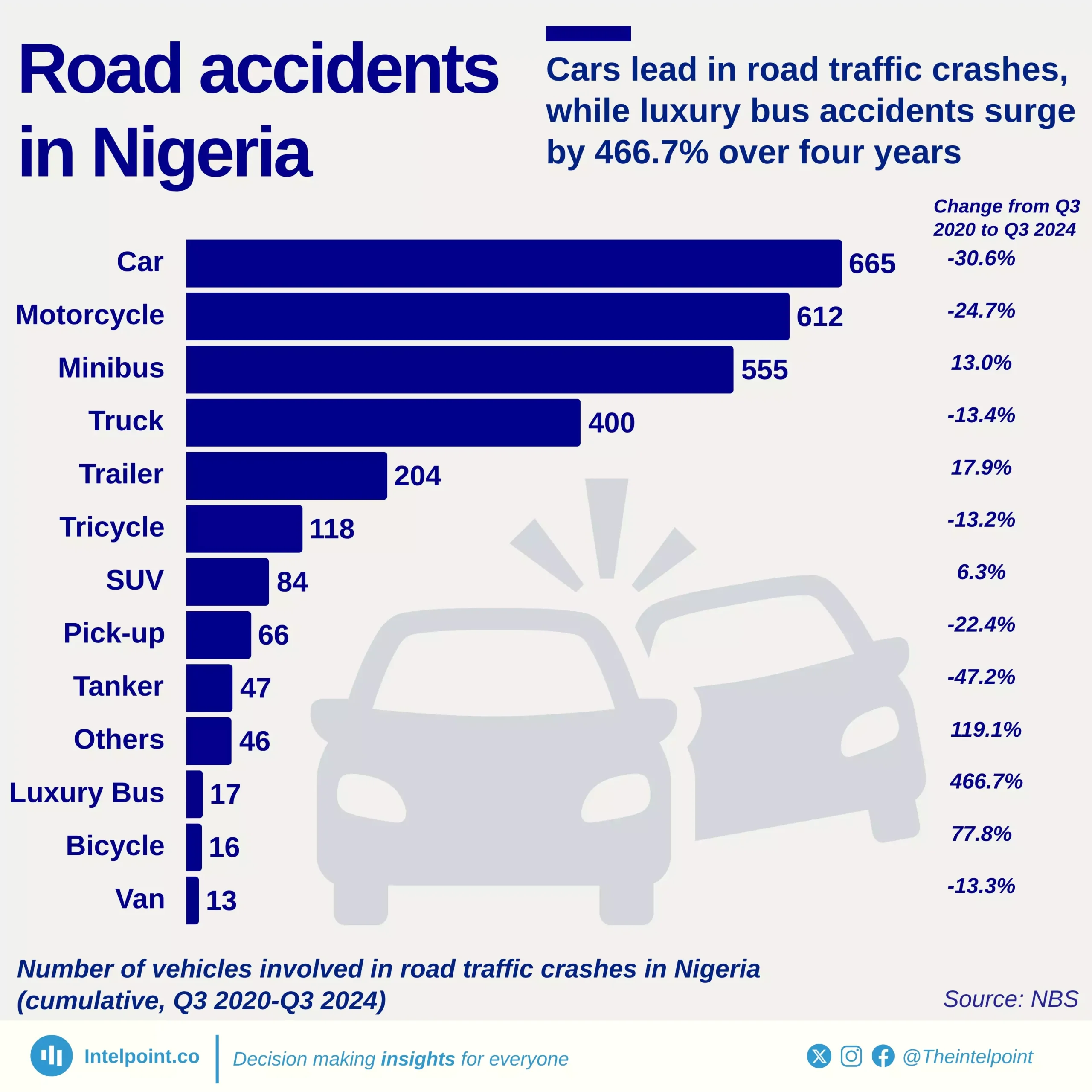
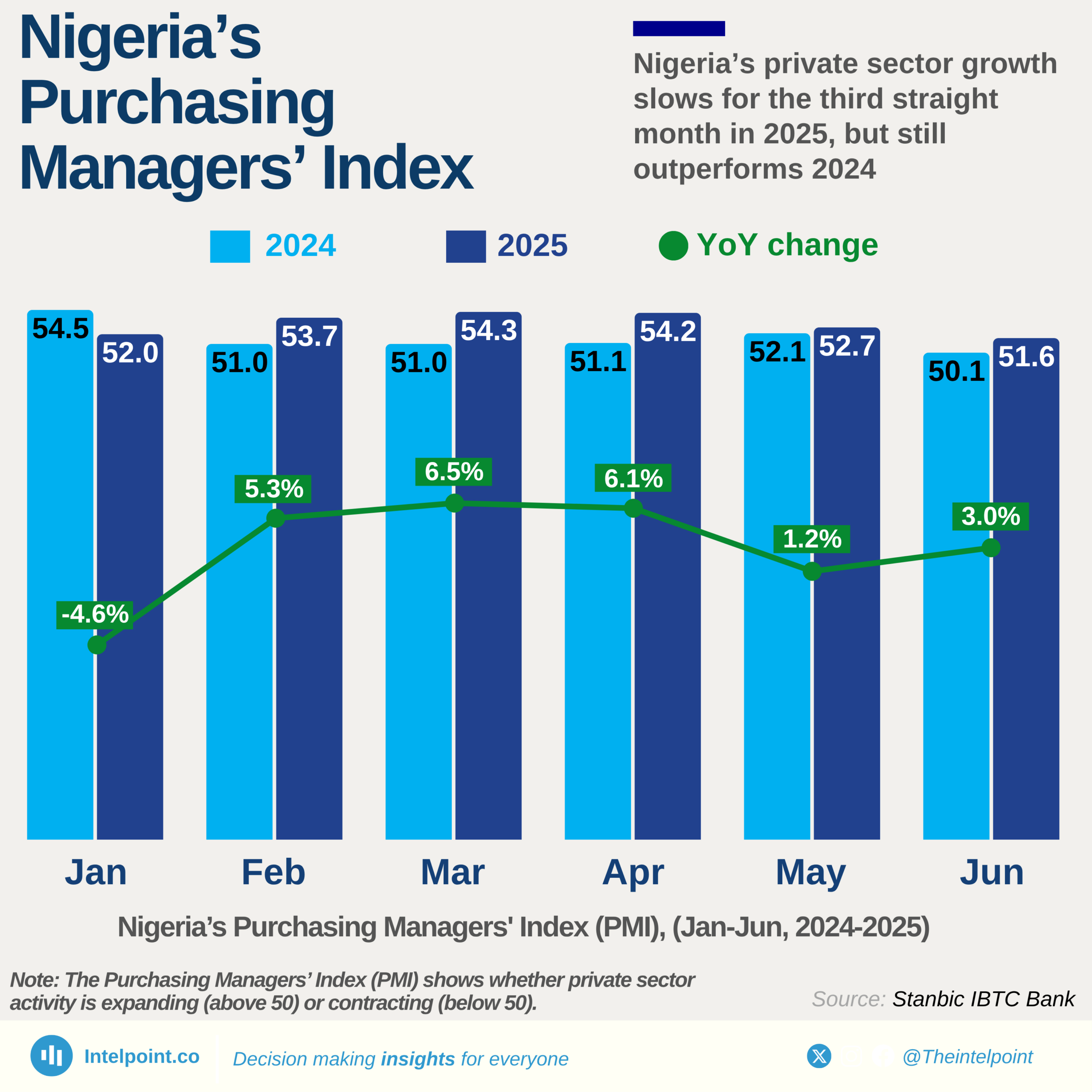
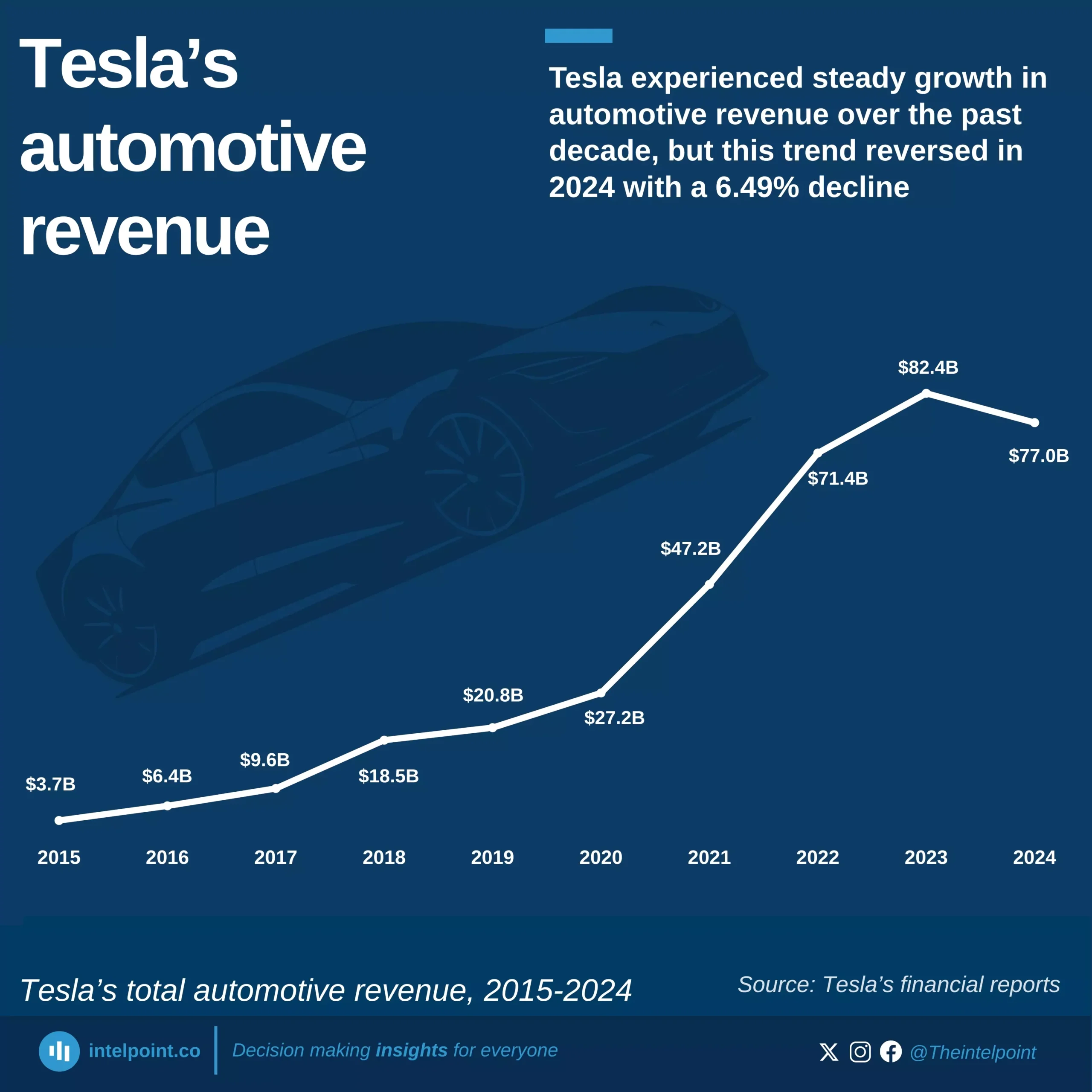
Nigeria’s capital expenditure as a percentage of GDP has seen a significant decline over the past two decades, dropping from an average of 4.33% (1981–2001) to just 1.58% (2002–2024). The data reveals a clear shift in government spending priorities, with capital investments taking a backseat despite the country’s growing infrastructure and development needs.
This drop is even more concerning when compared to historical peaks. Capital spending once hit 9.1% of GDP in 1999, but in recent years, it has struggled to cross 2%. The decline suggests that while Nigeria’s economy has expanded, public investments in critical infrastructure like roads, power, and healthcare have not kept pace. This raises crucial questions about the sustainability of economic growth in the absence of strong public sector investment.