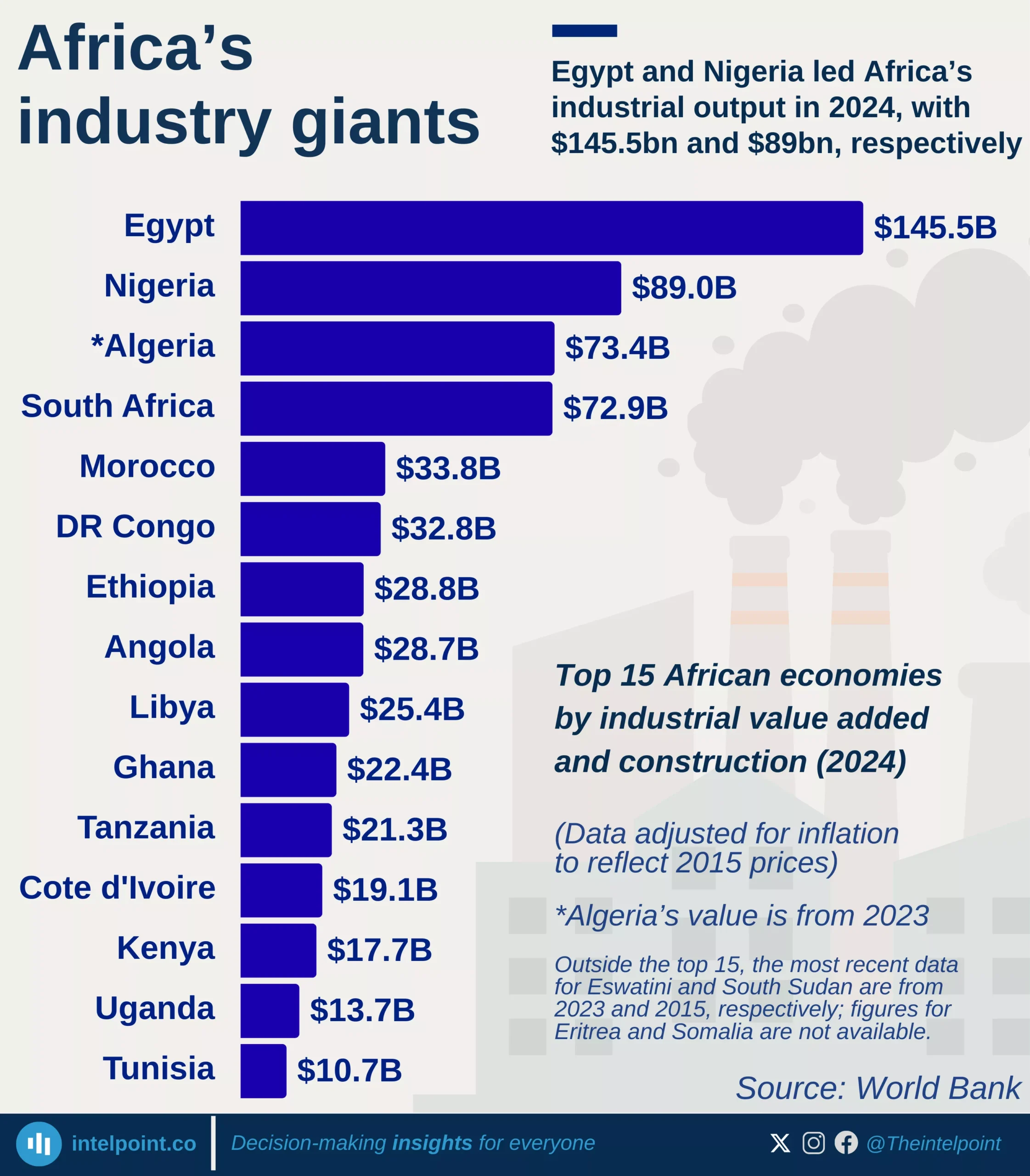
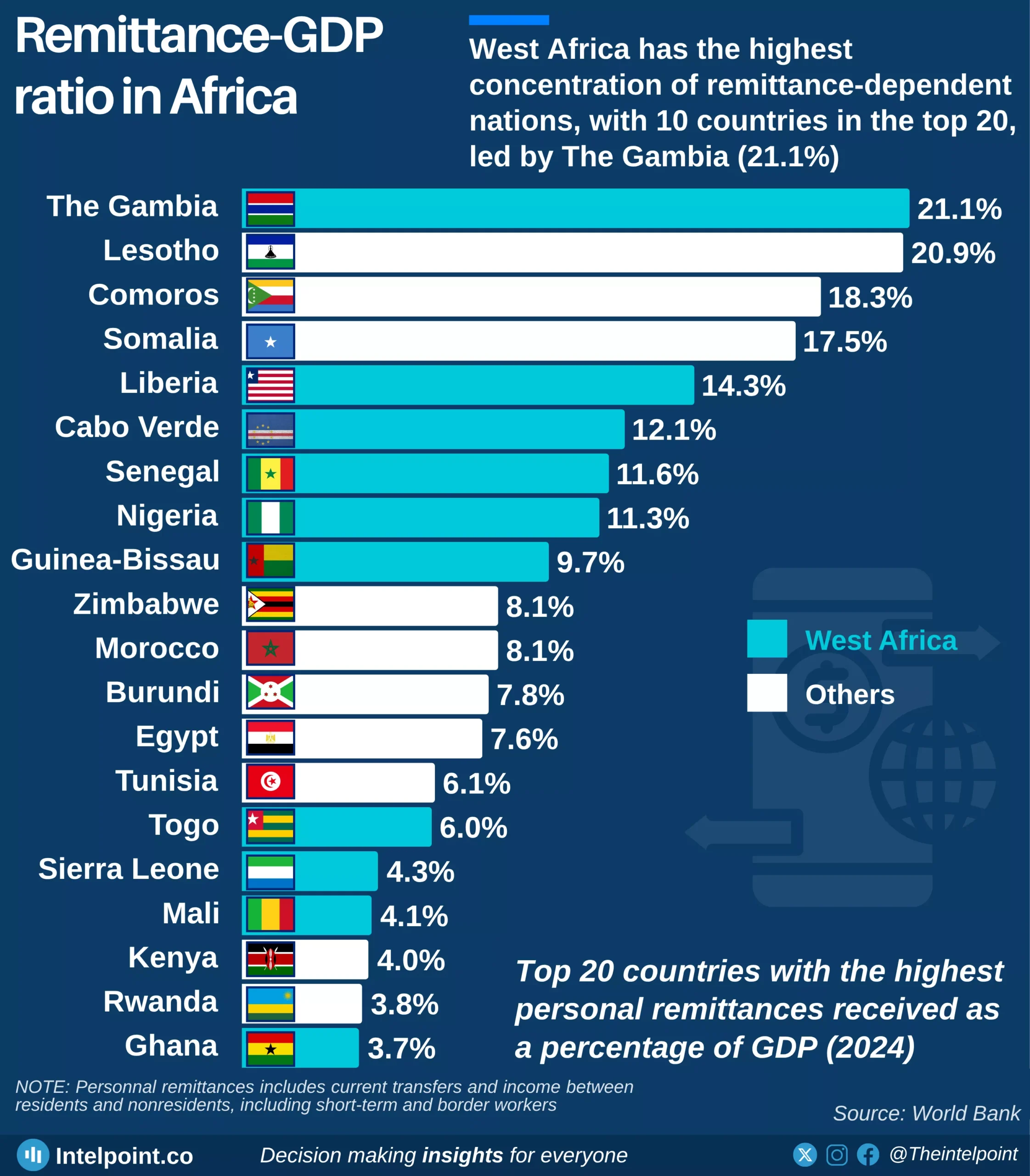
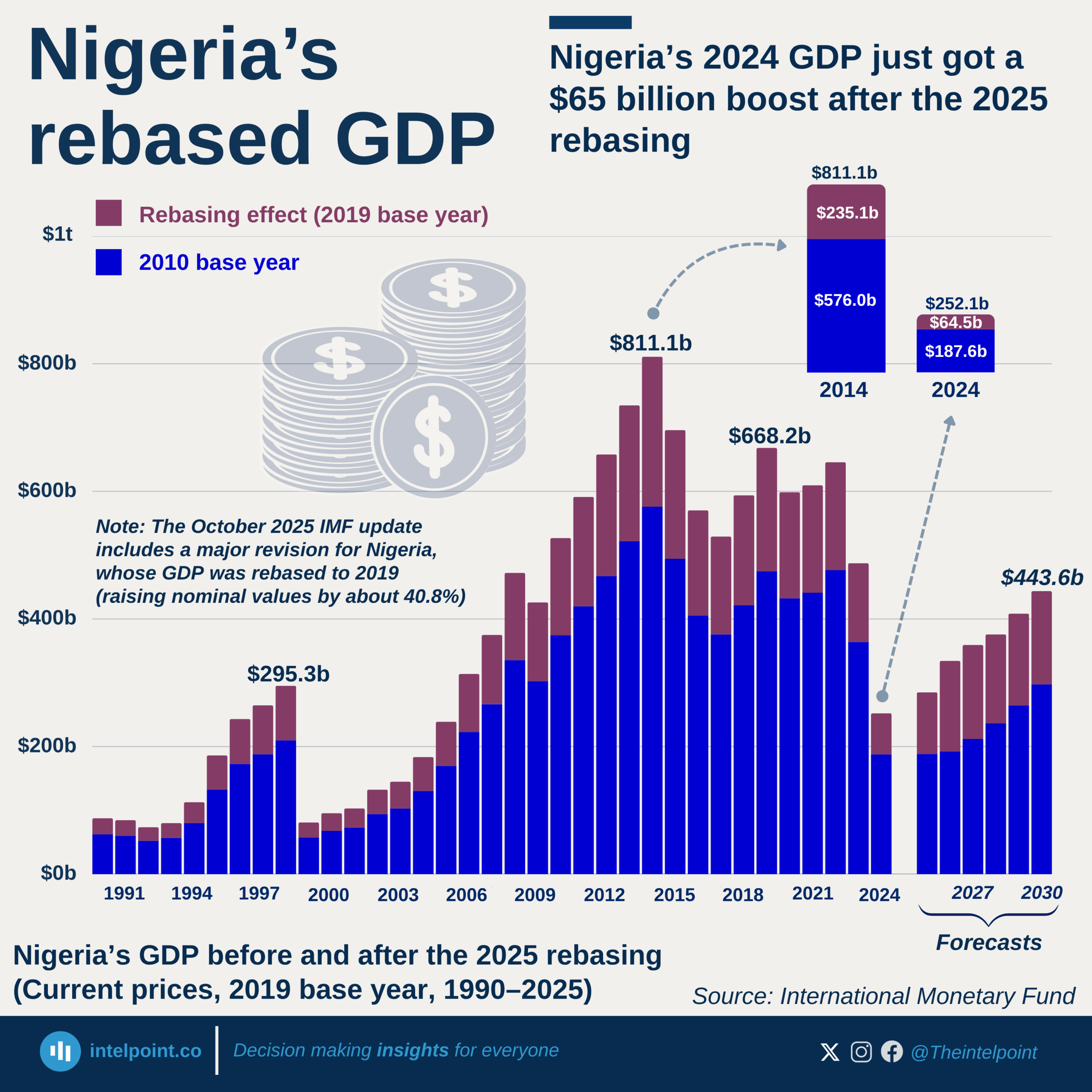
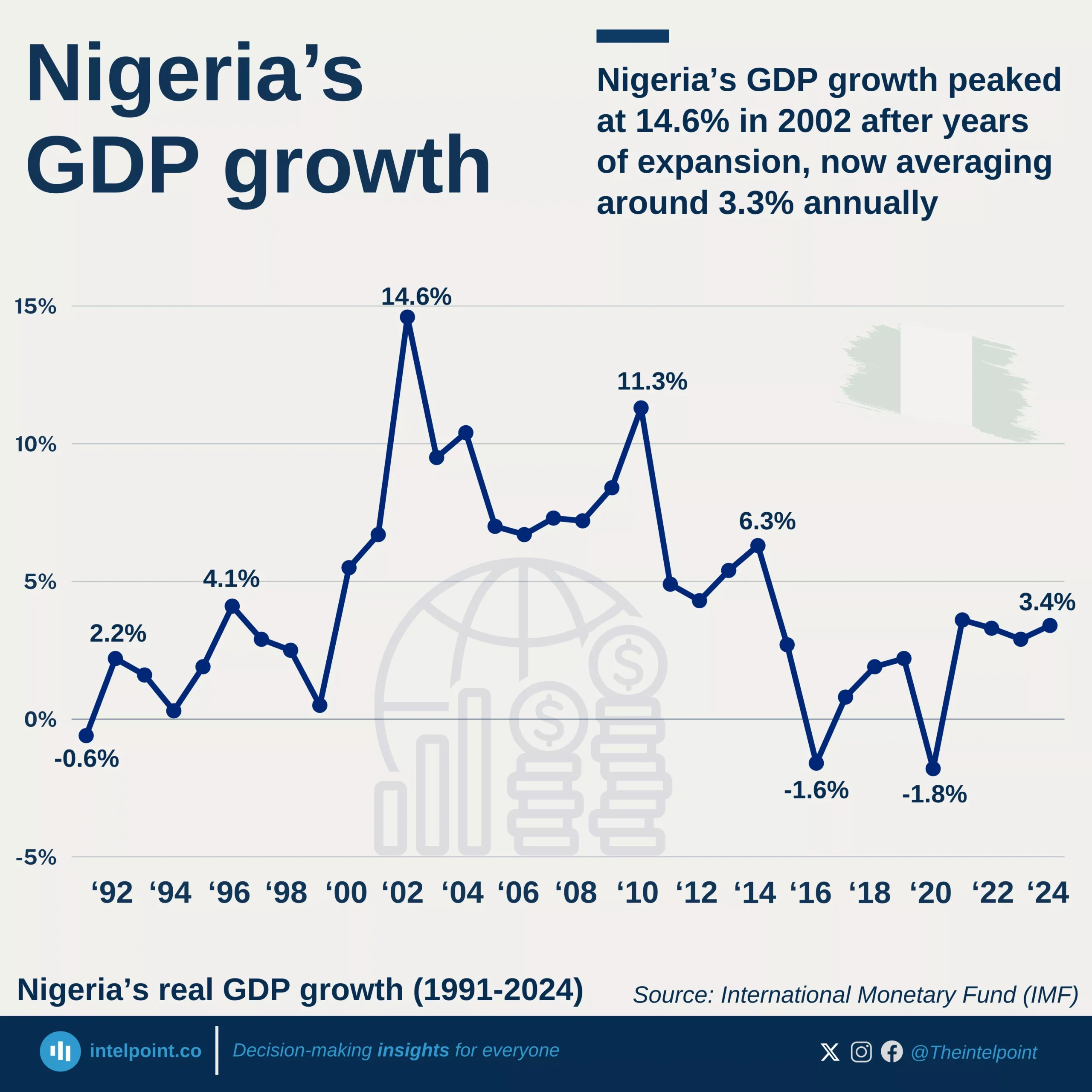
Following Nigeria’s 2025 GDP rebasing, where it adopted 2019 as the new base year, nominal GDP has climbed by more than 80%, rising from ₦205.1 trillion in 2019 to ₦372.8 trillion in 2024. In contrast, real GDP has barely shifted, inching up by just 6% over the same period. The divergence has grown particularly stark in recent years, with nominal gains accelerating while real output remains largely stagnant. The data underscores how much of Nigeria’s economic growth has been driven by price inflation rather than expanded production, leaving real economic progress subdued despite headline increases.