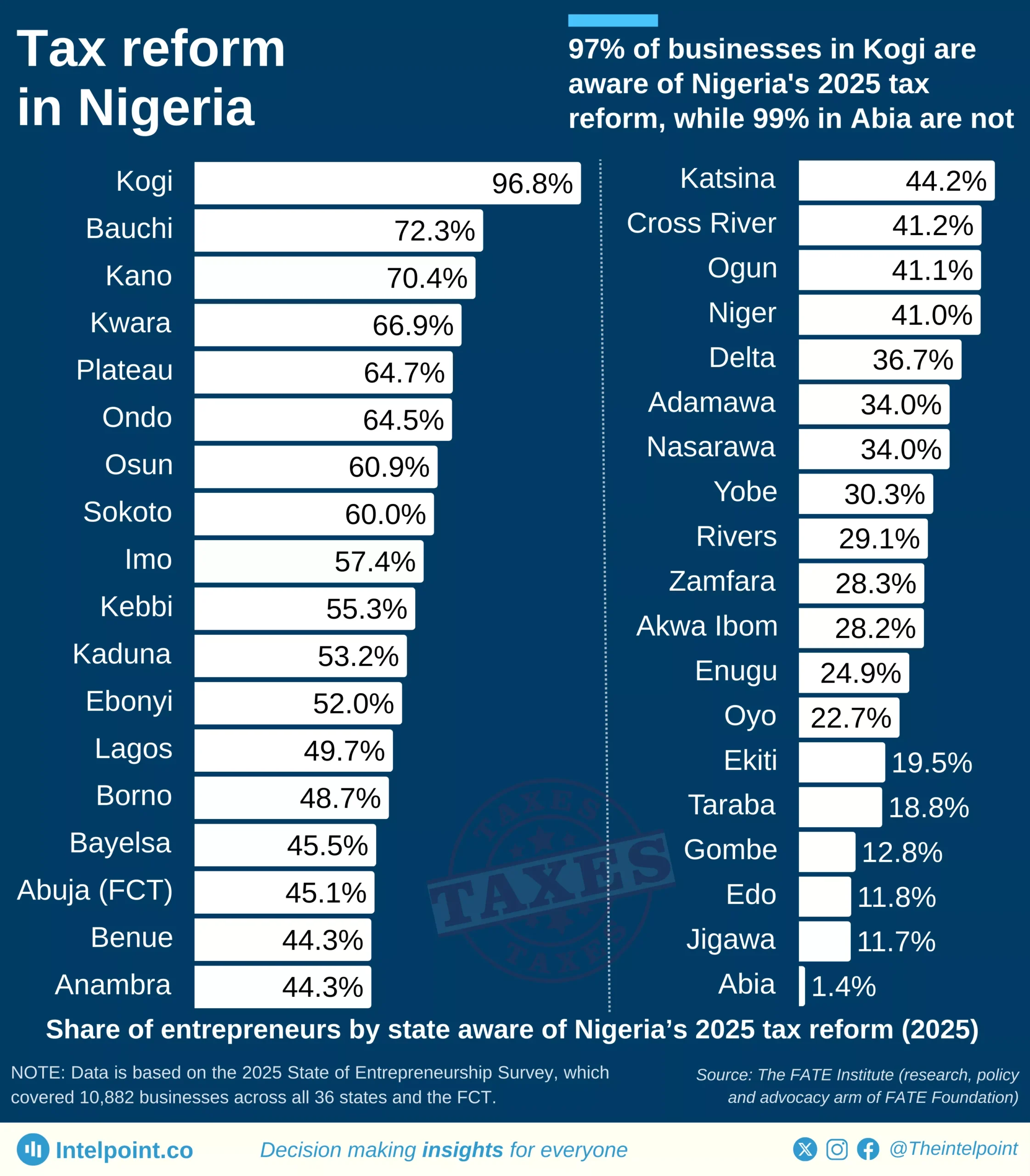
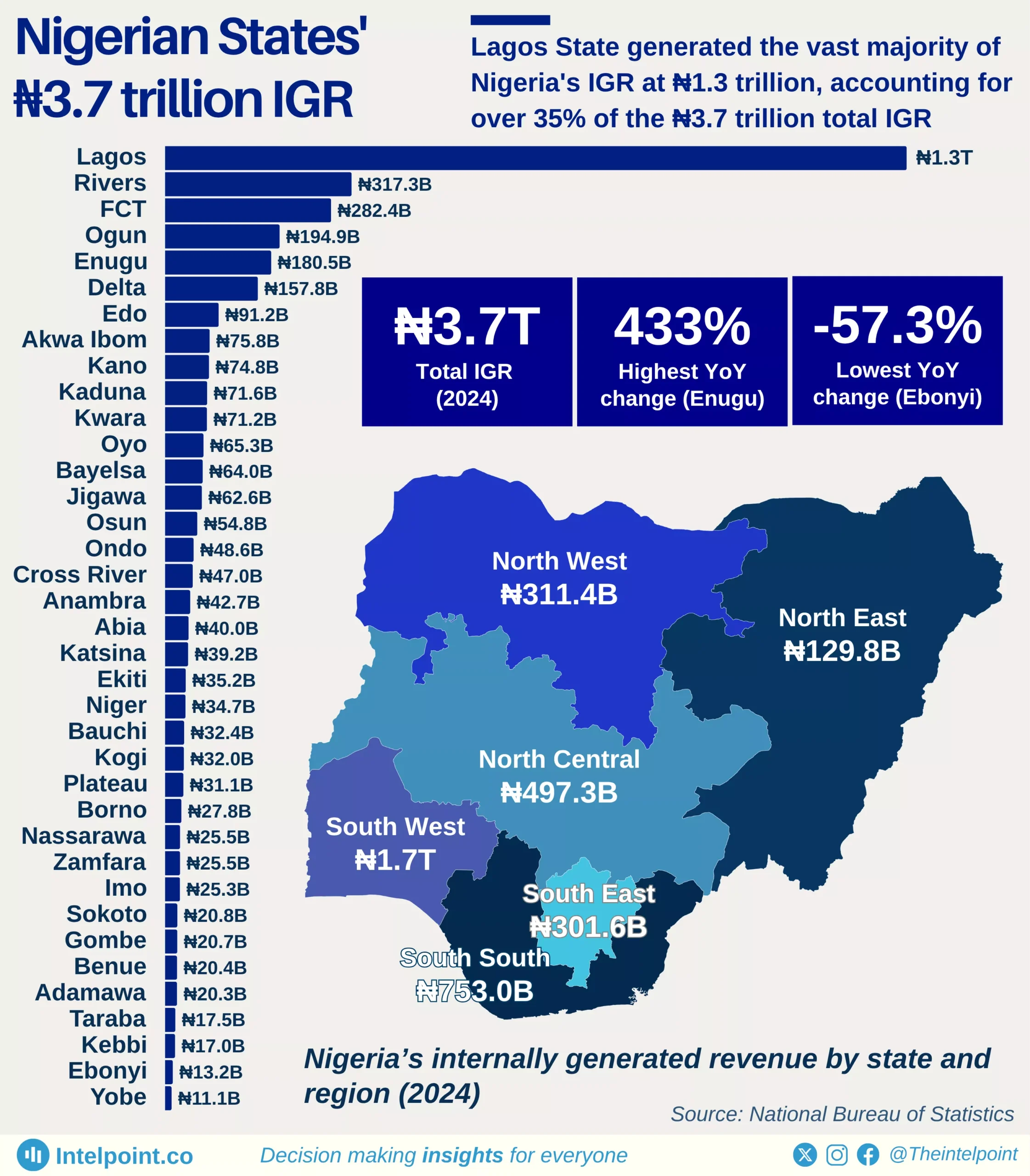
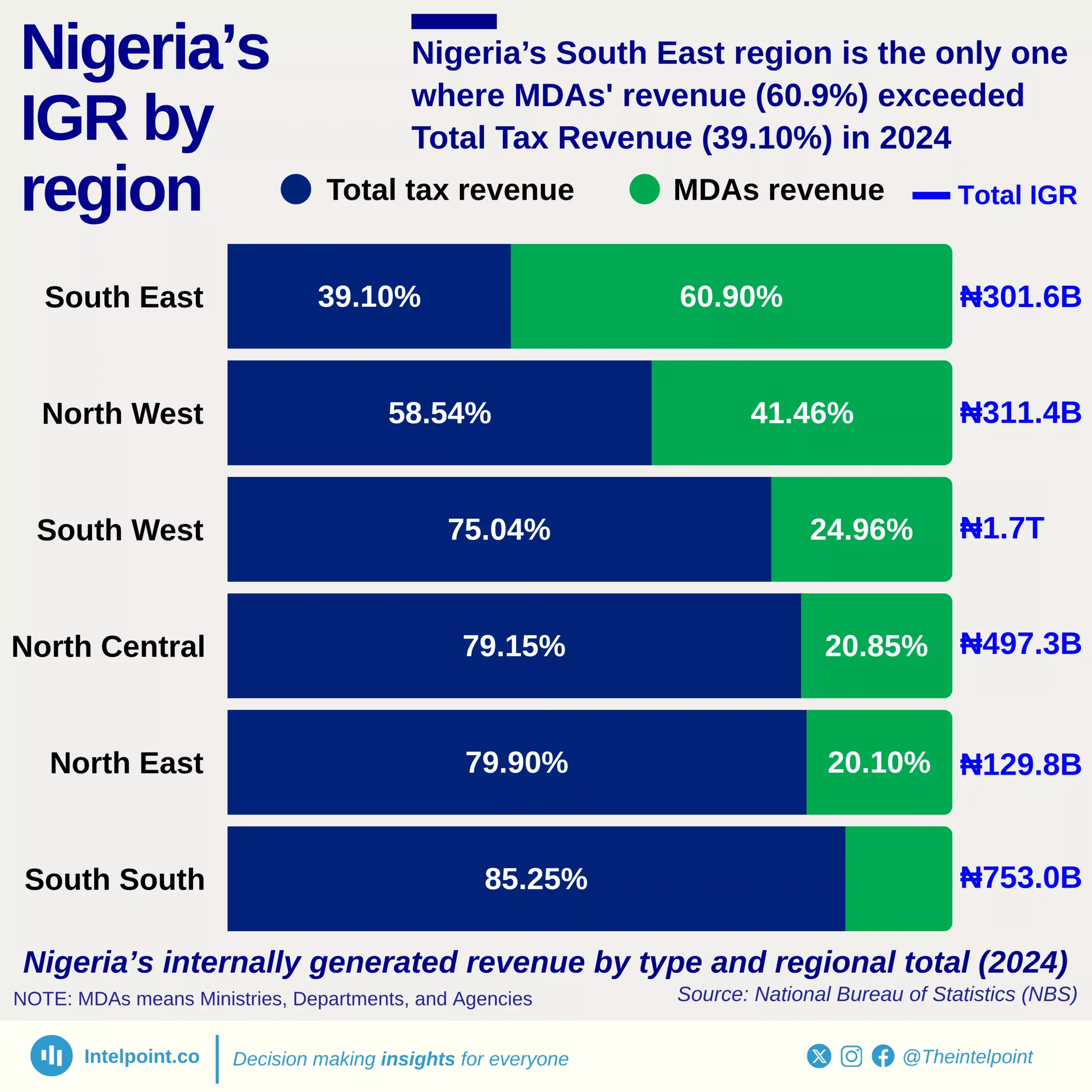
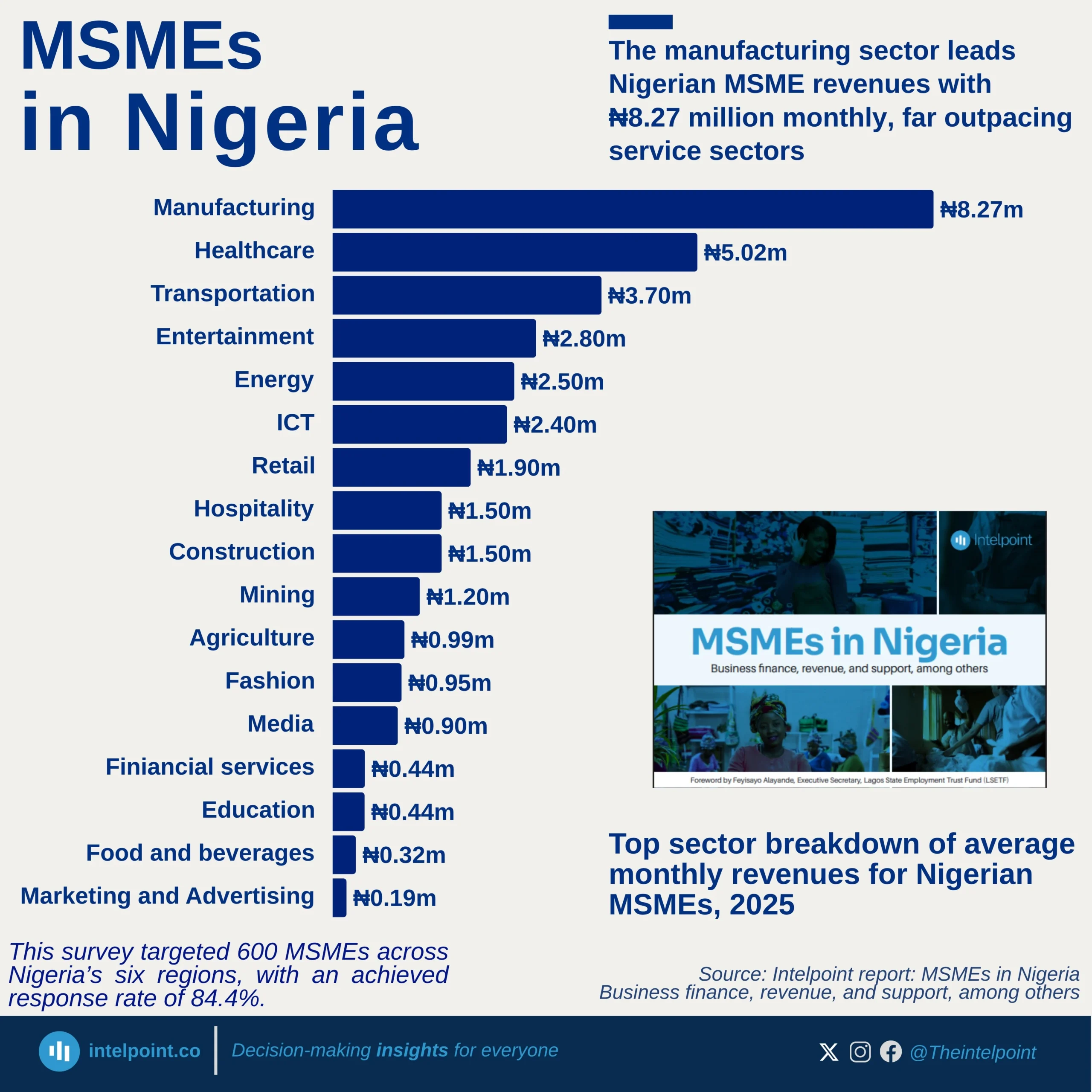
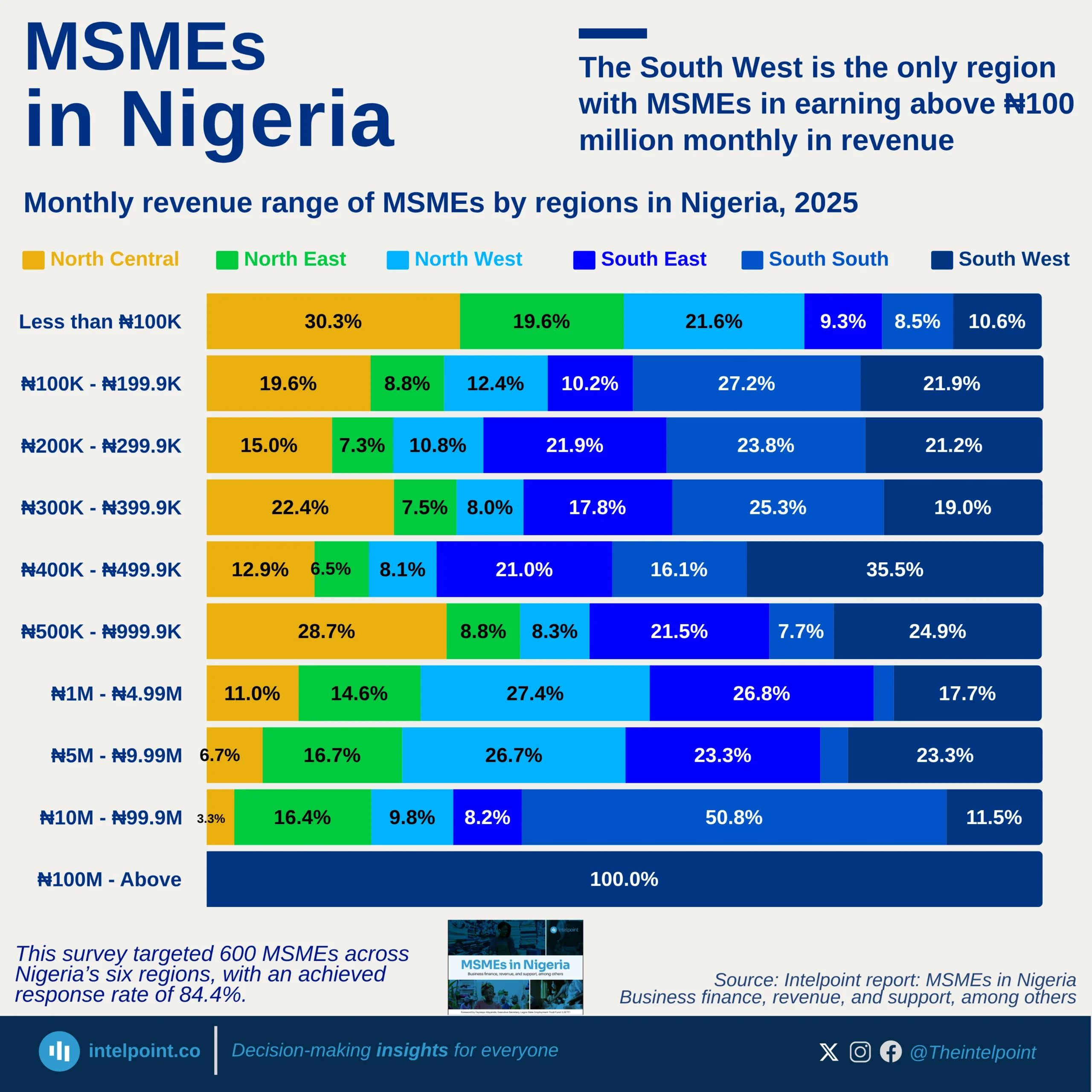
The Federal Inland Revenue Service (FIRS) recorded a landmark achievement in 2024 by collecting a total of ₦21.7 trillion, surpassing its government-set target of ₦19.4 trillion. This impressive performance marked the highest revenue ever recorded by FIRS since 2012. In fact, the 2024 tax revenue exceeded the amount collected in 2023 by a remarkable 75.6%, reflecting strong improvements in tax administration and compliance. When comparing the revenue figures from 2021, 2022, 2023, and 2024, a clear upward trajectory becomes evident. There was a significant shift in the values year-on-year from 2021, highlighting growth and efficiency in the system. This trend also signals increasing confidence in the nation's revenue generation framework.
The leap from previous years to 2024 is particularly notable given economic challenges faced globally. Enhanced digital systems and better enforcement strategies may have contributed to this growth. Onward, this development could shape future revenue policies and projections in Nigeria.