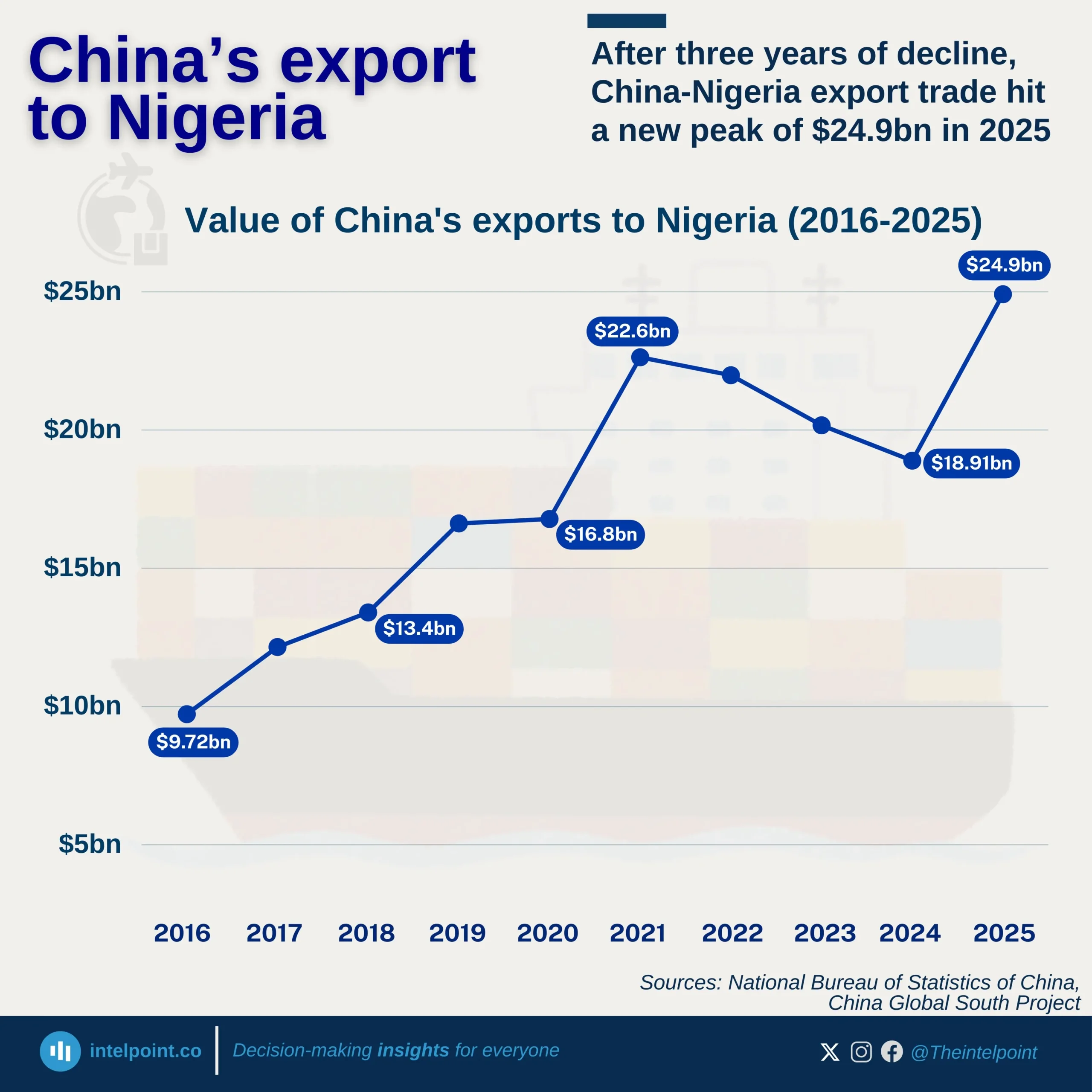
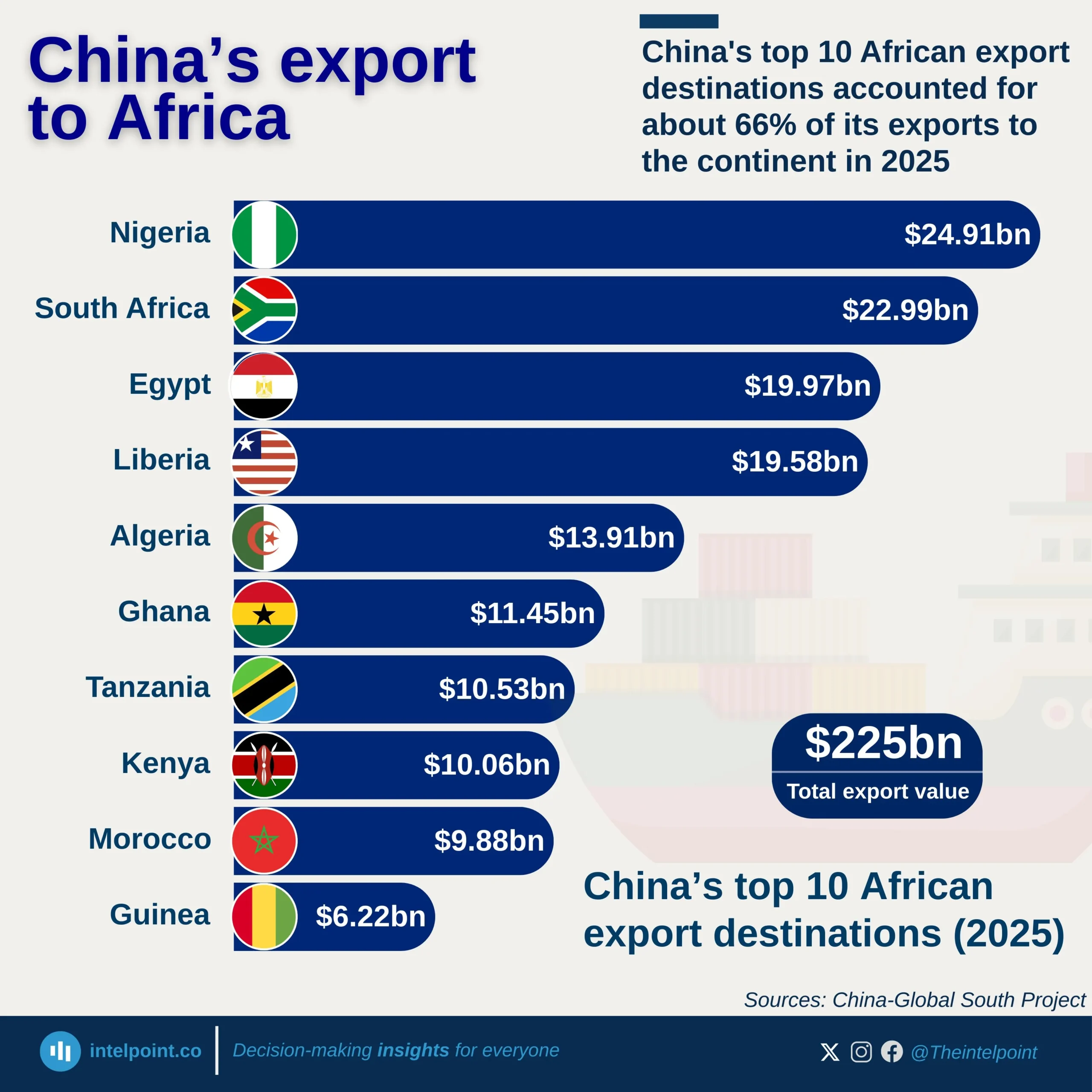
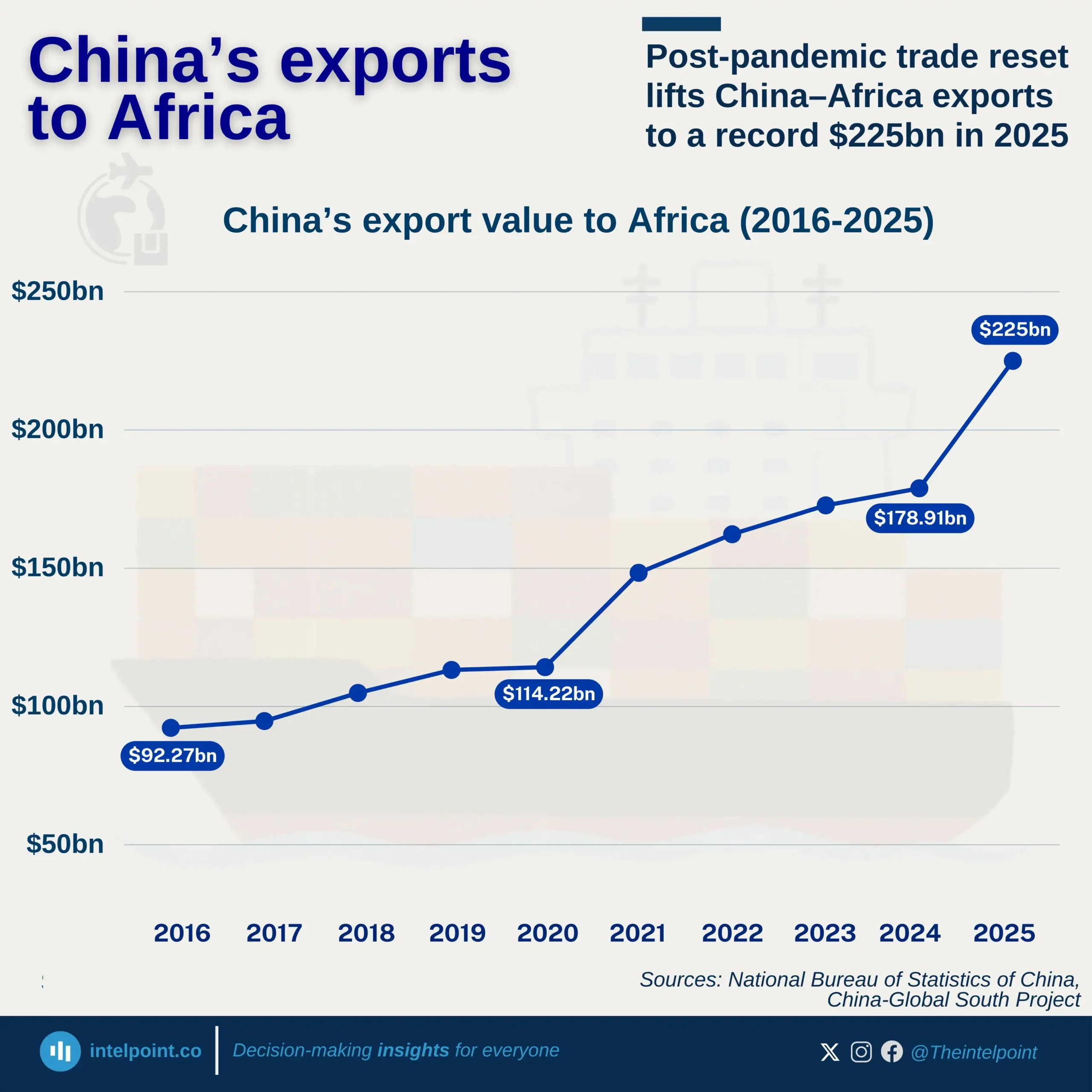
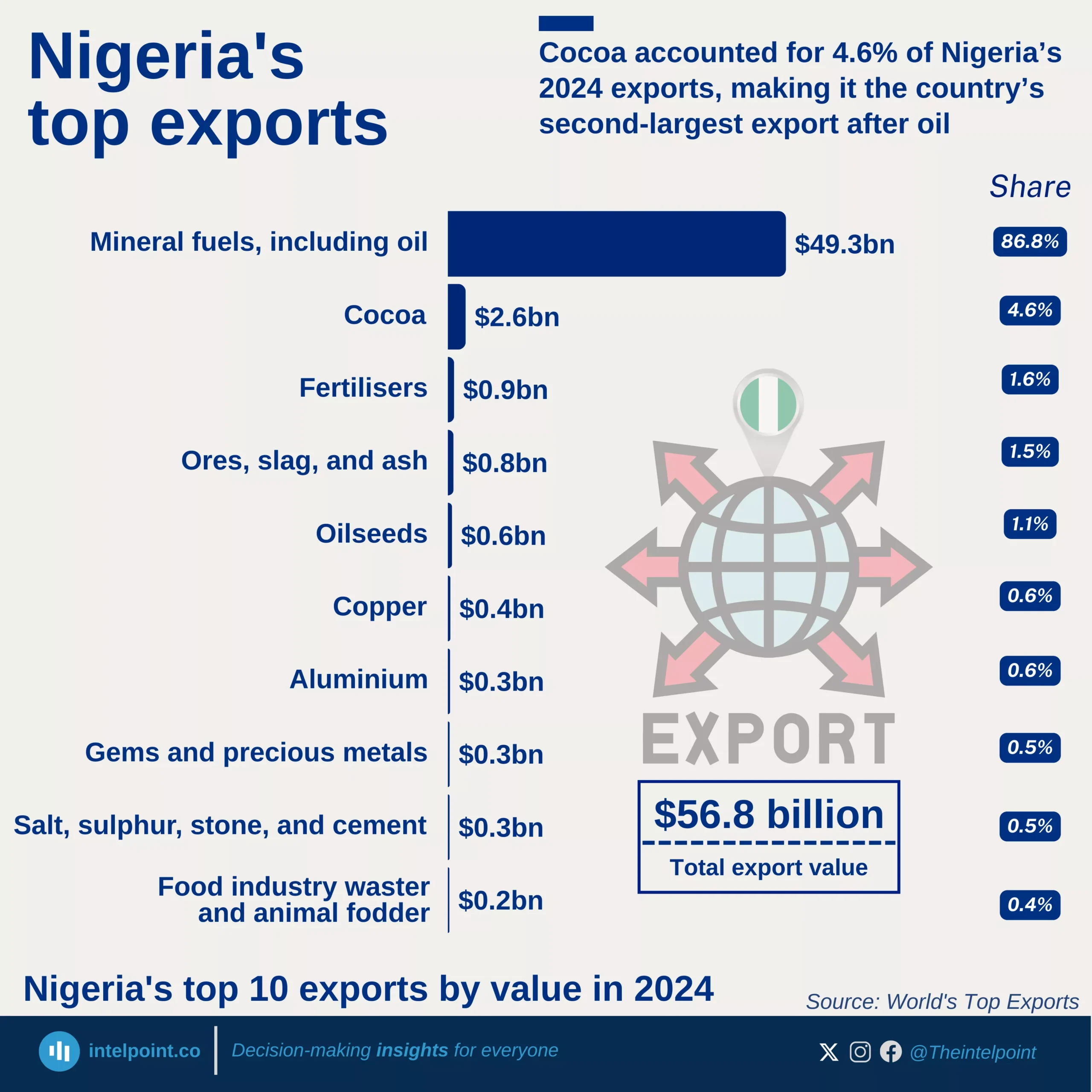
China continues to dominate Nigeria’s import relationship with Asia, maintaining a steady lead over the past decade. From 2013 to H1 2025, China consistently accounted for around 50%–55% of Nigeria’s total imports from the region, reaching a new high of 58.6% in H1 2025. This long-term dominance highlights China’s strong foothold in Nigeria’s trade structure, a result of deep economic ties built on affordable manufactured goods, machinery, electronics, and construction materials. In contrast, other Asian countries like India and Japan hold smaller but notable shares, reflecting a more diversified but uneven import mix within Asia.