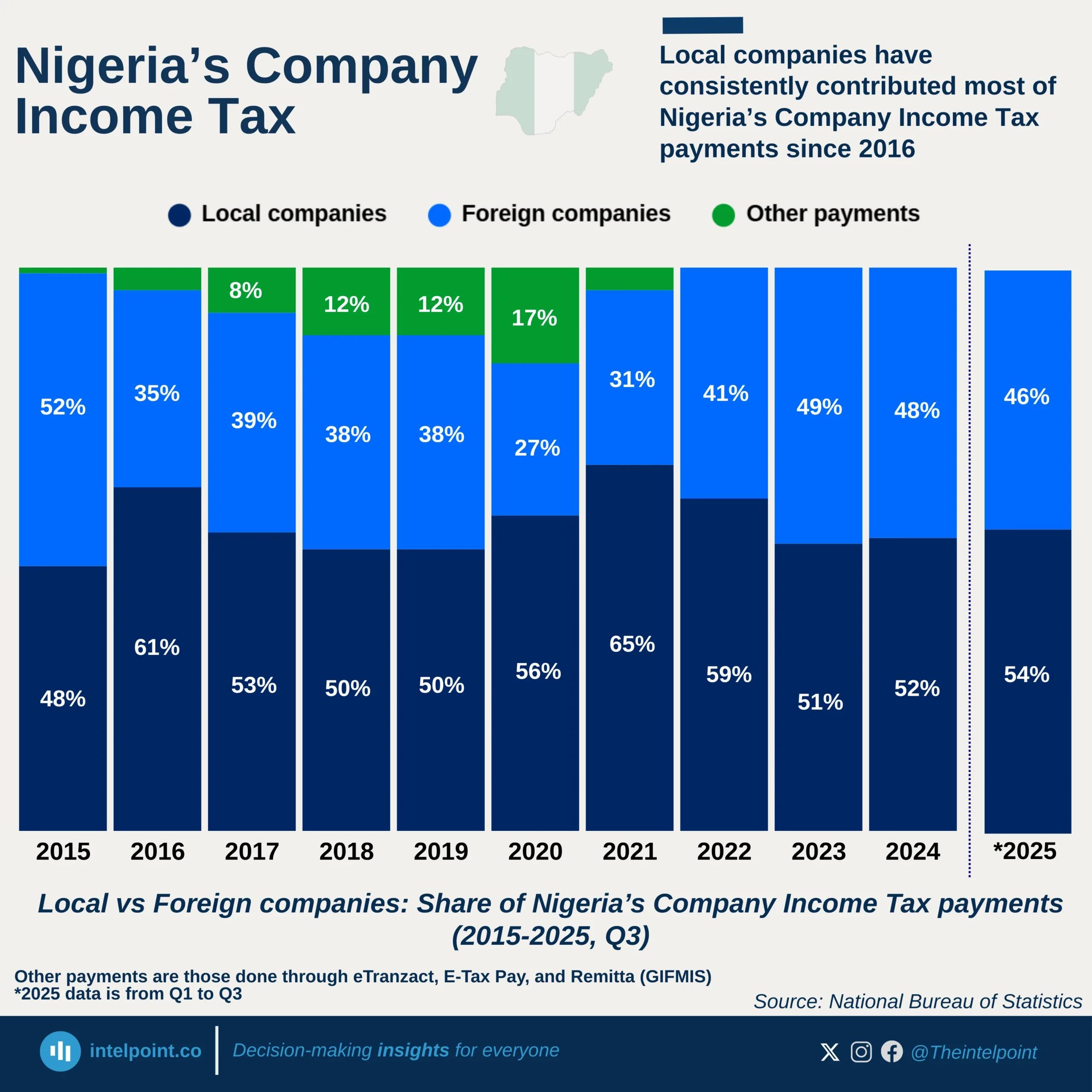
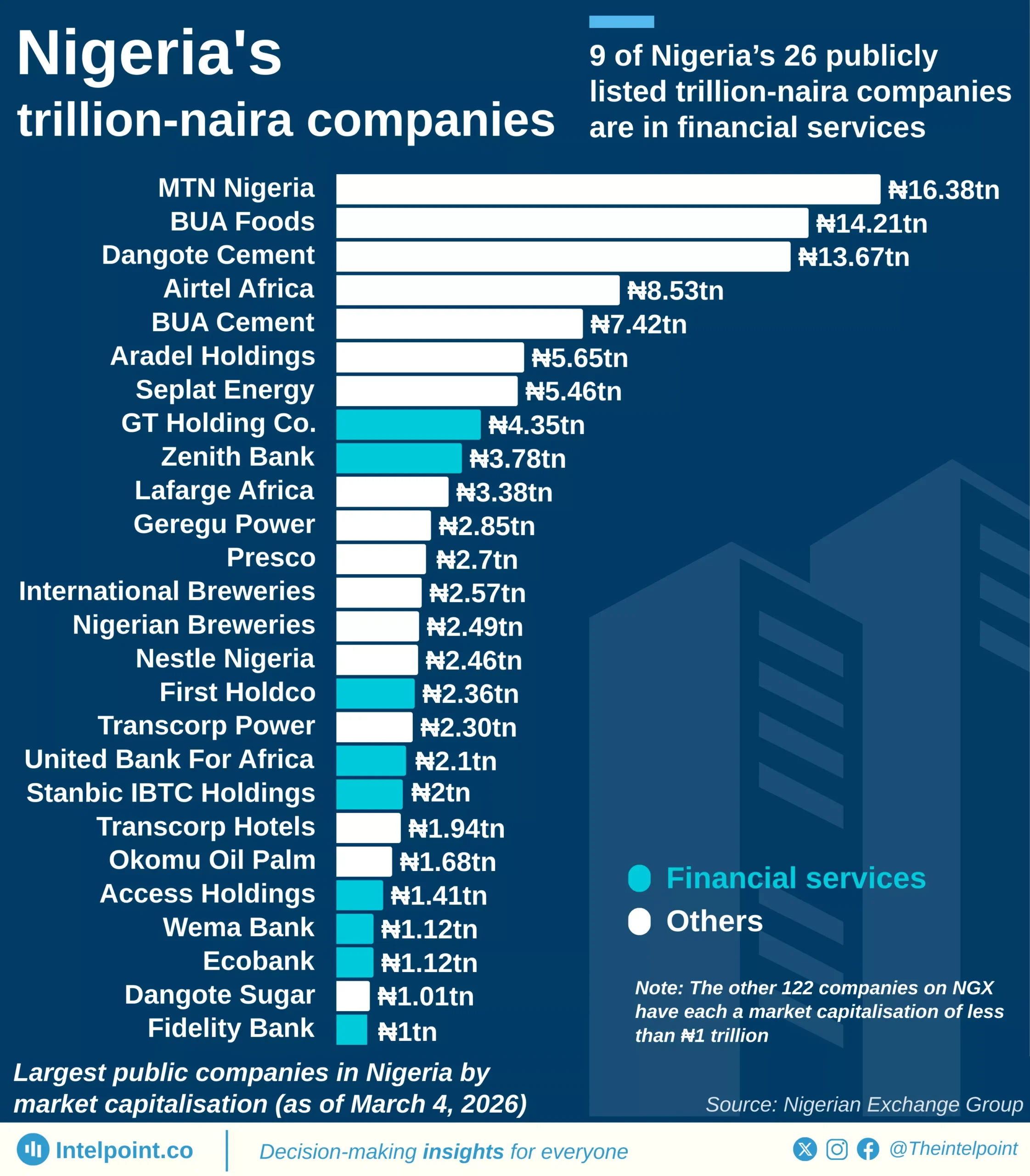
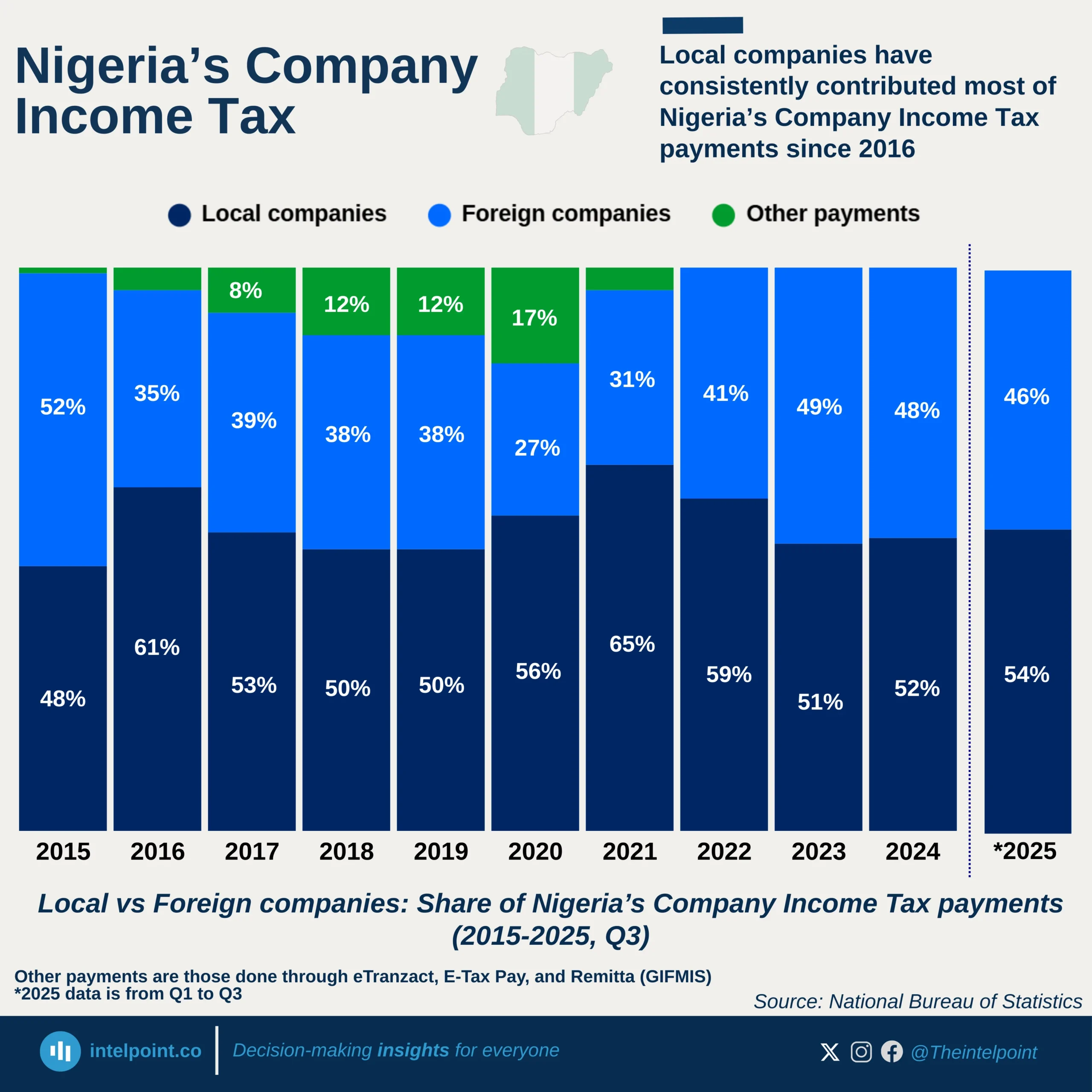
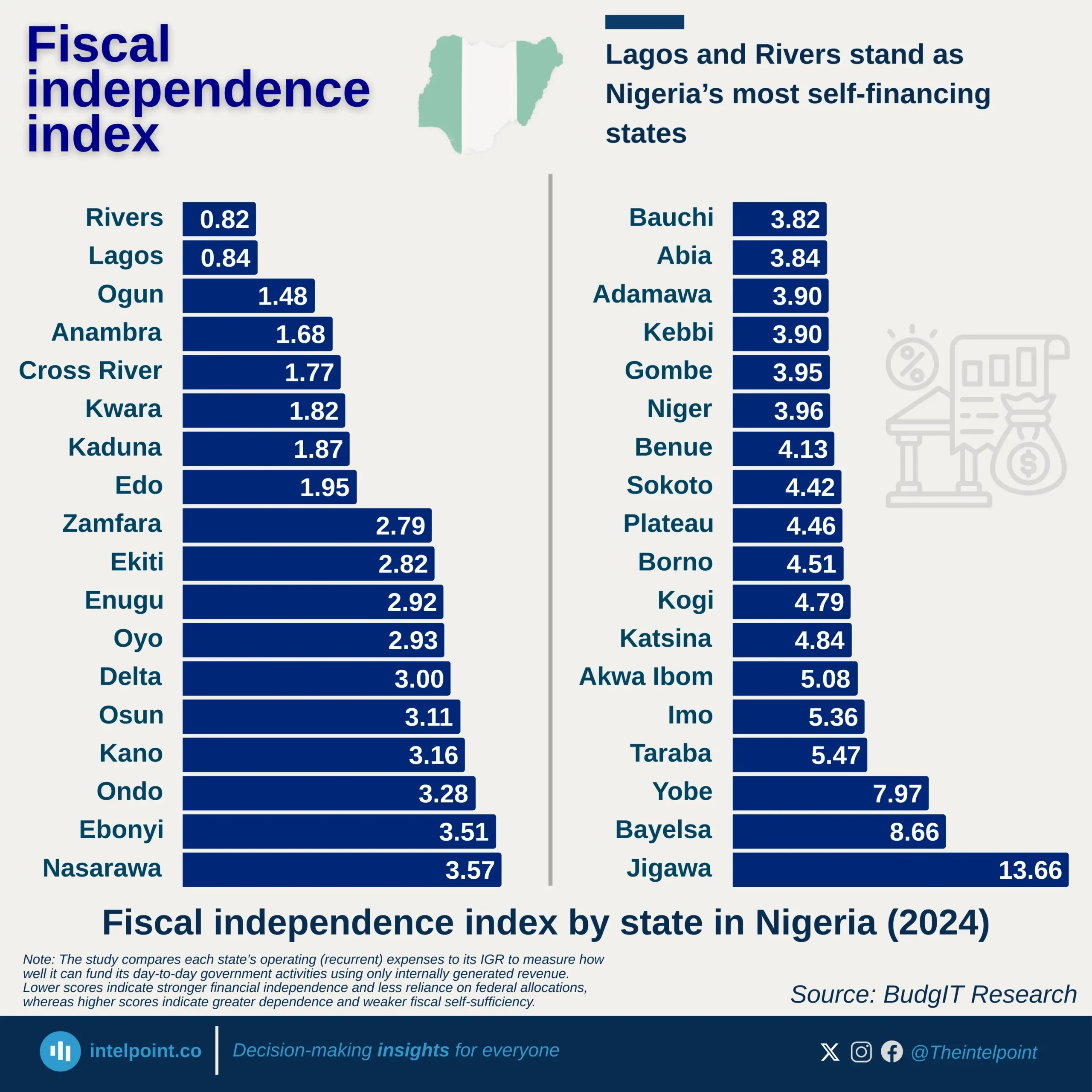
Ghana’s external debt interest payments tell a striking story of economic transition. For decades, from the 1970s through the early 2000s, the burden was modest, rarely exceeding $200 million. However, as the country pursued ambitious development goals and tapped into global capital markets, the cost of servicing debt grew rapidly. By 2016, payments approached $1 billion, and just six years later, they peaked at $1.49 billion in 2022, underscoring the intensity of Ghana’s debt exposure. In 2023, the figure dropped dramatically to $780 million, nearly half the previous year’s level, signalling a potential turning point linked to economic adjustments, fiscal reforms, or international debt relief efforts.