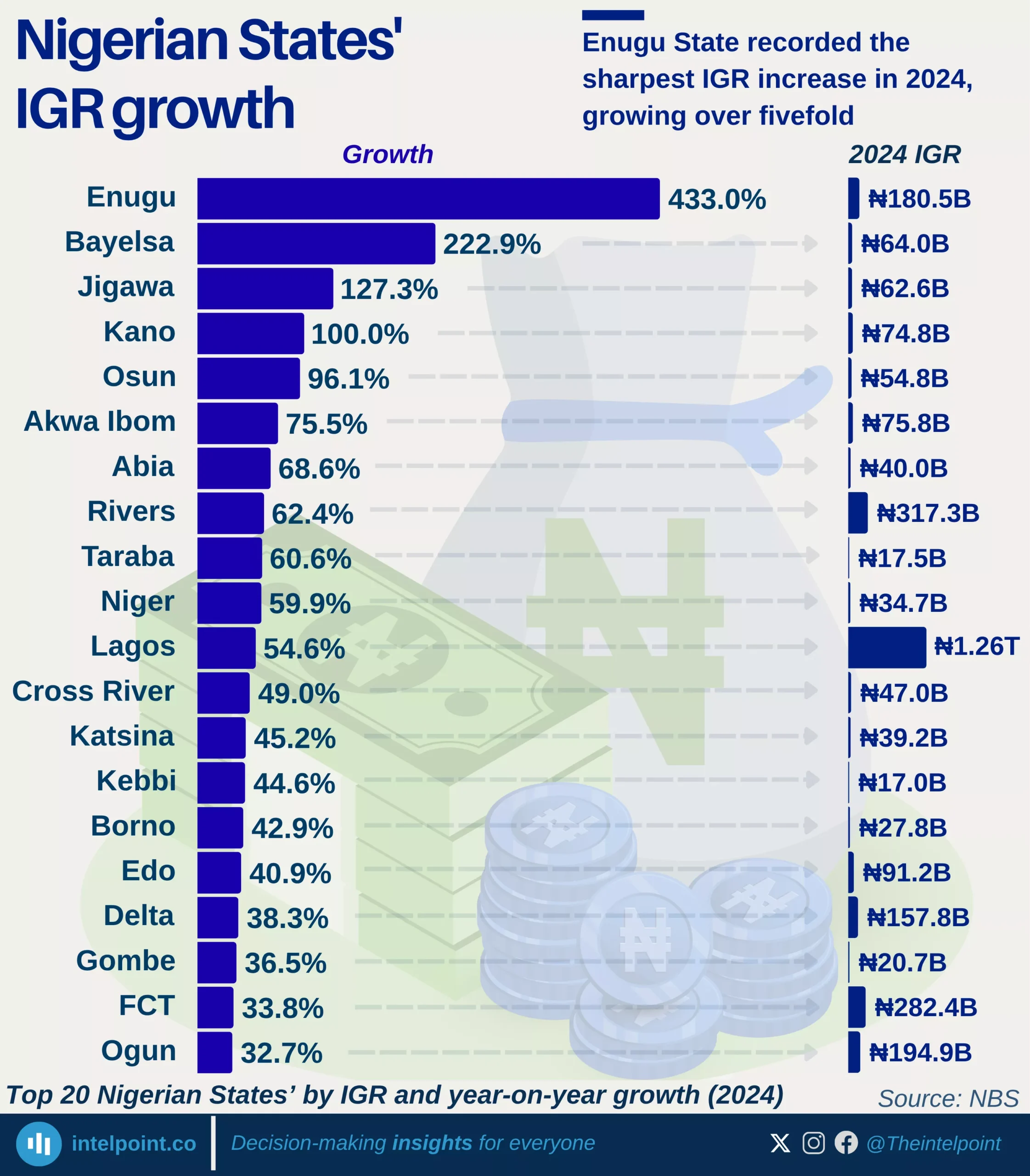
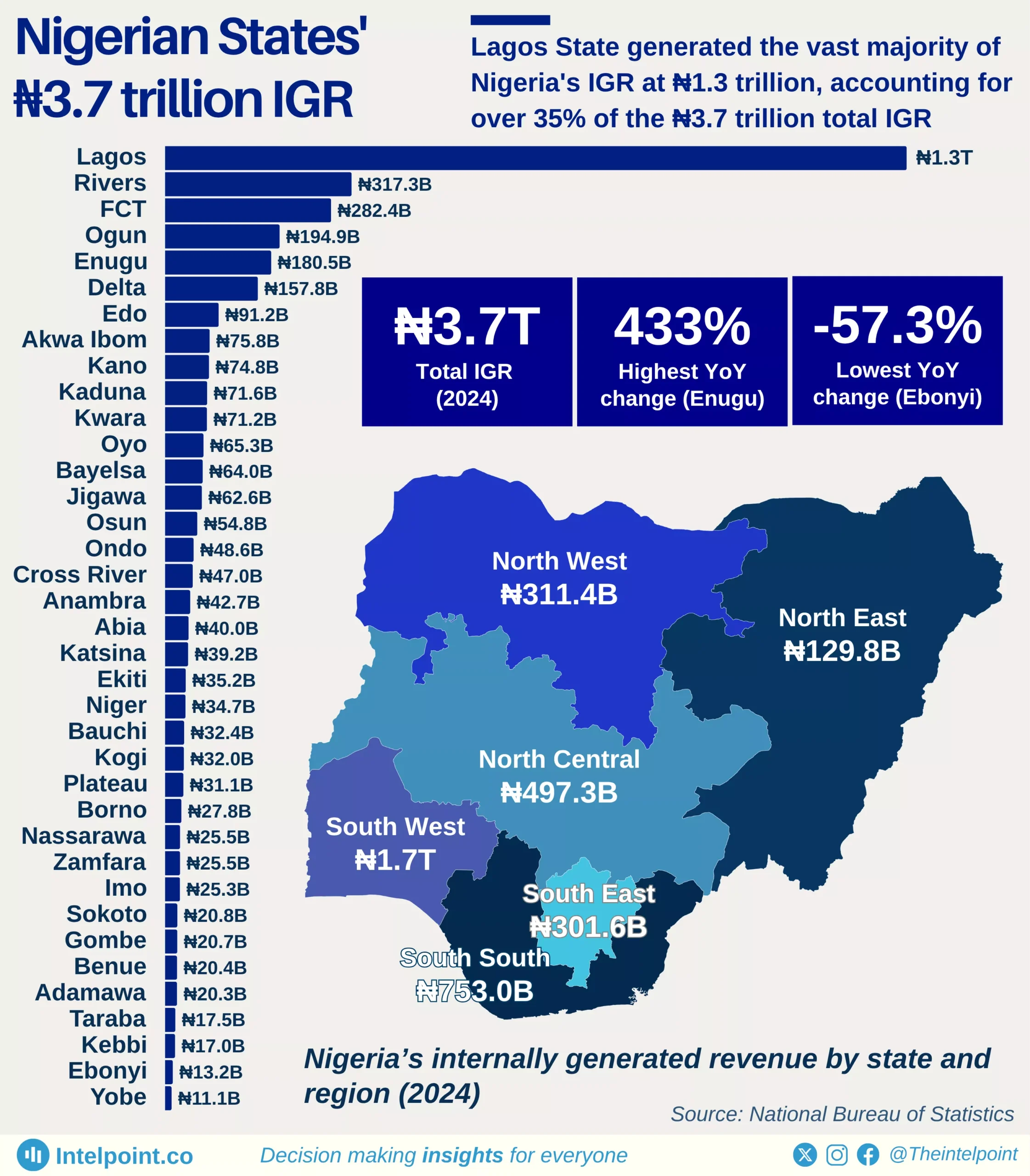
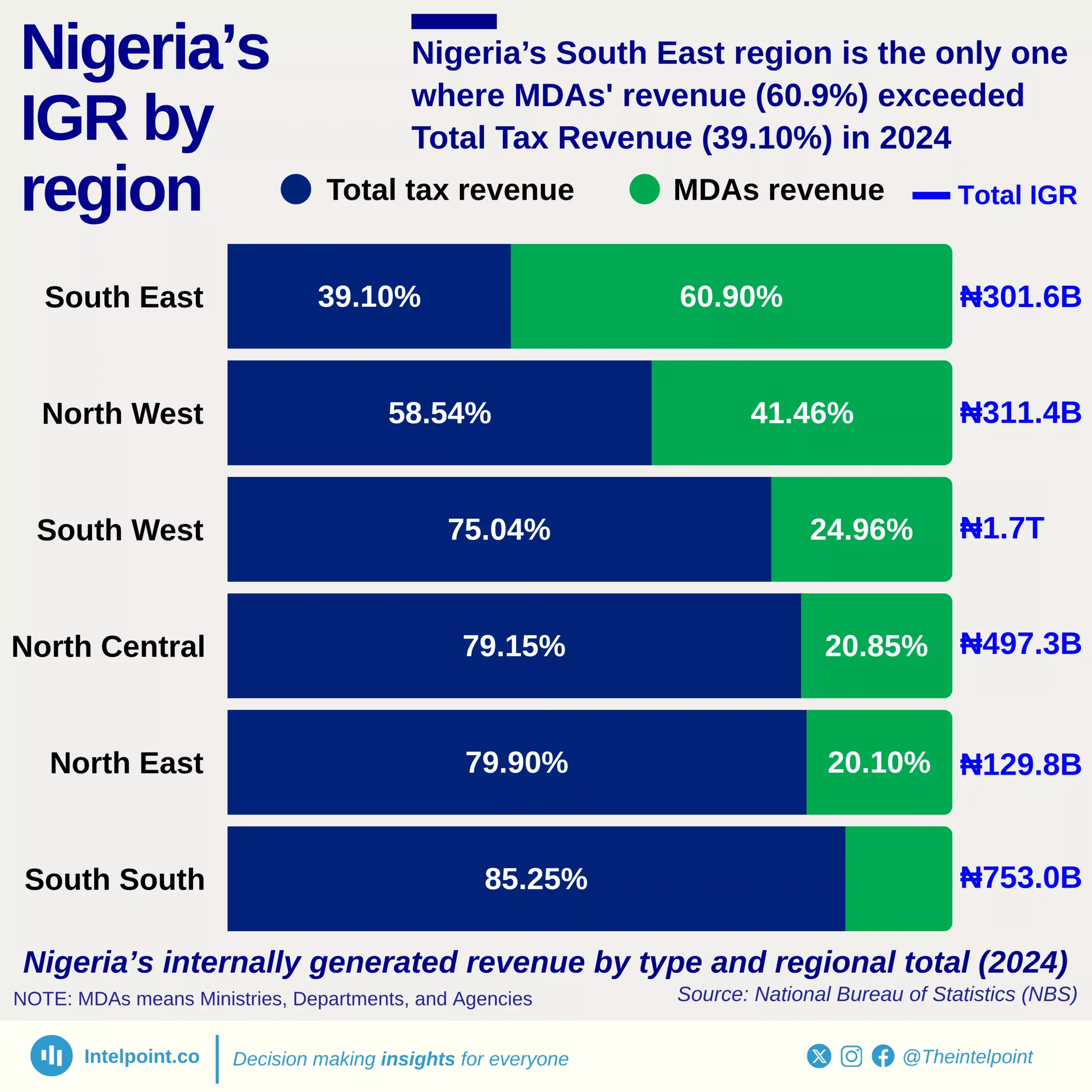
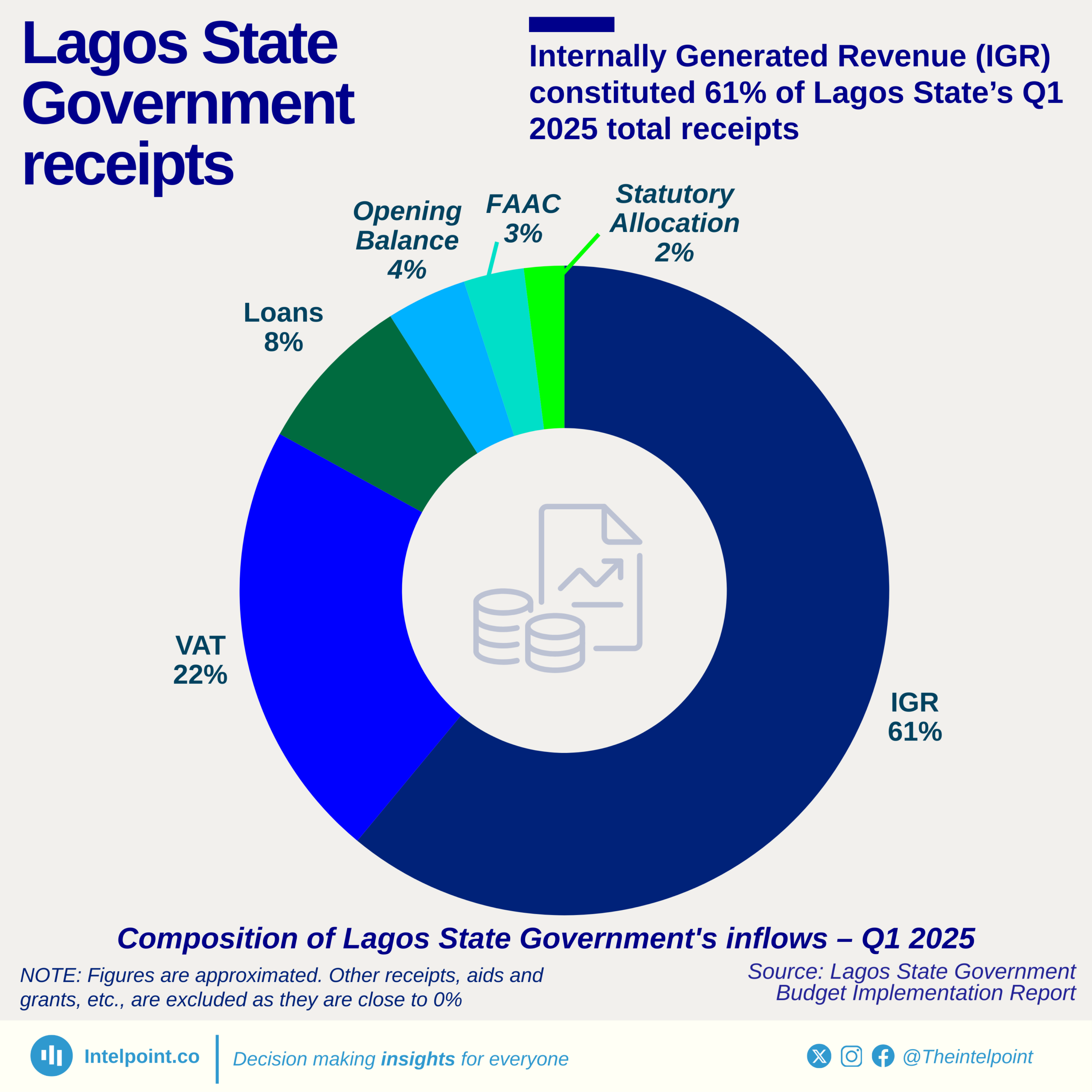
Lagos’ IGR in 2024 was more than 3x the combined IGR of the rest of the South West, highlighting the concentration of fiscal capacity in one state.
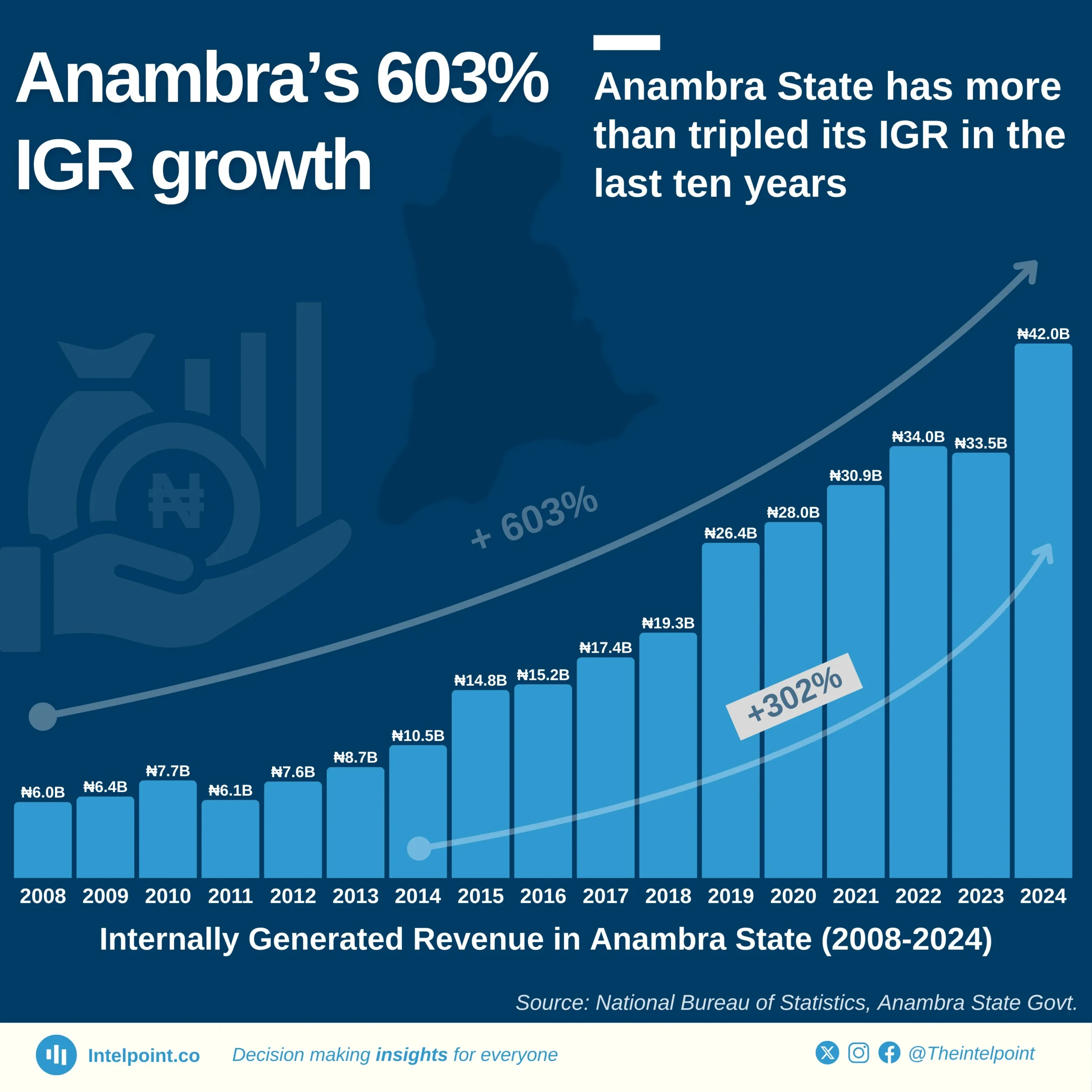
Across zones, each region has one clear revenue anchor state: Rivers in the South South, the FCT in the North Central, Enugu in the South East, Kano in the North West, and Bauchi in the North East. These leading states account for a significant share of their regions’ IGR, showing how economic activity and tax capacity remain unevenly distributed.