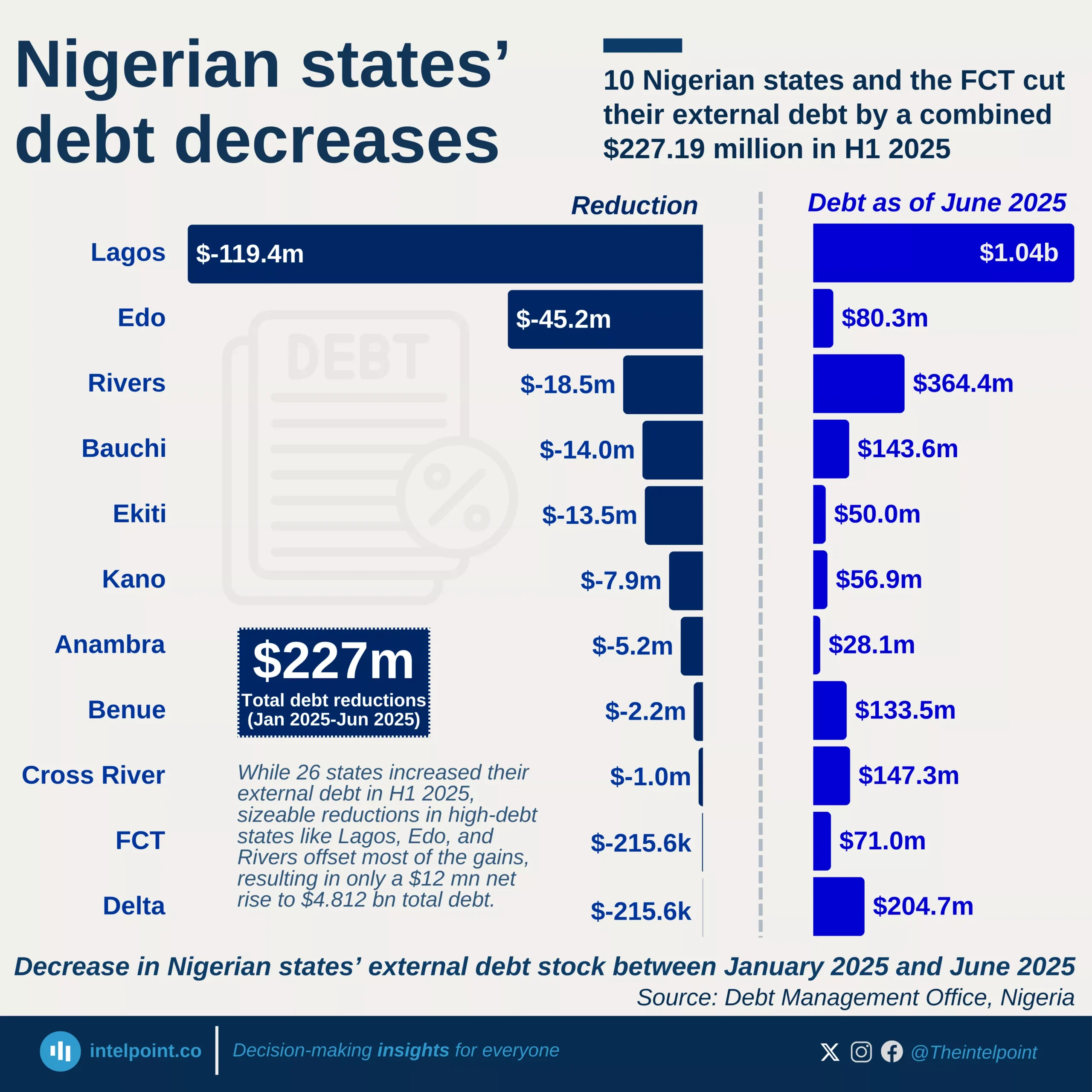
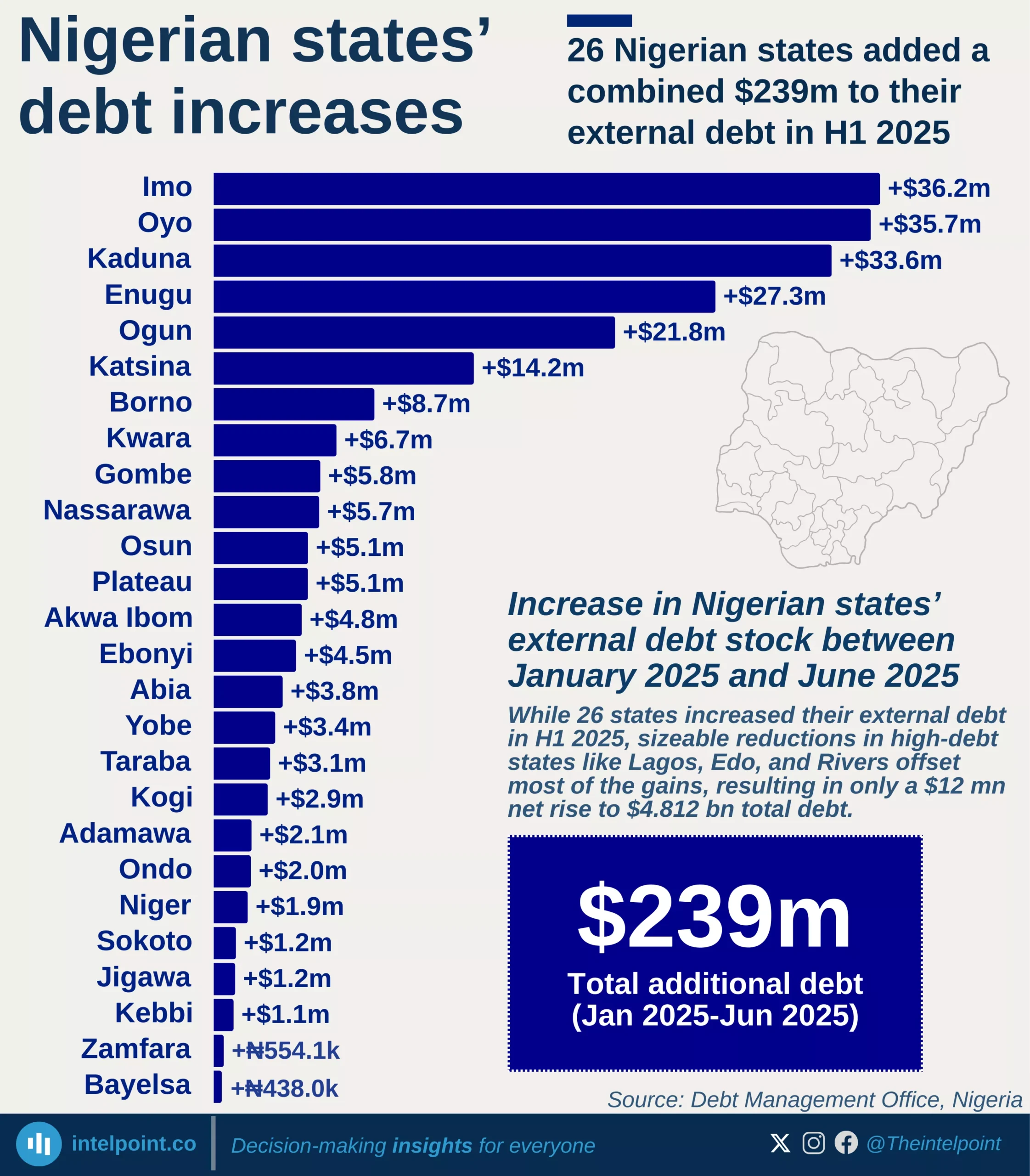
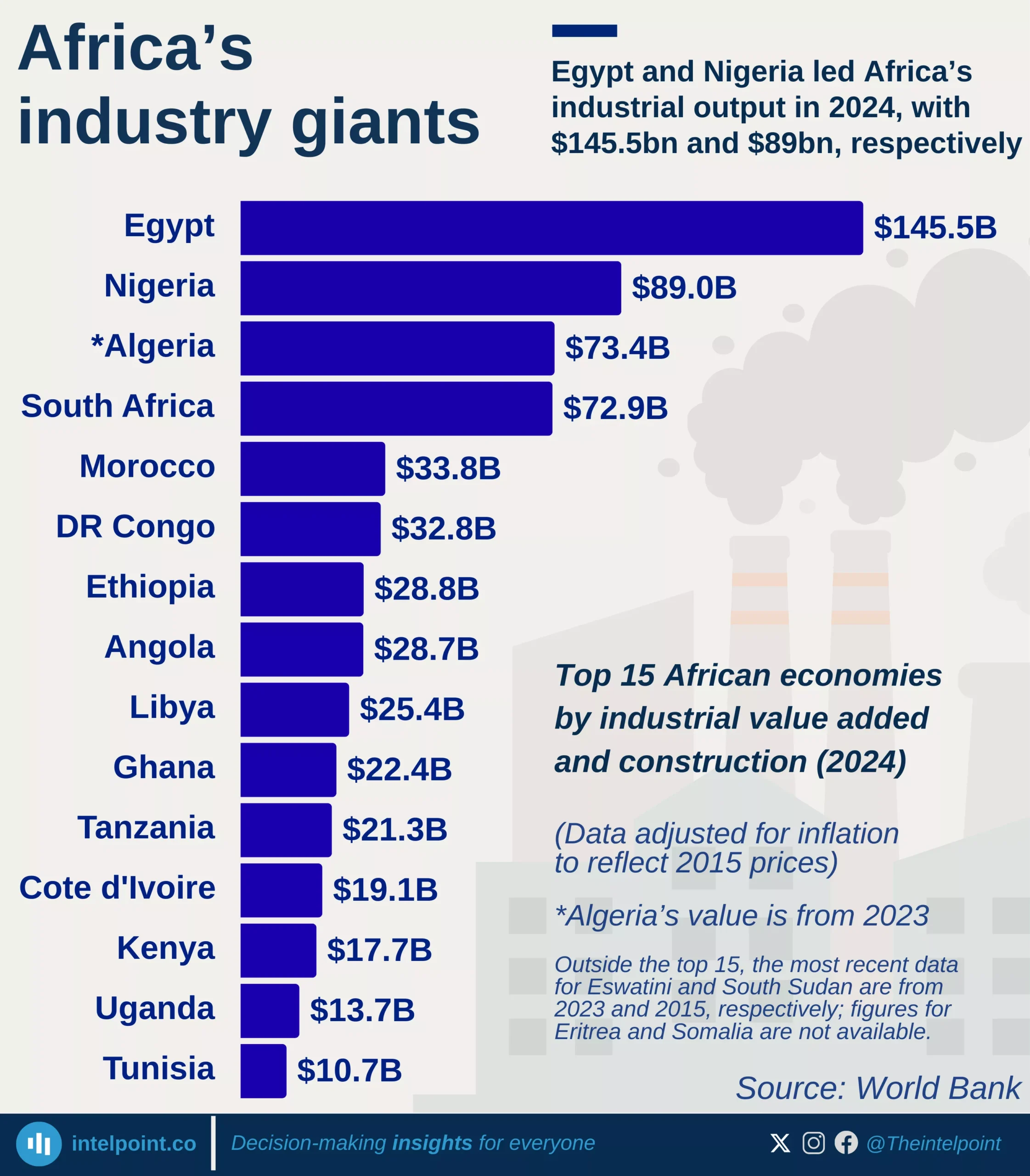
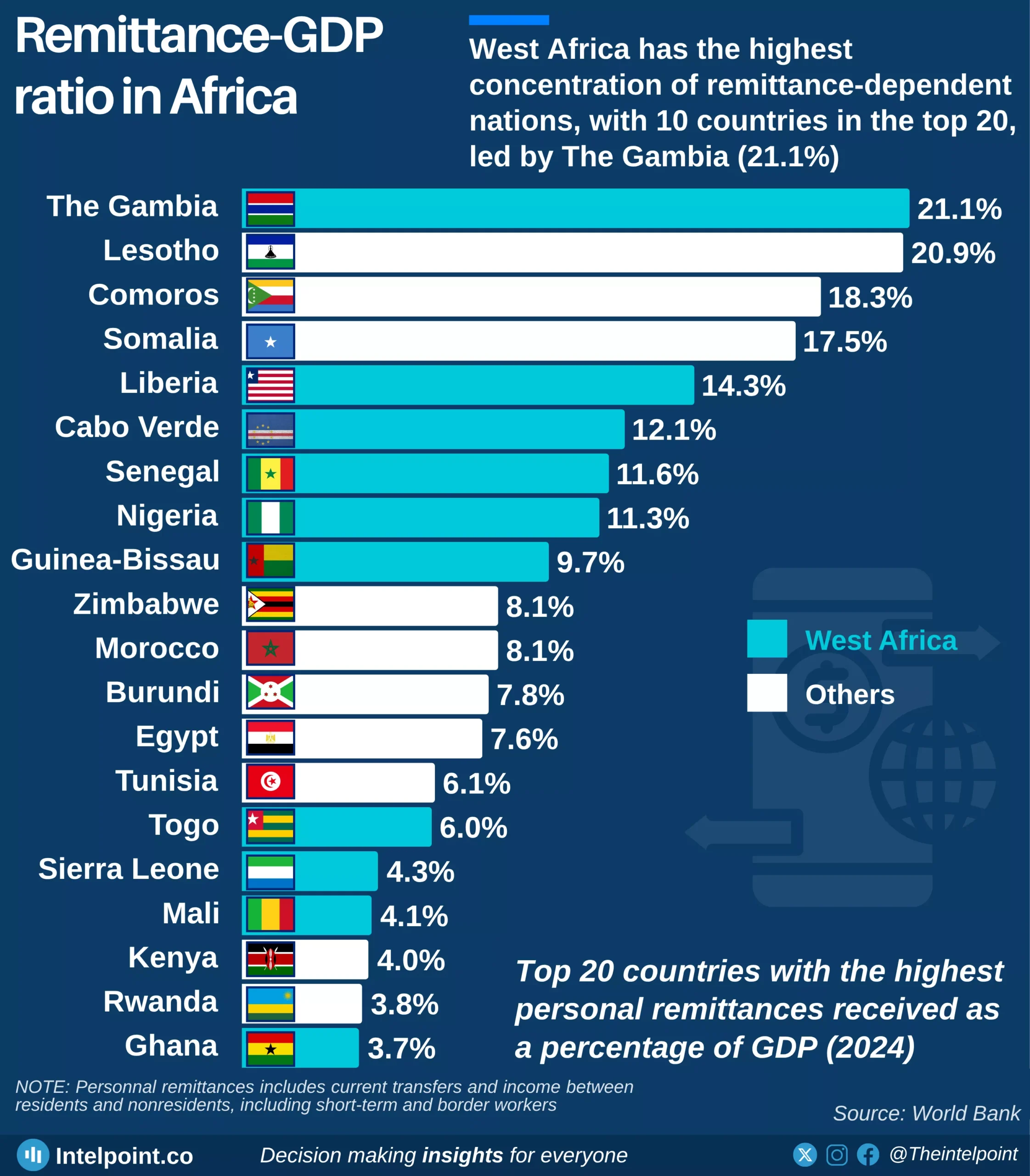
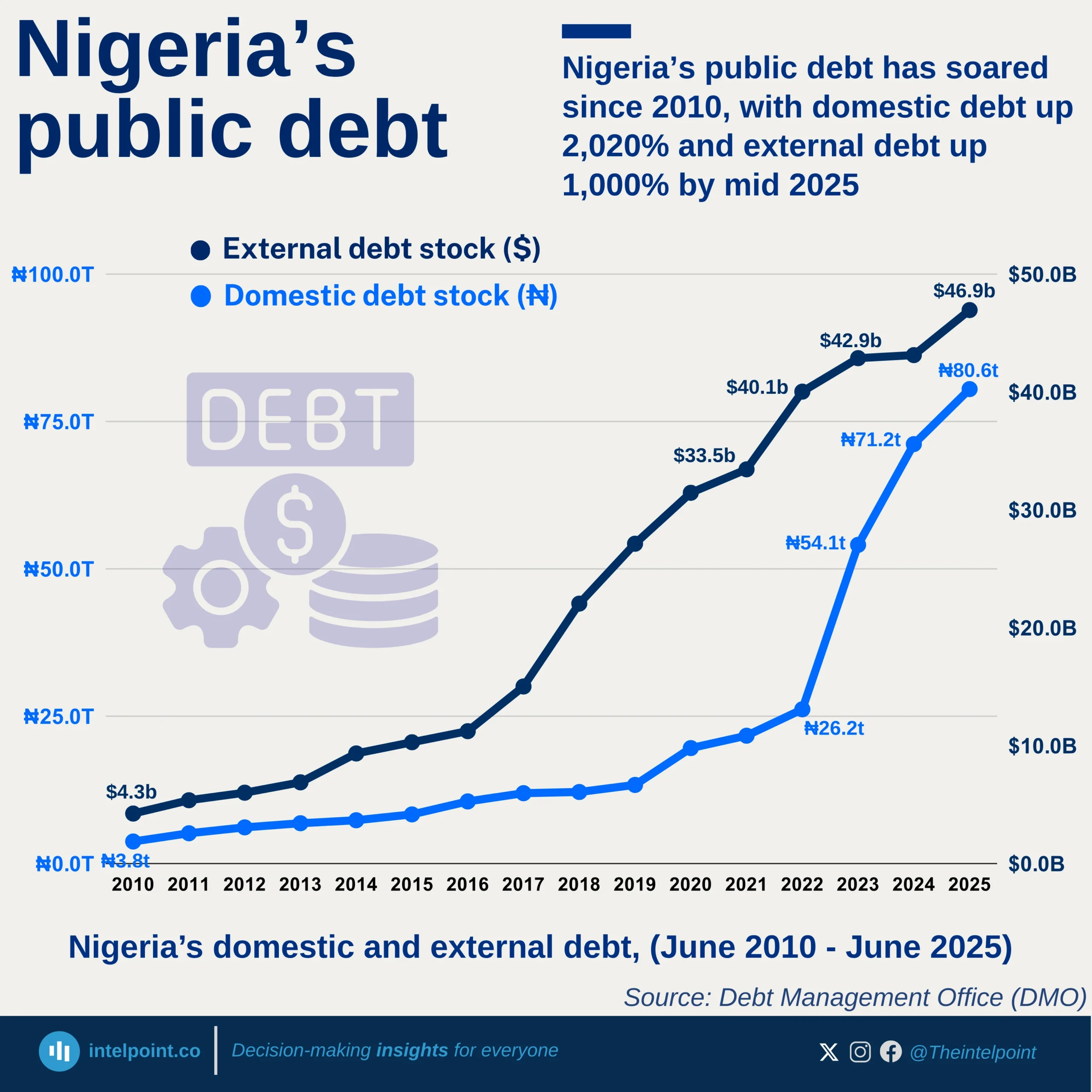
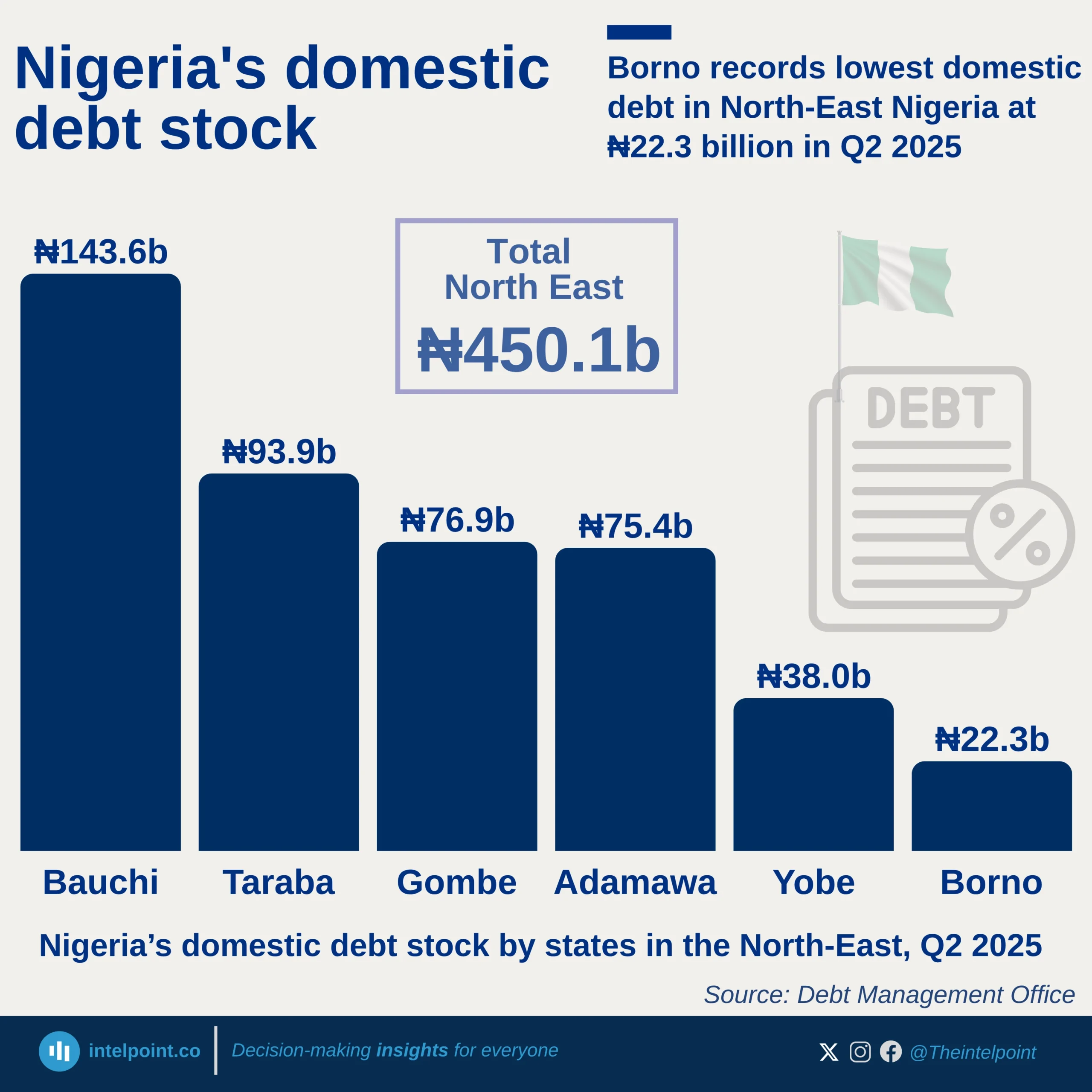
Africa's debt landscape remains a source of concern, with some countries now owing more than their economies produce in a year. As of 2024, Sudan leads the continent with a debt-to-GDP ratio of 238.8%, followed by Cabo Verde at 109.7% and Zambia at 100.8%. These figures suggest that while borrowing can be a tool for development, it can also signal deep fiscal imbalance, especially when not matched with productive investments or economic growth.
A closer look reveals that all of the top 10 most indebted African countries have debt levels exceeding 75% of their GDP. This high debt burden places pressure on public finances, leaving less room for spending on crucial sectors like health, education, and infrastructure. Even countries like Egypt and Mozambique, which have made strides in sectors like tourism and natural resource exports, still find themselves weighed down by heavy debts.
Interestingly, while some economies are struggling under high debt levels, others like Nigeria appear relatively stable in comparison, with a debt-to-GDP ratio of 41.3%. But this doesn’t tell the whole story, as it’s possible to have low debt ratios yet still struggle with revenue generation, debt servicing, or currency instability.