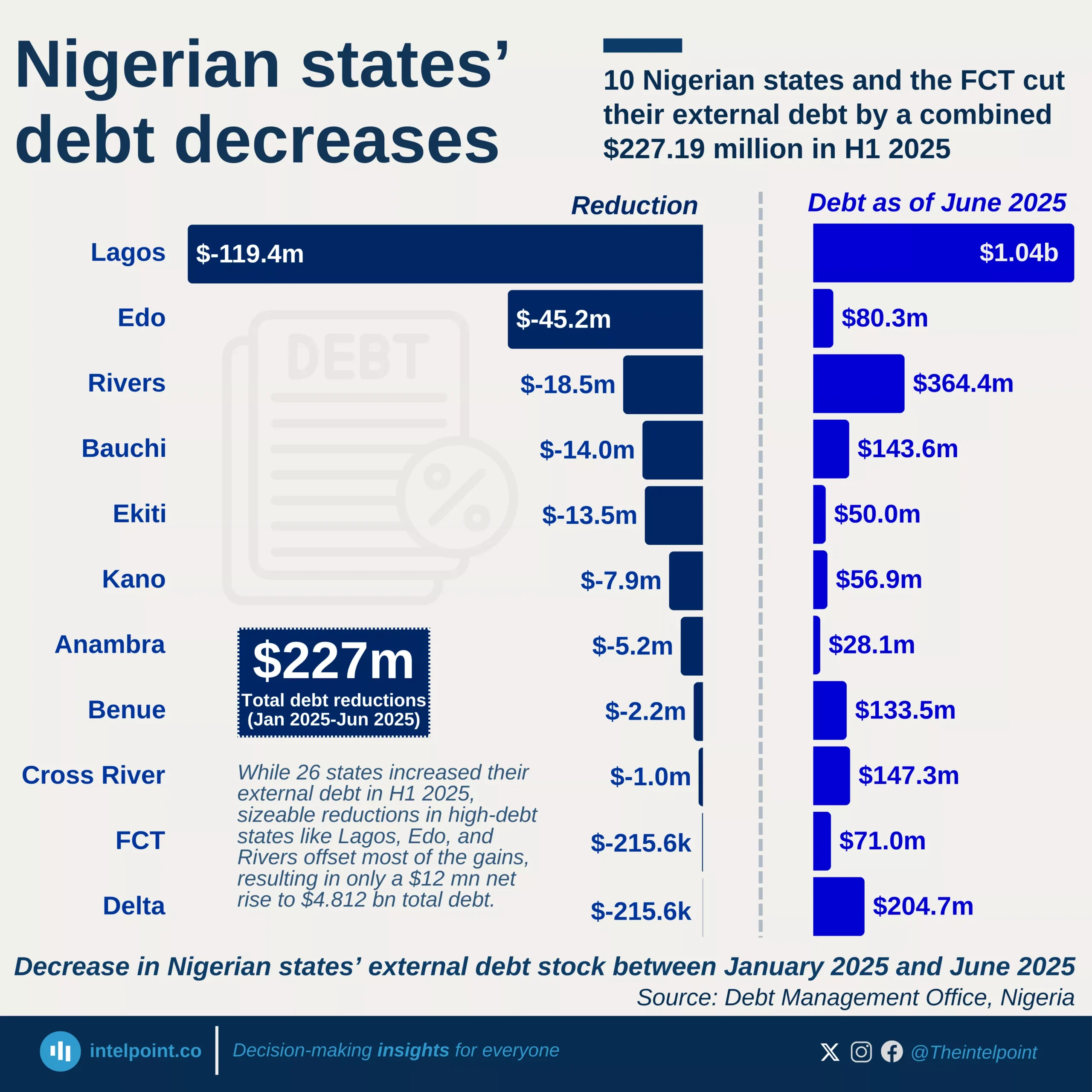
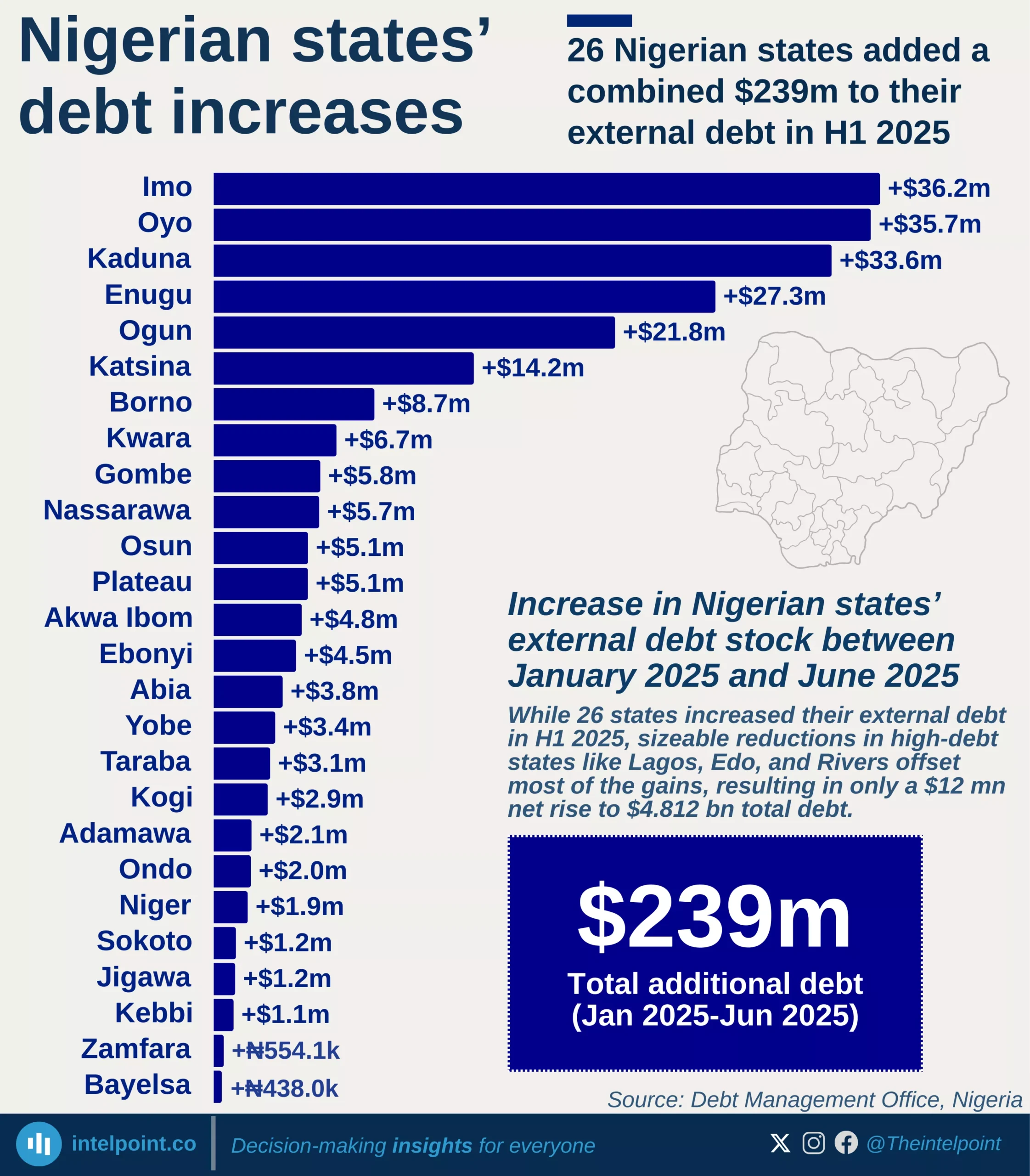
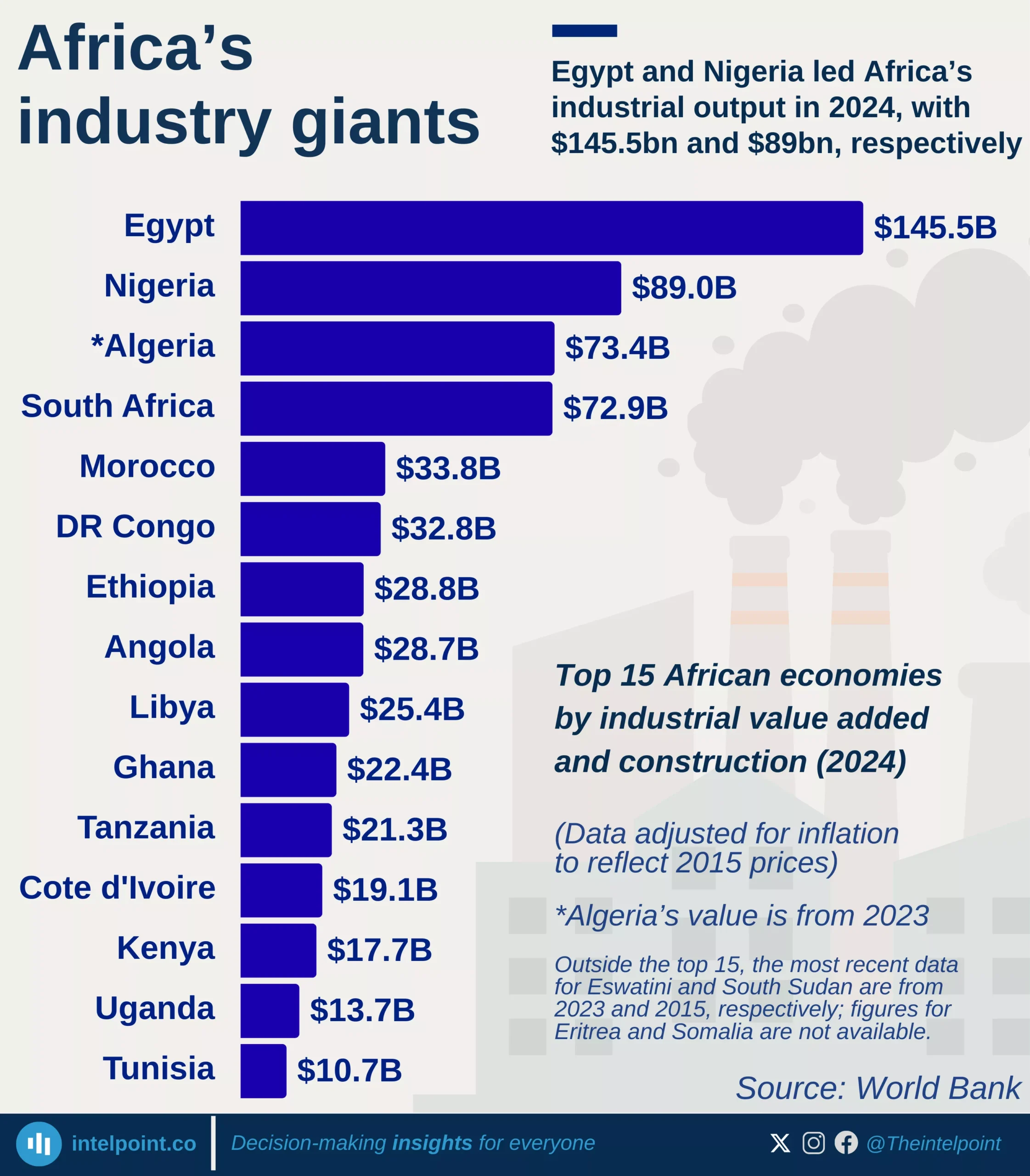
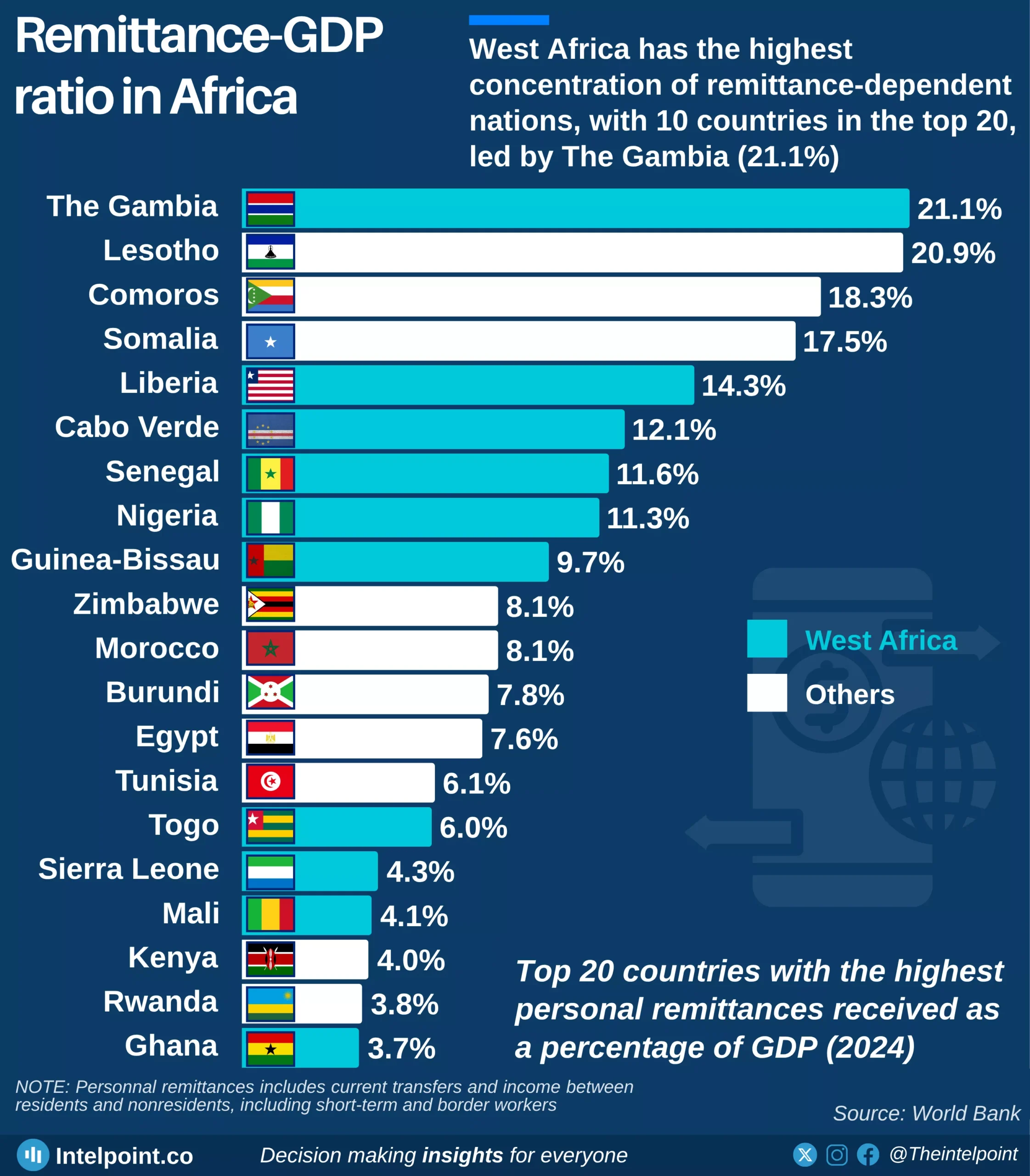
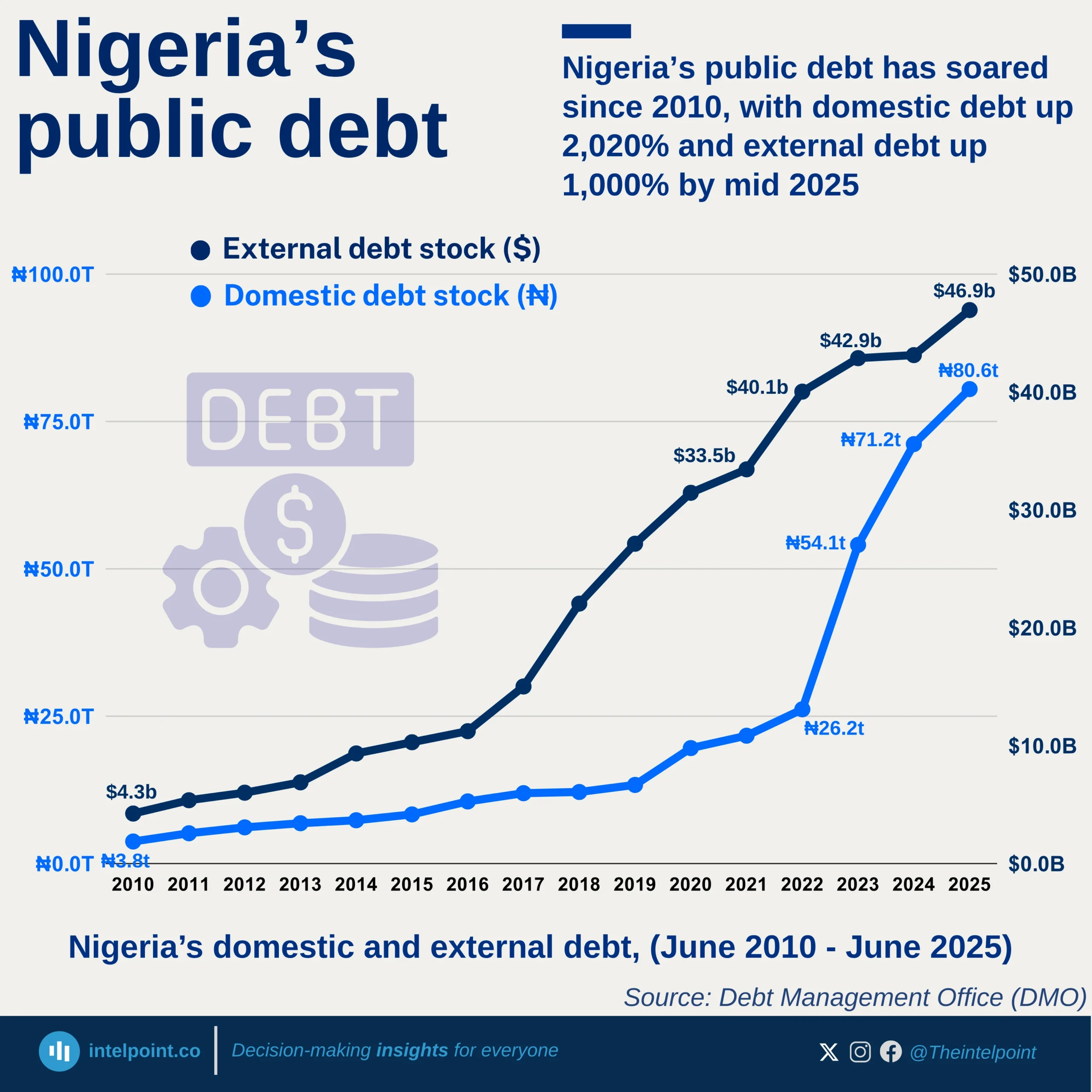
Debt service obligations across African countries in 2024 reveal sharp contrasts in how different economies are managing the burden of repaying their public debt. Angola leads the continent with the highest debt service-to-GDP ratio at 68.25%, followed closely by Ethiopia at 67.01%, underscoring the strain that debt repayments place on their economies. Remarkably, five of the top ten countries with the highest ratios are in East Africa, signalling a regional concentration of debt pressure that could affect fiscal space for development spending.
This trend is especially worrying considering the fiscal limitations many African countries face. For example, in economies like Ethiopia, high debt servicing eats into budgets that could otherwise be allocated to infrastructure, education, or healthcare. In day-to-day terms, it’s like a household spending most of its income on loan repayments with little left for essentials.
On the flip side, countries like Algeria, Zimbabwe, and Botswana sit at the bottom of the debt service-to-GDP chart, with Algeria at a strikingly low 0.10%. While low debt servicing may suggest better fiscal balance, it’s important to note that it doesn’t necessarily equate to stronger economies; it could also reflect limited borrowing or deferred obligations. Nonetheless, the range between Angola’s 68% and Algeria’s 0.1% reflects a stark divergence in how African countries are managing their debt landscapes.