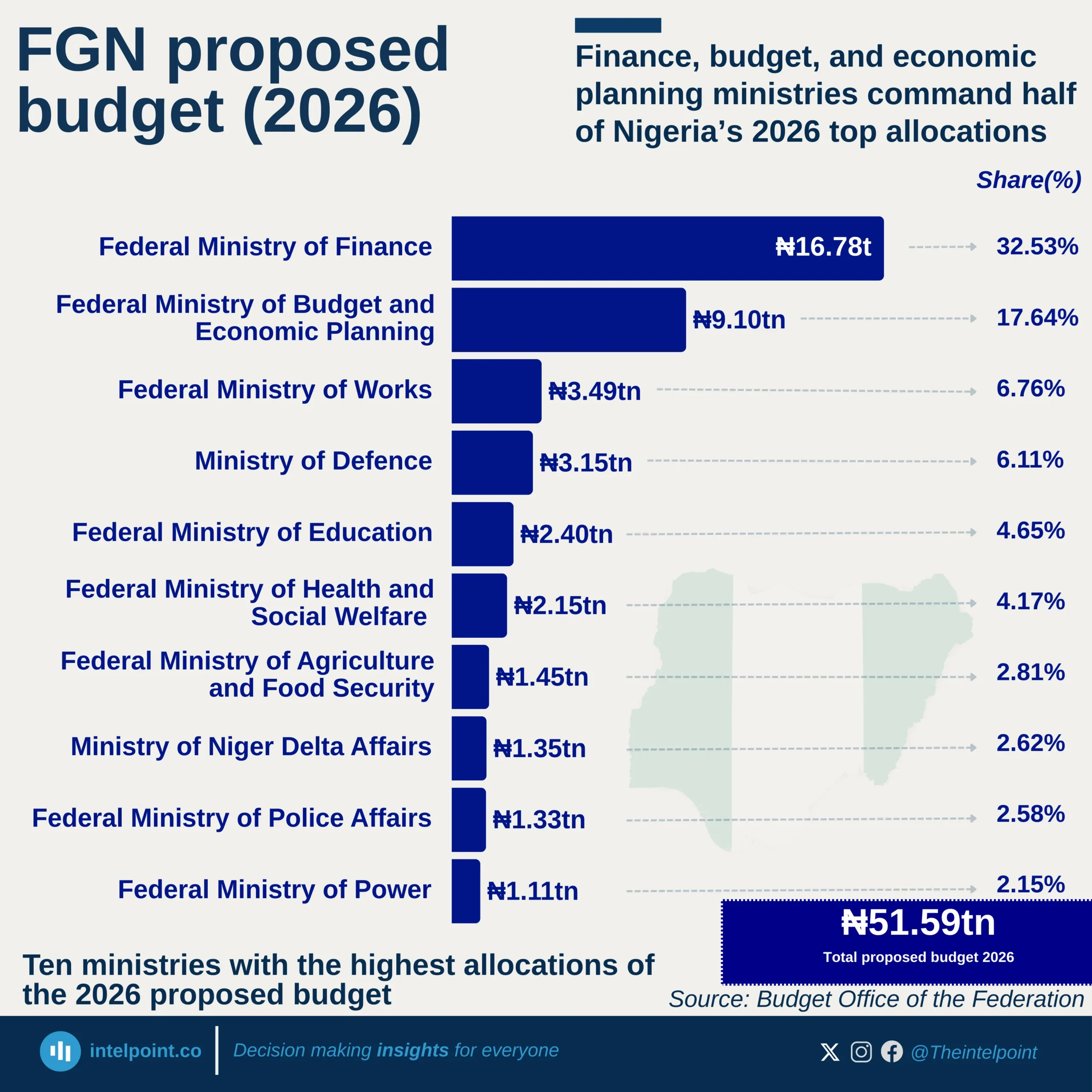
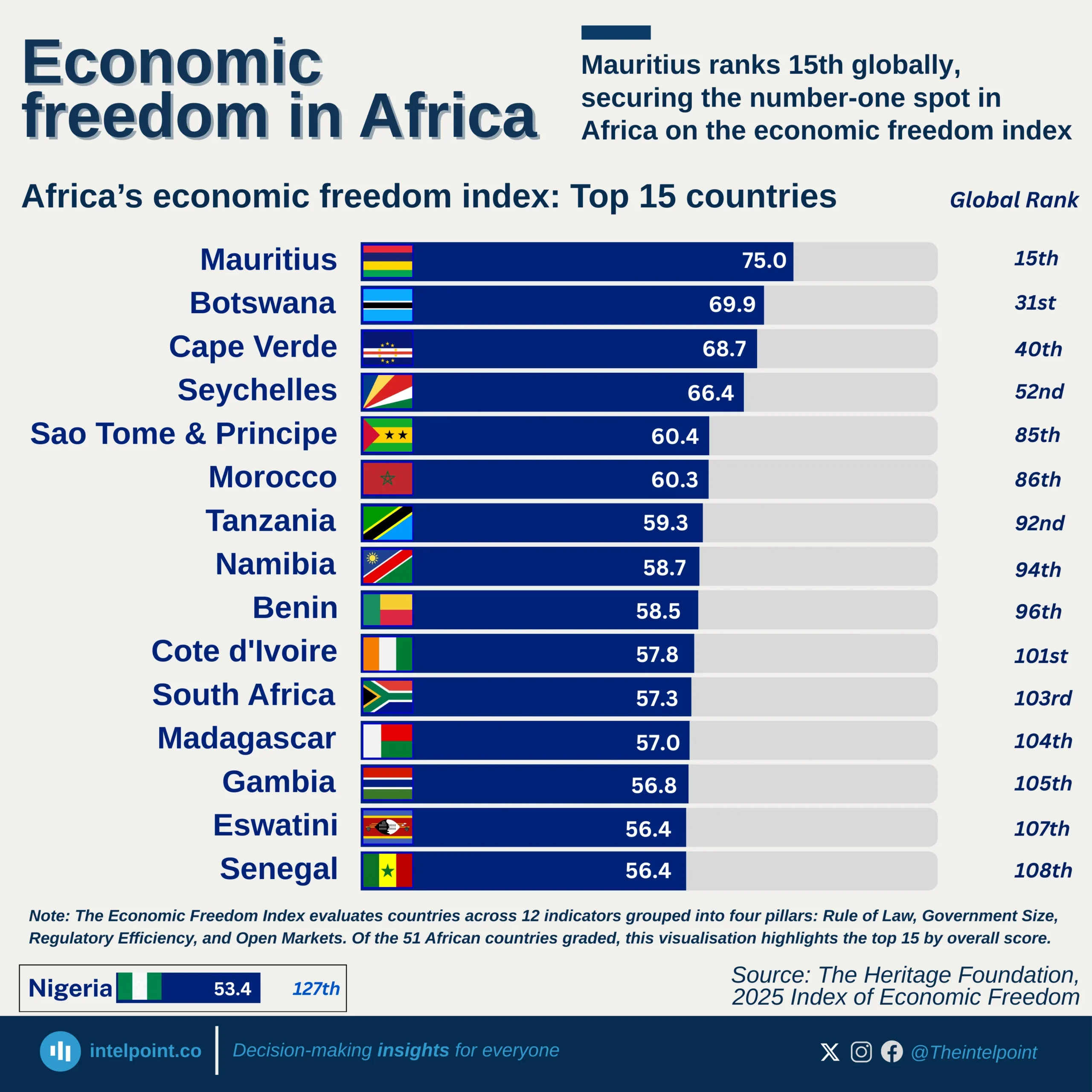
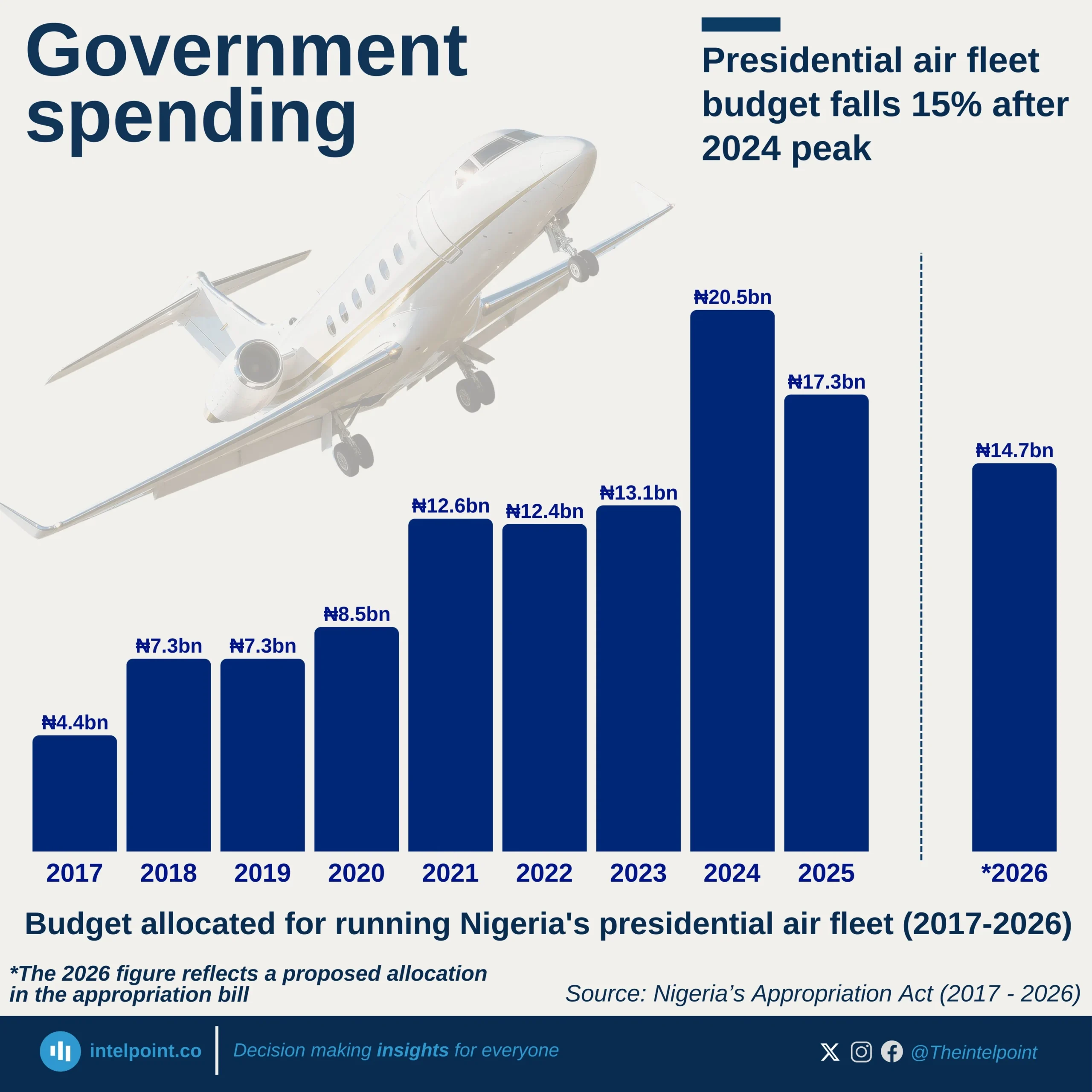
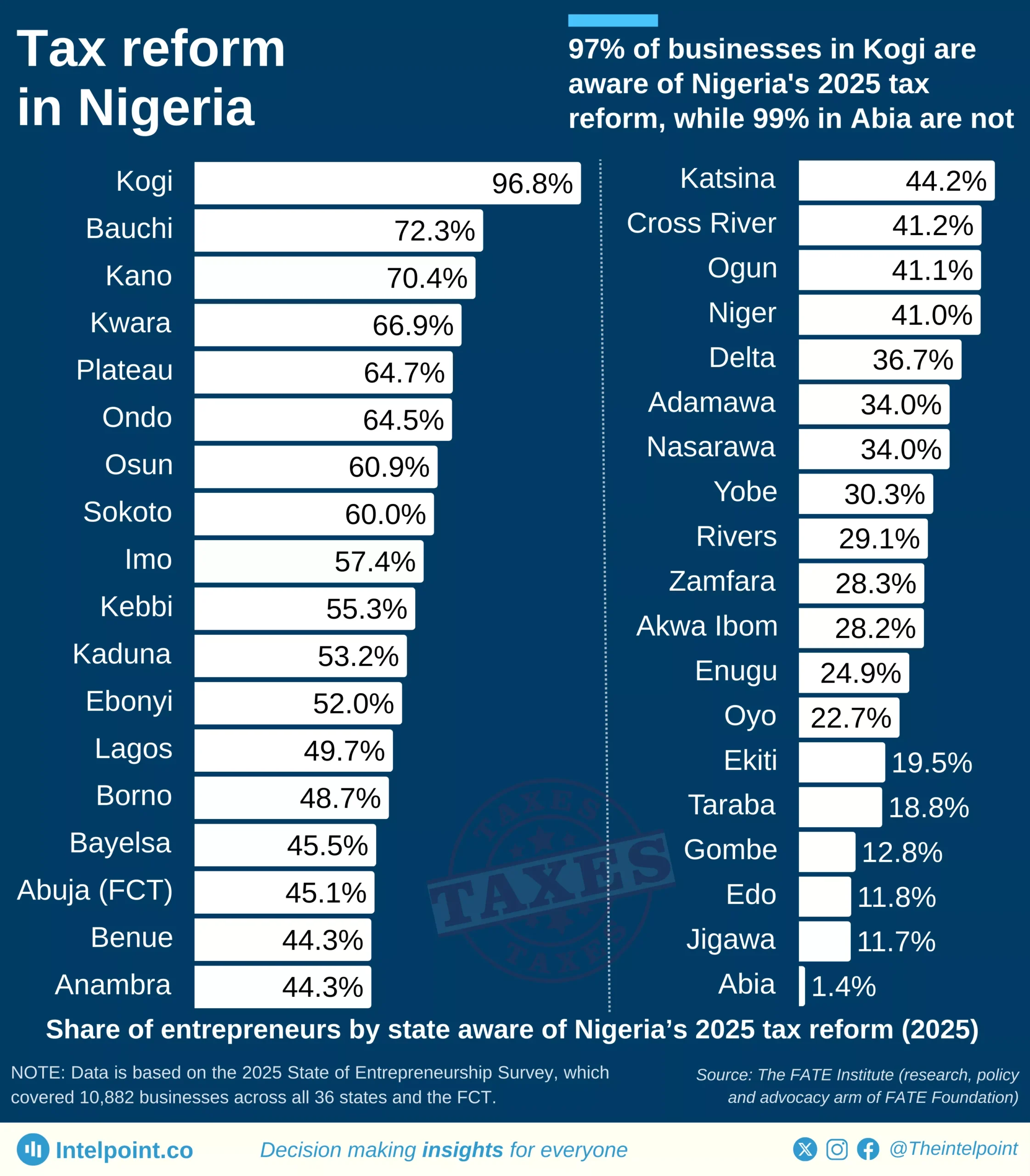
From 2013 through to 2024, Ghana’s economic structure has shown a remarkably consistent pattern in which the Services sector has been the leading contributor to GDP, while agriculture has persistently been the smallest of the three major sectors. Over the years, the decline in agriculture’s share has been gradual but persistent, while services has either held steady or edged up, and industry has been in between.
A large share of Ghana’s population (especially in rural areas) depends on farming for income. If agriculture contributes the least to GDP, it often means incomes in rural communities grow more slowly than in urban, service-driven areas. A relatively weak agricultural sector can make Ghana more dependent on food imports, which raises risks during global price shocks. While services can dominate GDP, they cannot absorb all labour. Agriculture’s stagnation reduces its role as a labour buffer, leading to higher disguised unemployment.