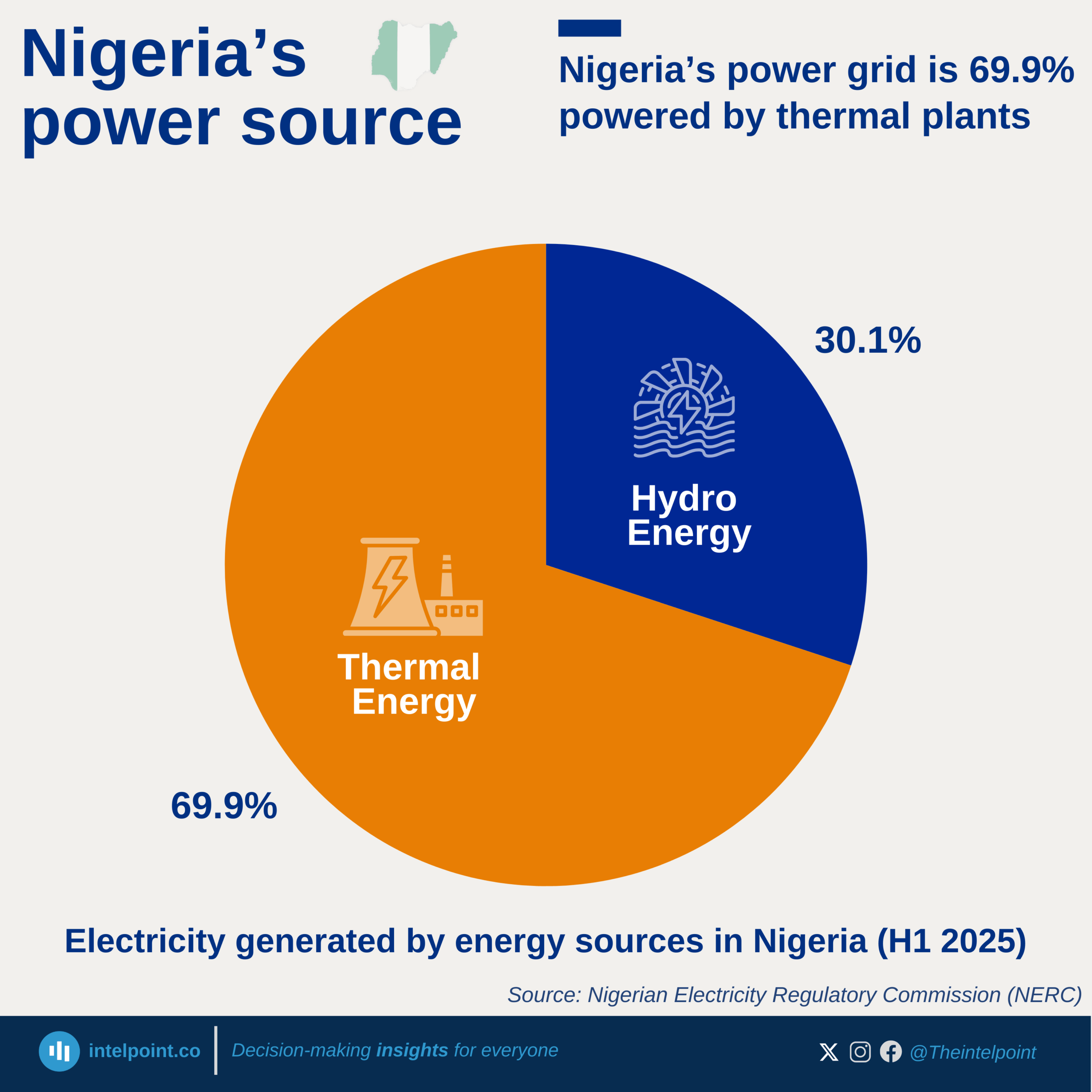
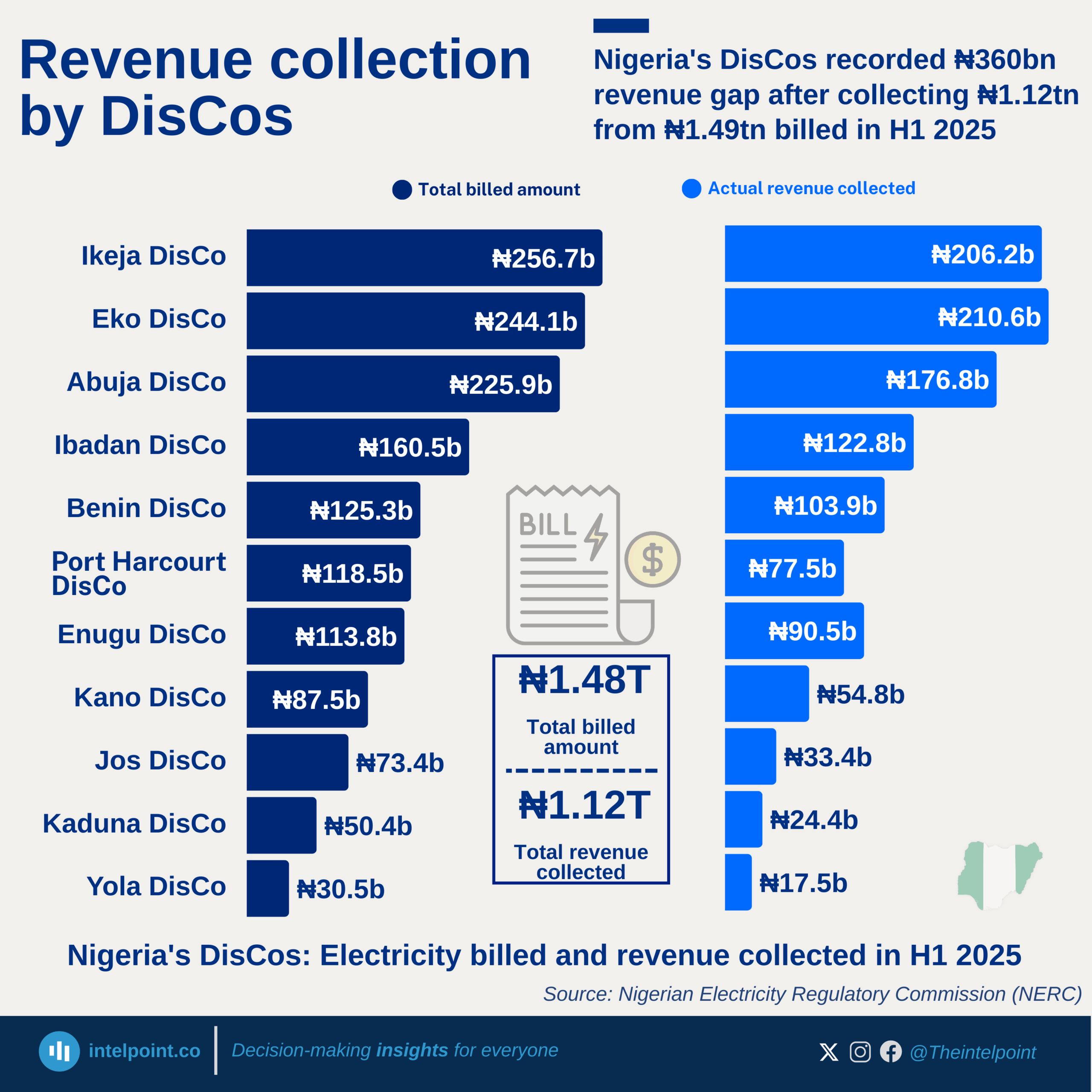
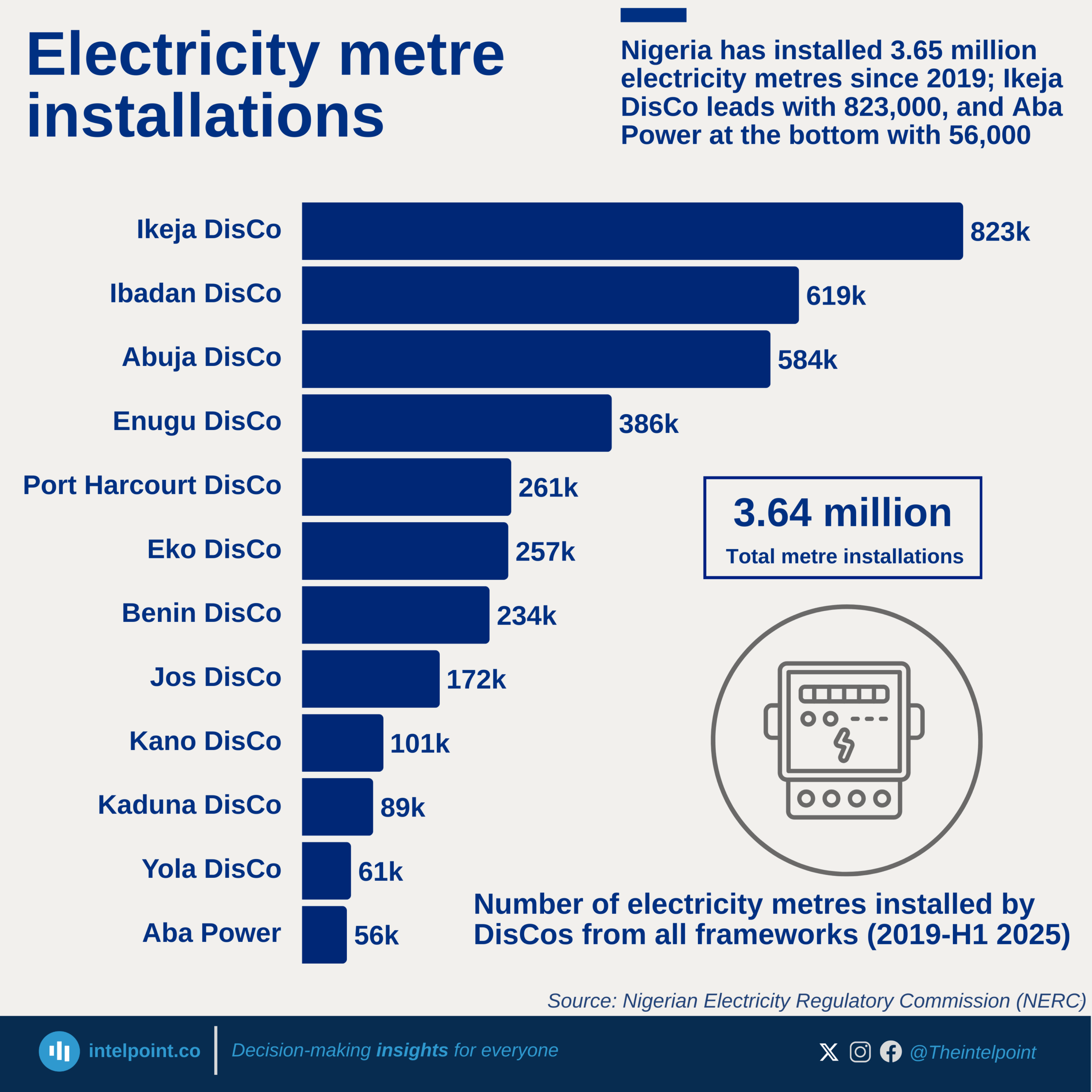
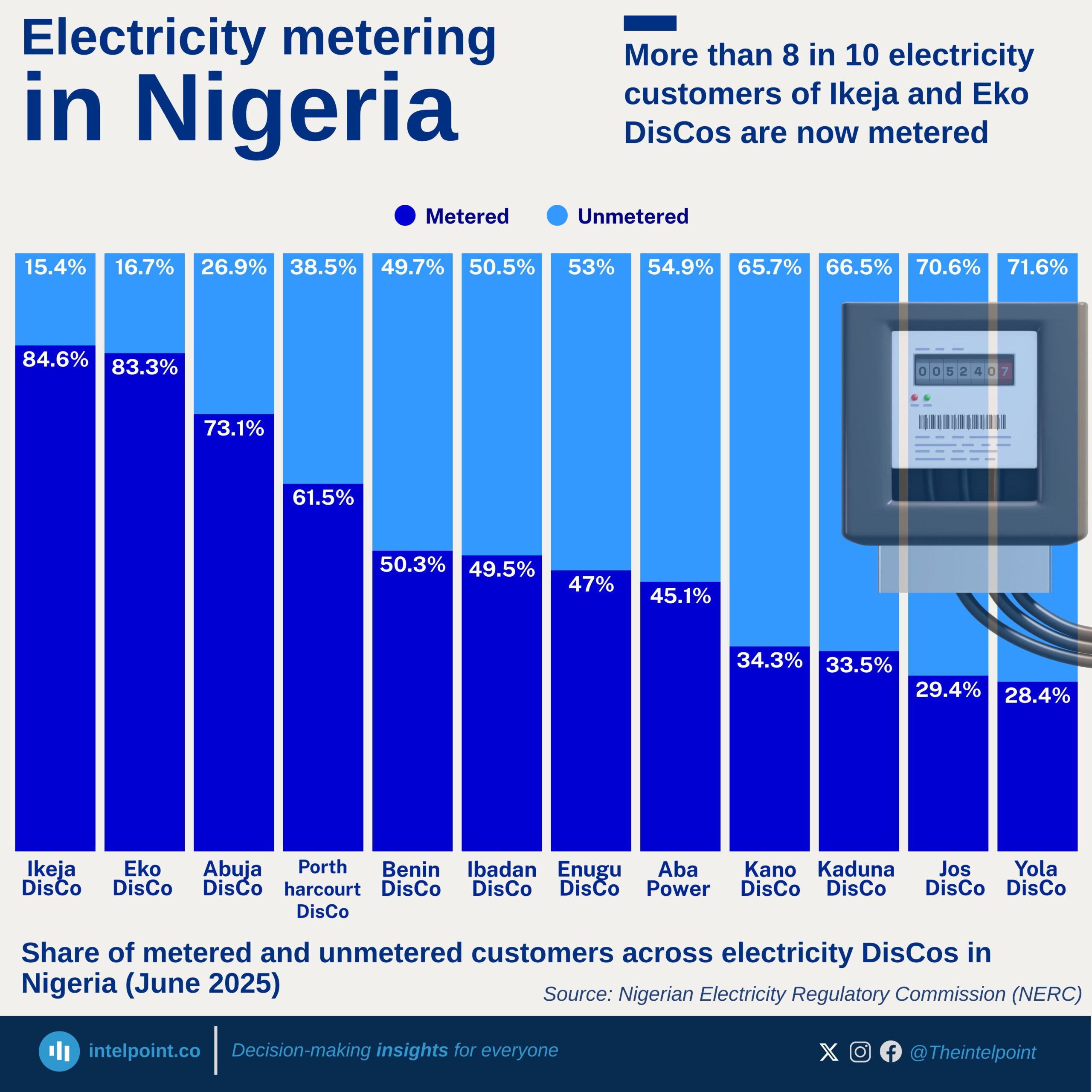
In 2025, Nigeria’s financial landscape sees a broadly positive shift in public trust, with nearly all adults expected to show either high or moderate confidence in financial institutions. Transparency emerges as the strongest foundation for building trust, as almost half of Nigerians highlight clear policies and fair fees as the most important factor. At the same time, security is becoming a central concern, with nearly a third pointing to stronger safeguards as essential in a digital-first financial environment.
Customer service continues to carry weight, with one in six Nigerians underscoring the need for more responsive and reliable support. Meanwhile, only a small share emphasise stronger regulation, suggesting that Nigerians place more value on day-to-day clarity, fairness, and safety rather than oversight alone. This indicates that for banks and financial service providers in Nigeria, building lasting trust will require more than compliance. It will also demand transparency, robust security, and customer-centric service delivery as the true cornerstones of loyalty and confidence.