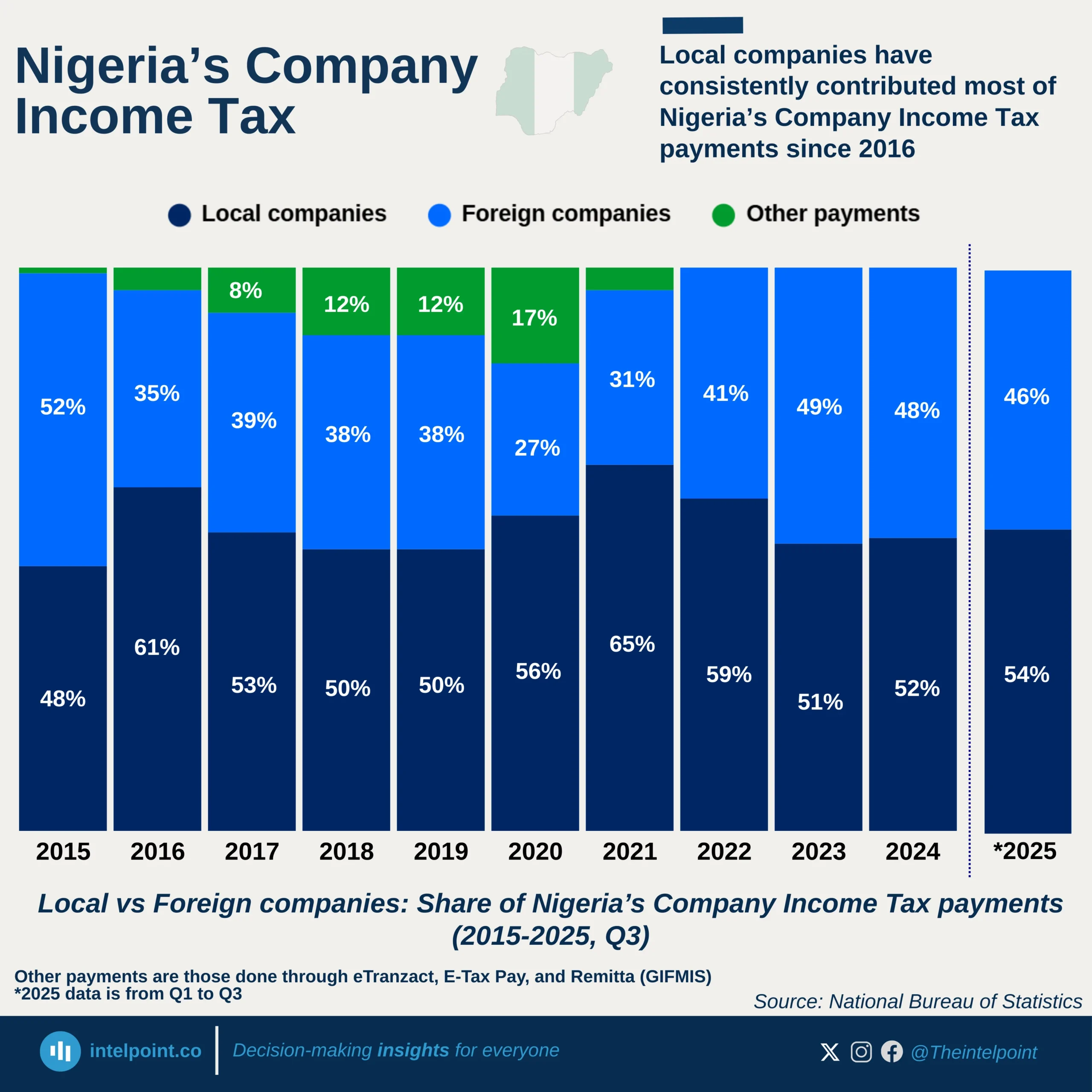
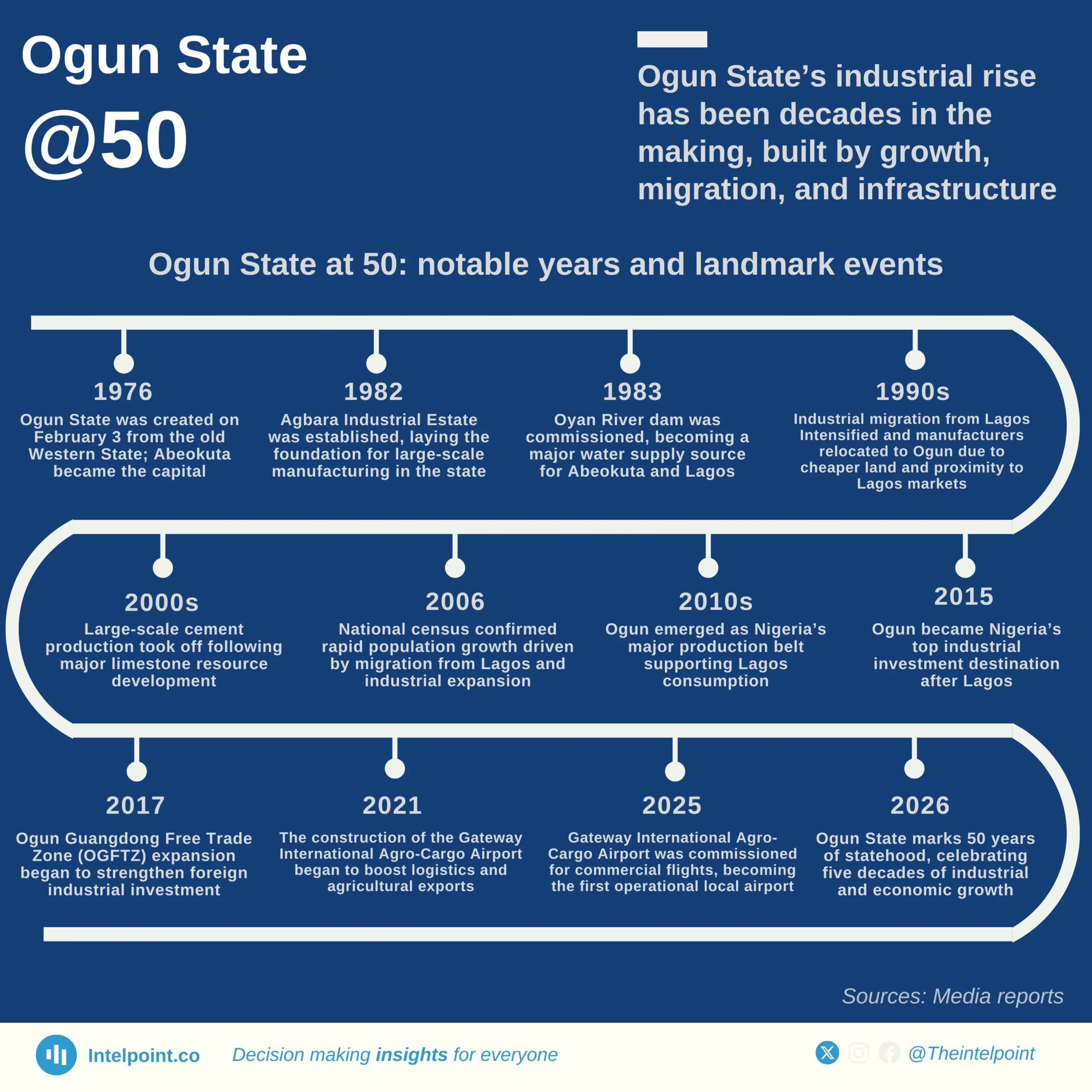
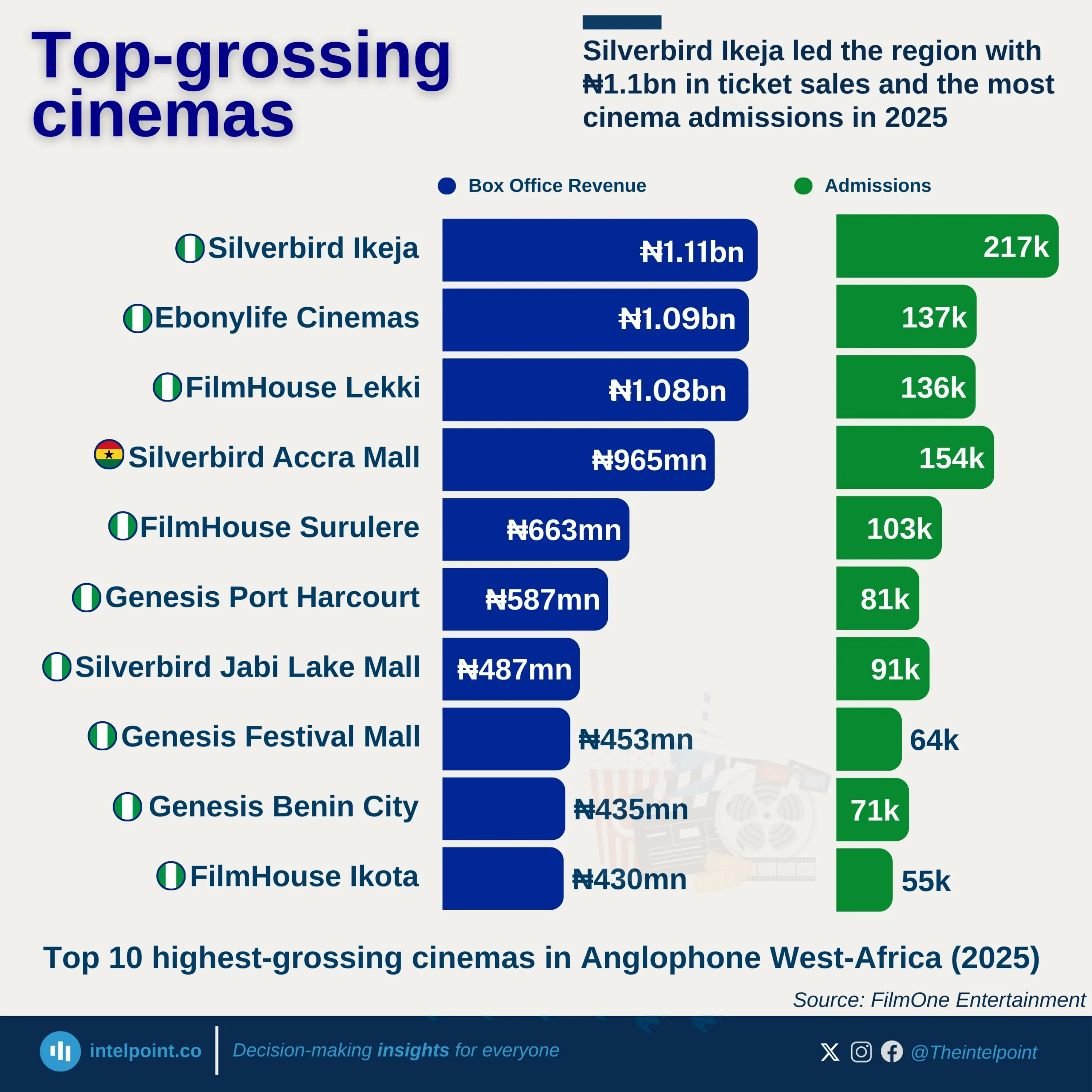
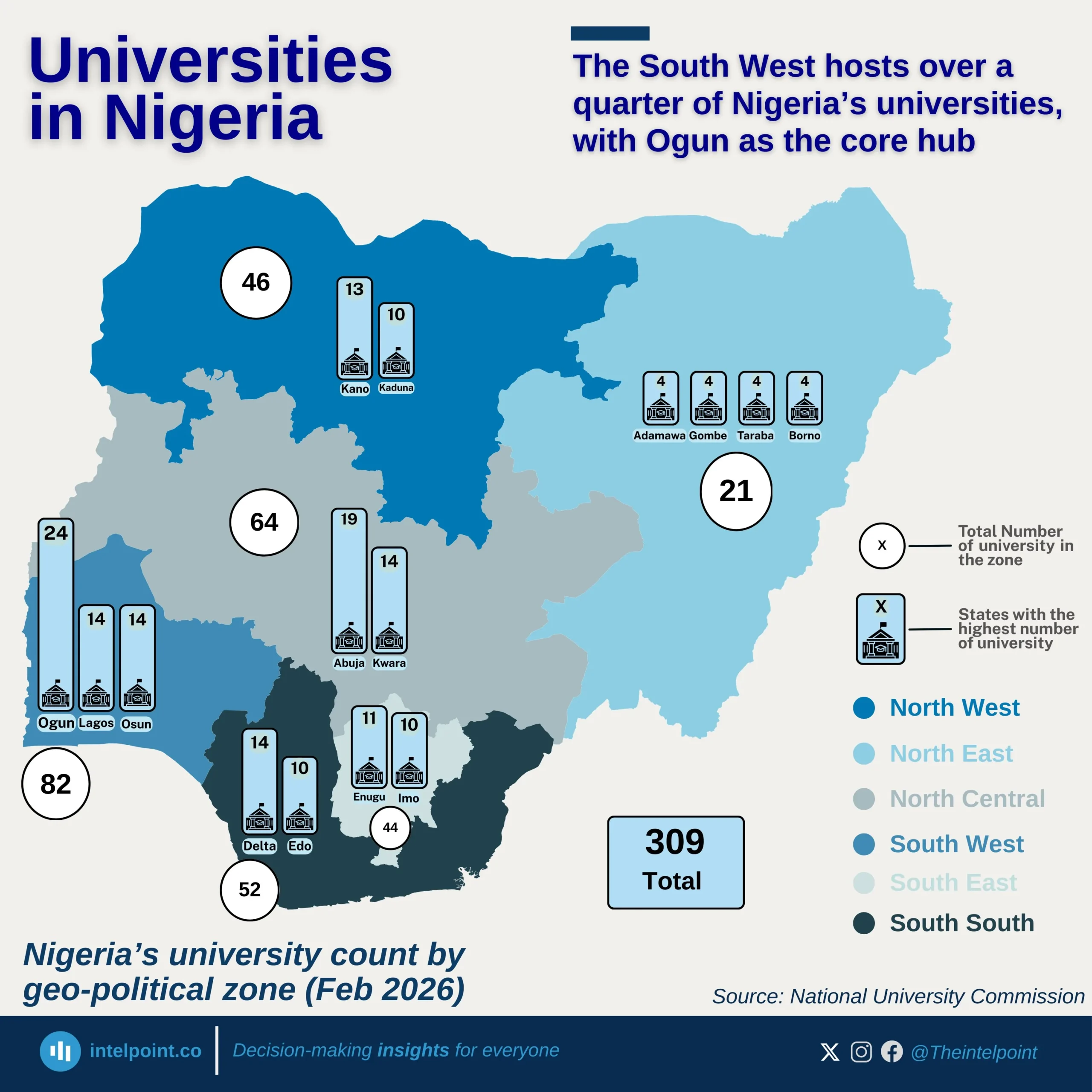
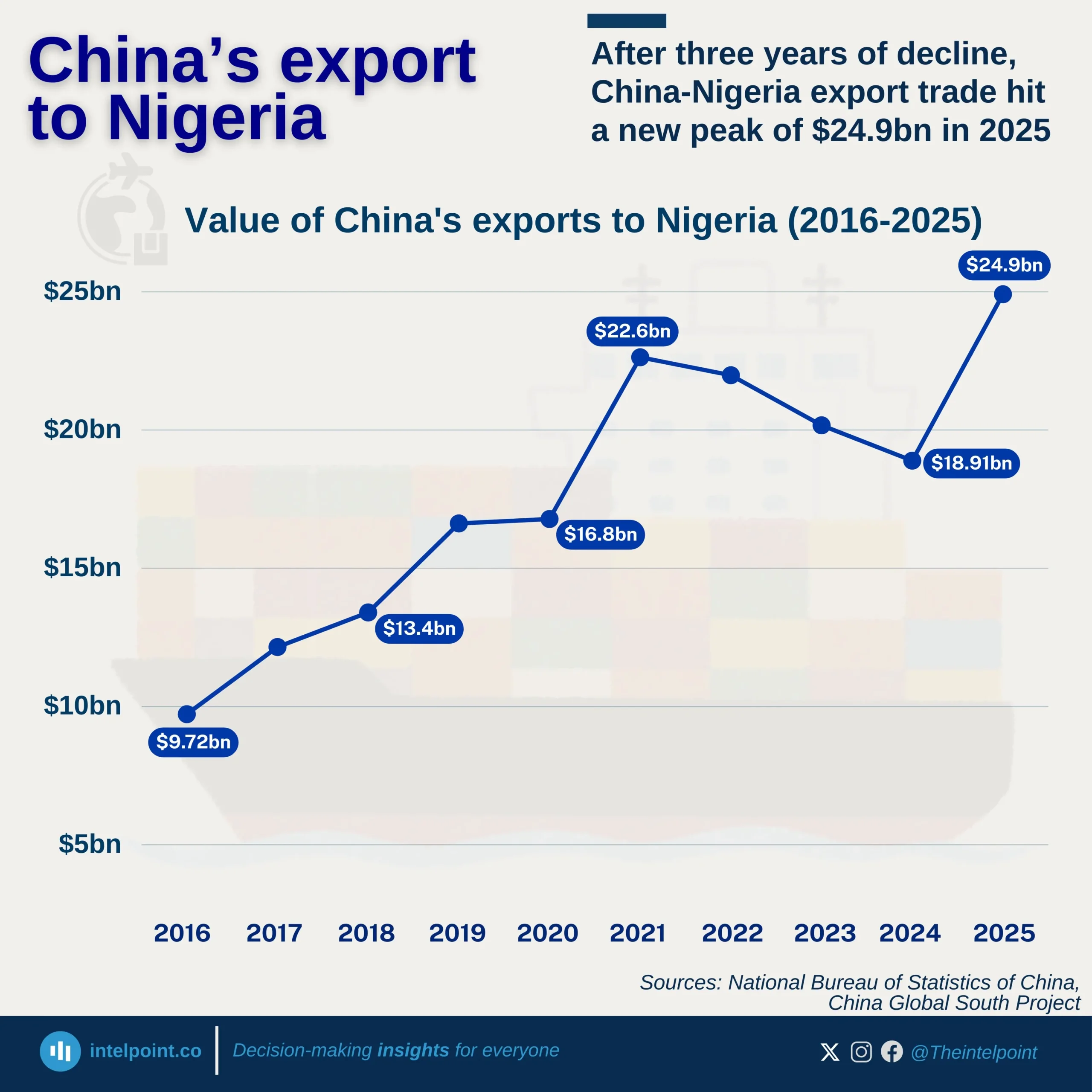
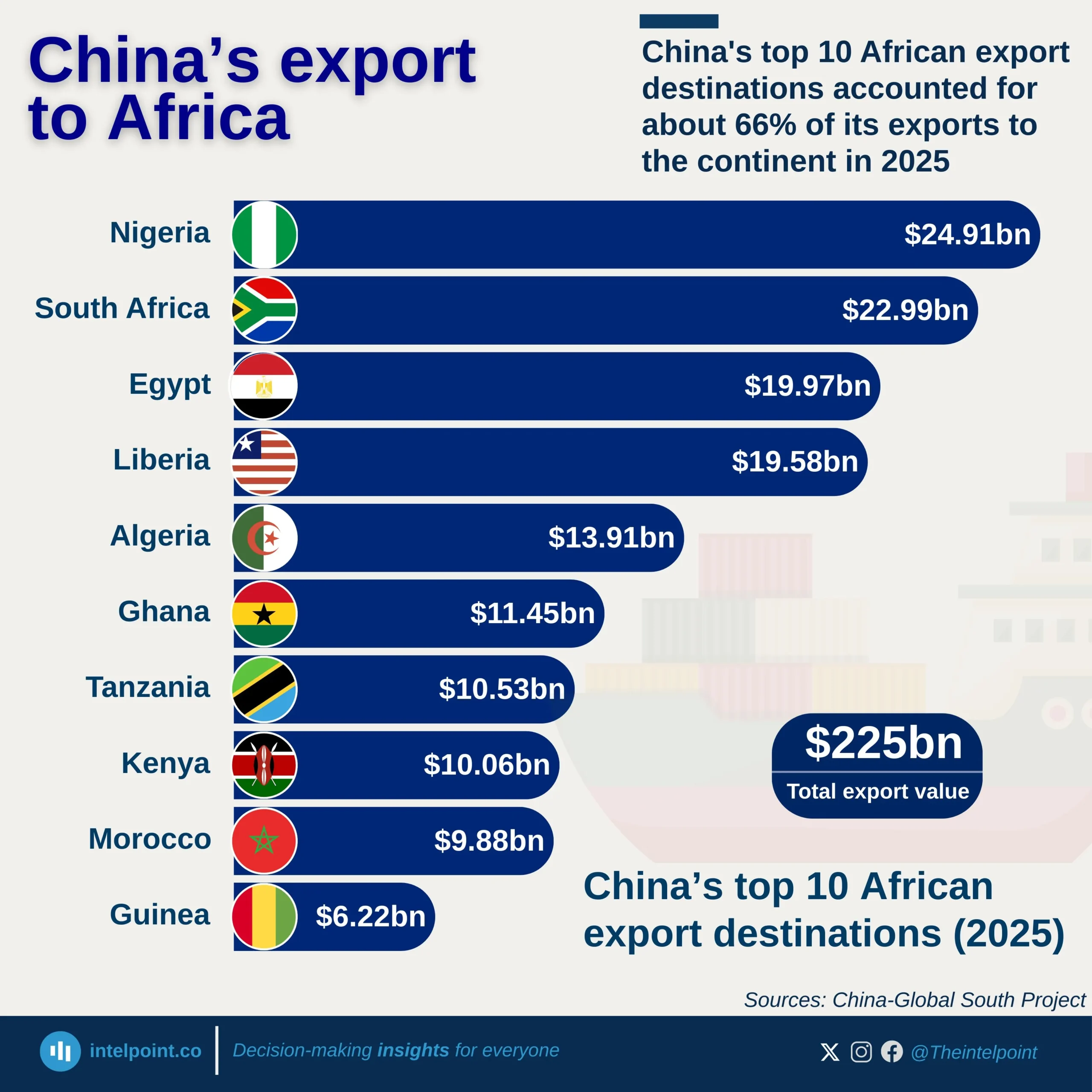
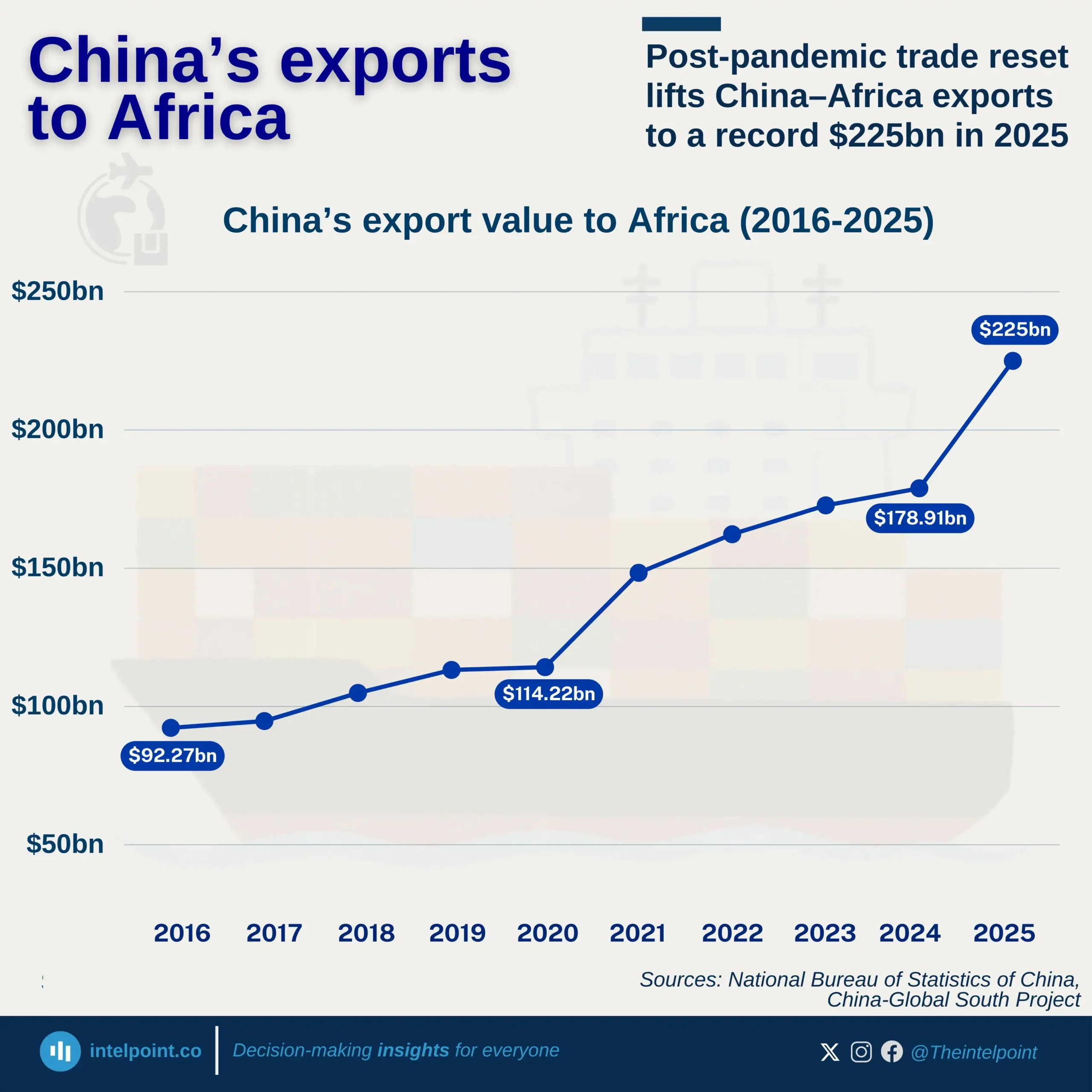
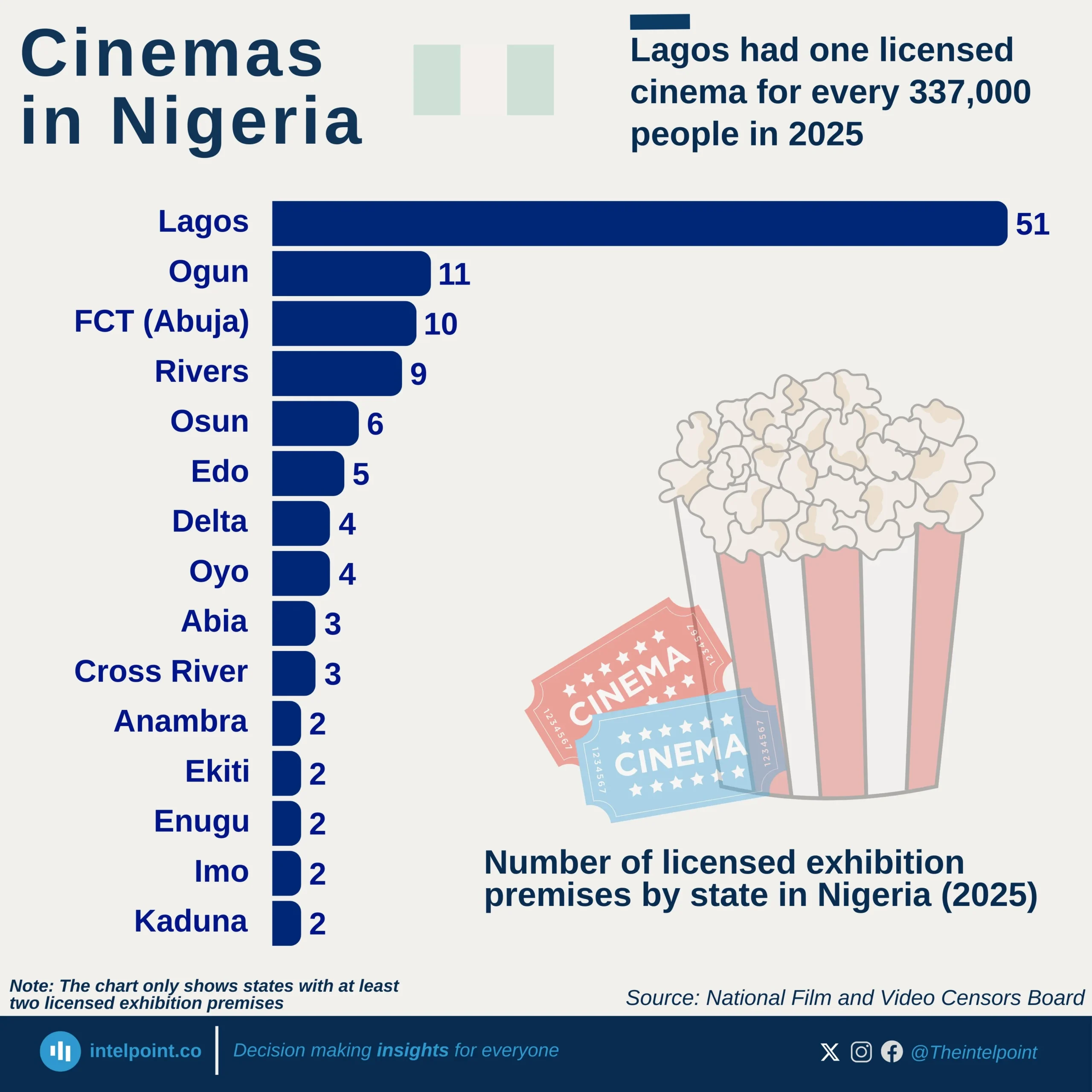
Bite-sized Insights about
Providing you with data-based insights about things happening around you.
Can’t find what you’re looking for? Please fill the form below
SIGN UP TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Get periodic updates about the African startup space, access to our reports, among others.
Subscribe Here
A product of Techpoint Africa. All rights reserved
Subscribe to our newsletter