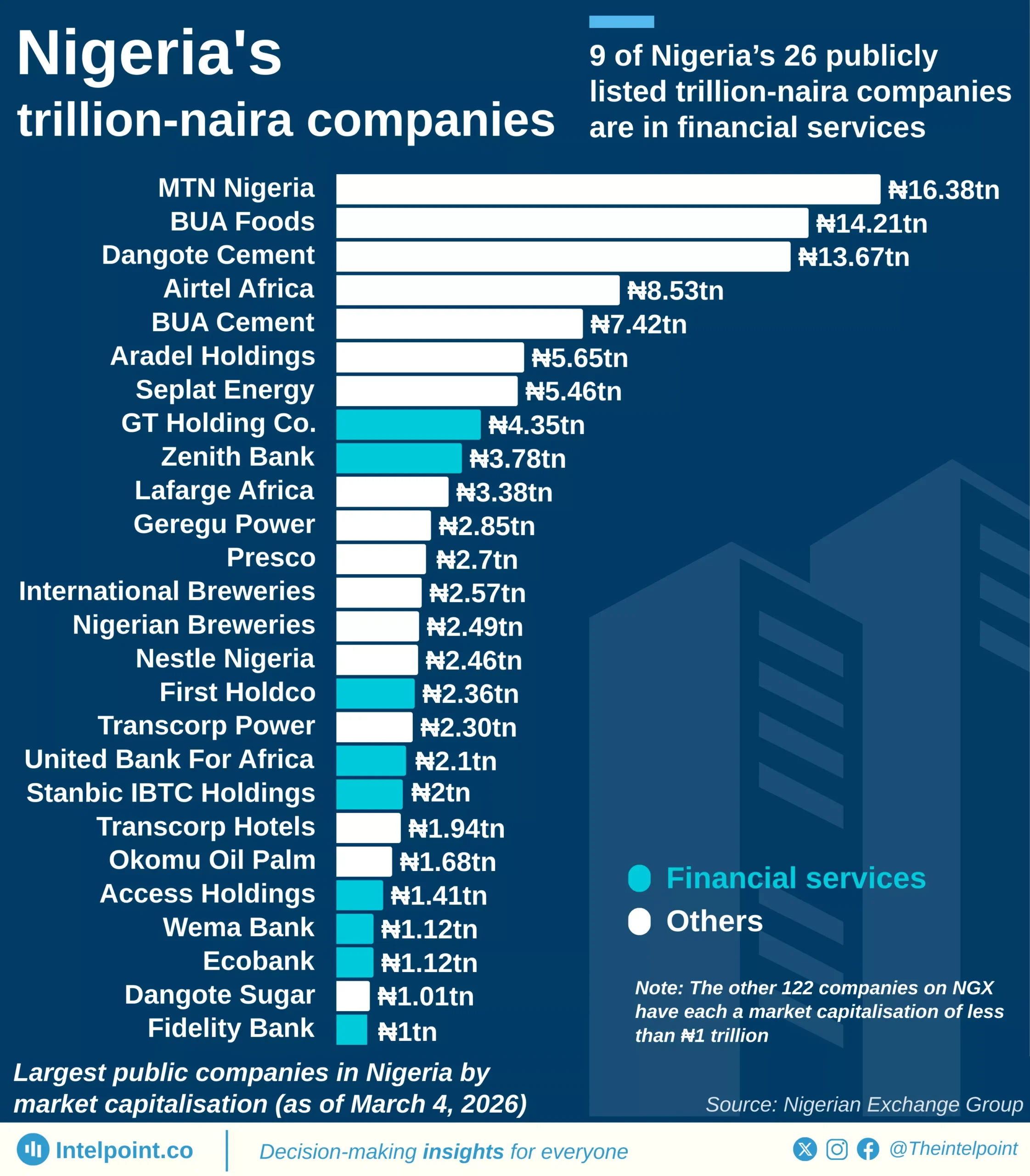
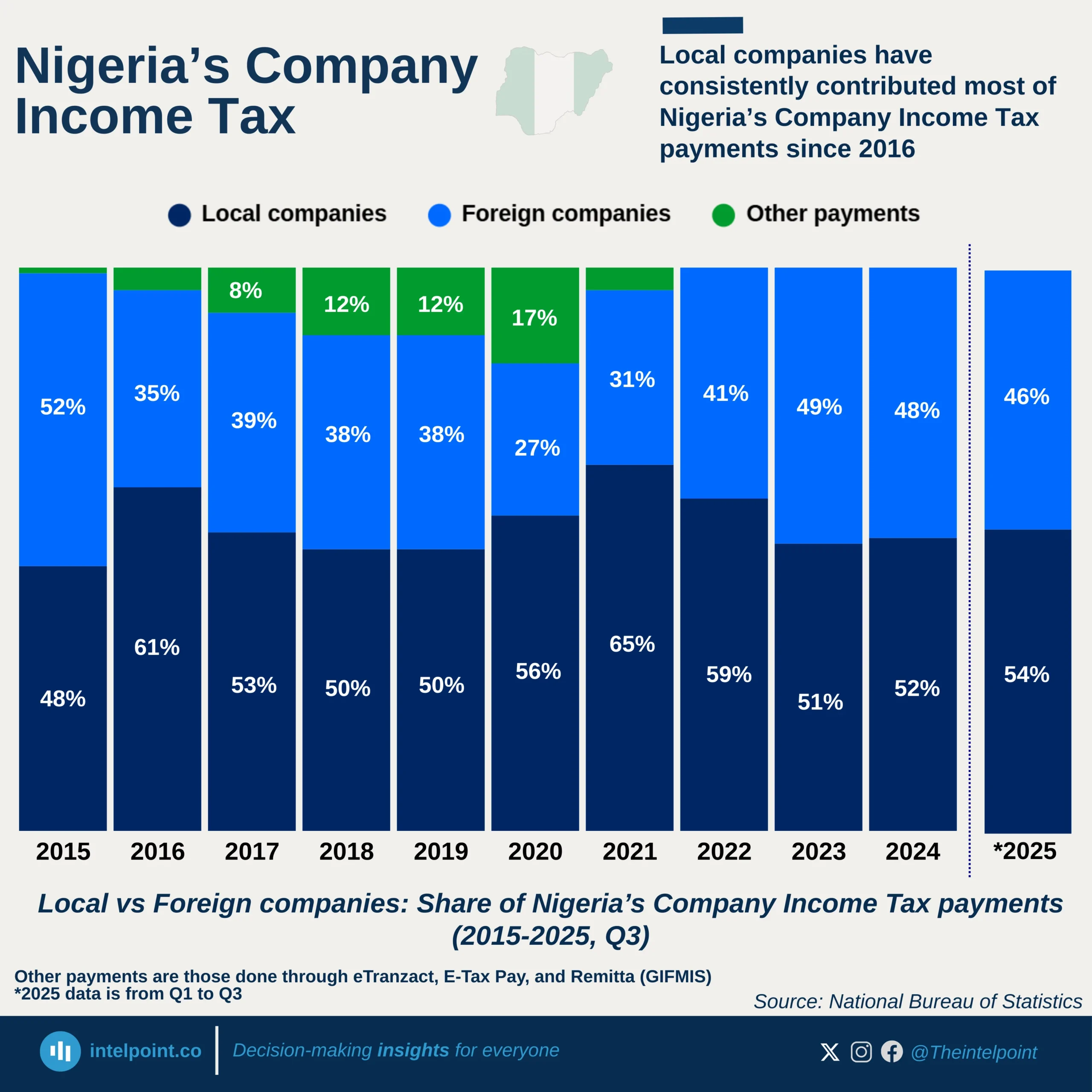
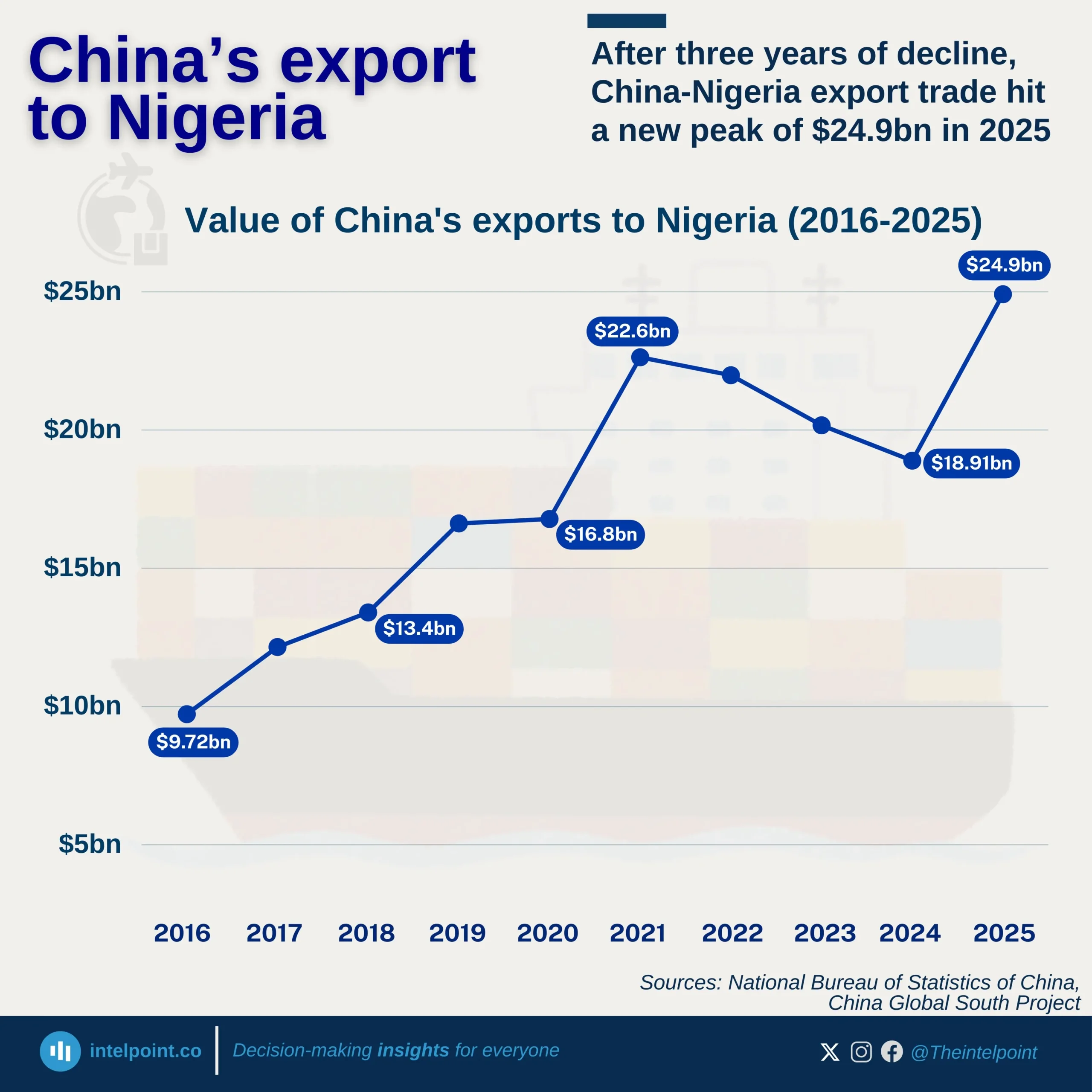
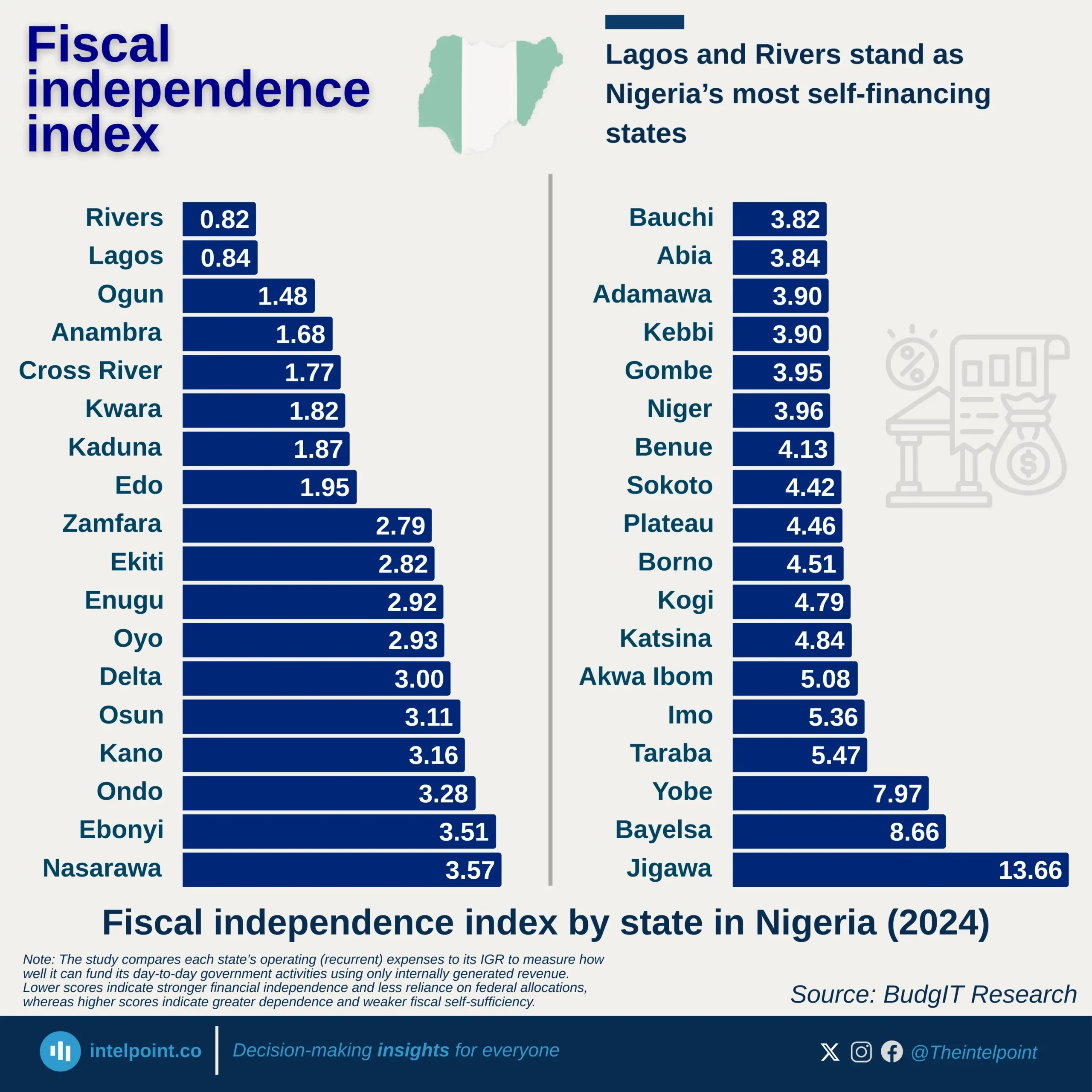
South Africa’s digital services trade between 2005 and 2024 reveals a consistent imbalance. Over this 20-year period, the country exported a total of $76.418 billion worth of digital services. However, imports were significantly higher, totaling $113.67 billion during the same time-frame. This gap created a trade deficit of $37.252 billion, highlighting the country’s dependence on foreign digital services.
In 2005, South Africa’s digital service exports were modest, at just $1.71 billion. By 2024, exports had grown substantially to $7.05 billion, reflecting a steady upward trajectory. Despite this growth, imports continued to outpace exports, limiting the benefits of export expansion.
On average, South Africa exported $3.8 billion annually in digital services across the two decades. By contrast, annual imports averaged around $5.68 billion, creating a persistent yearly gap. This imbalance points to structural challenges in the digital economy and service provision sector. The steady rise in exports shows that South Africa has developed competitive capabilities in certain digital niches. Yet the even faster growth in imports suggests strong domestic demand for foreign platforms and solutions. Encouraging investment in local platforms could reduce reliance on imports. At the same time, expanding export markets would help boost foreign exchange earnings.
Ultimately, South Africa’s digital services trade tells a story of growth overshadowed by imbalance.