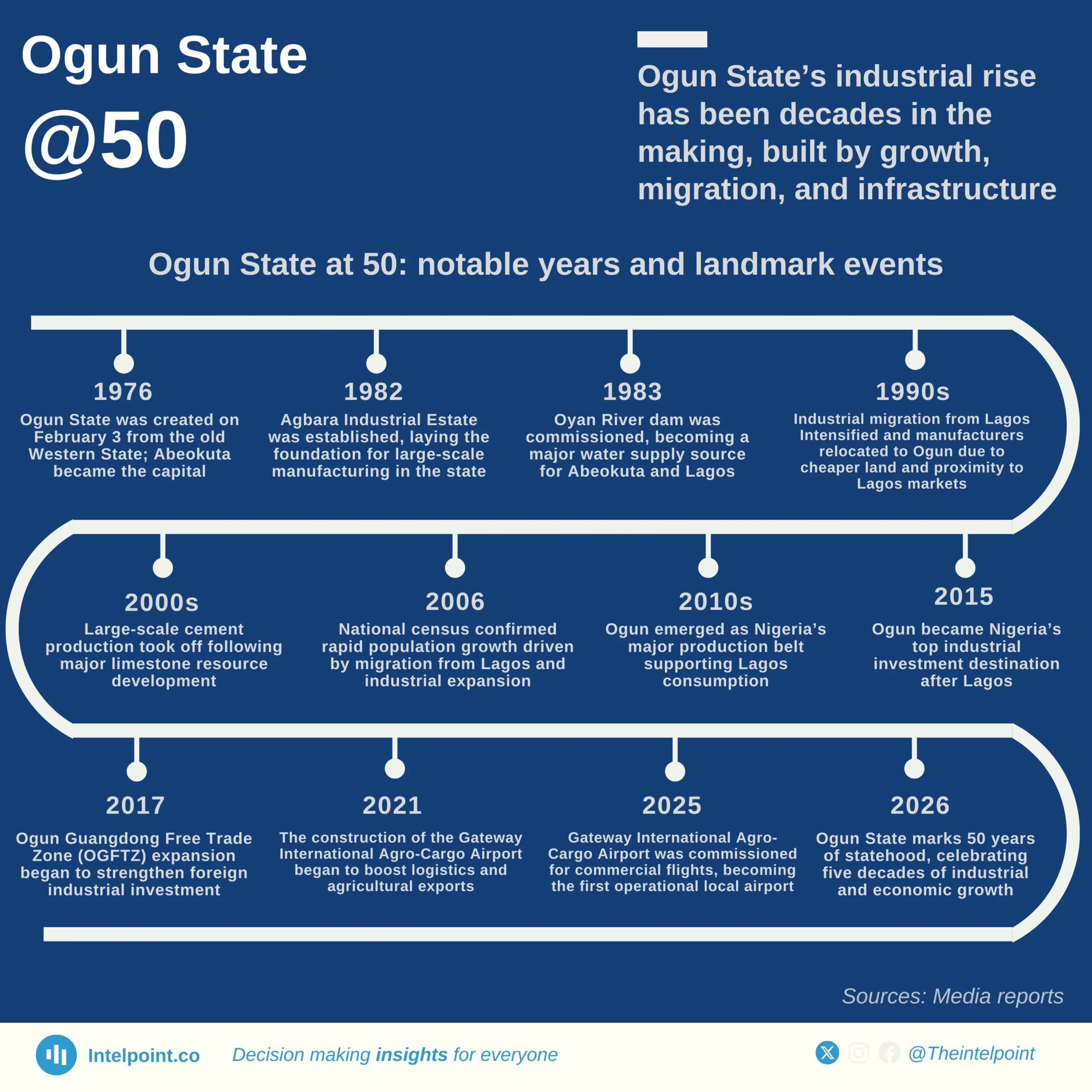
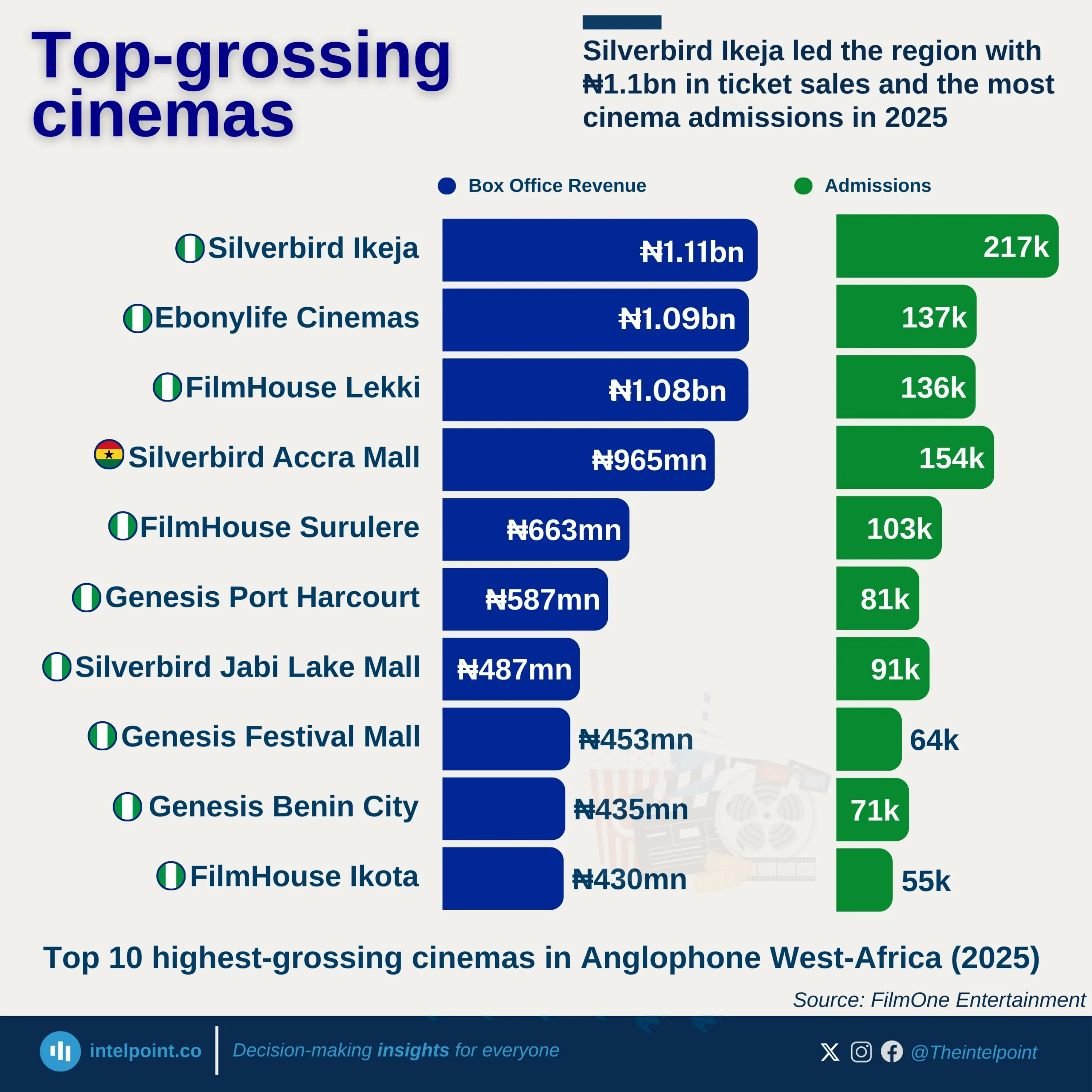
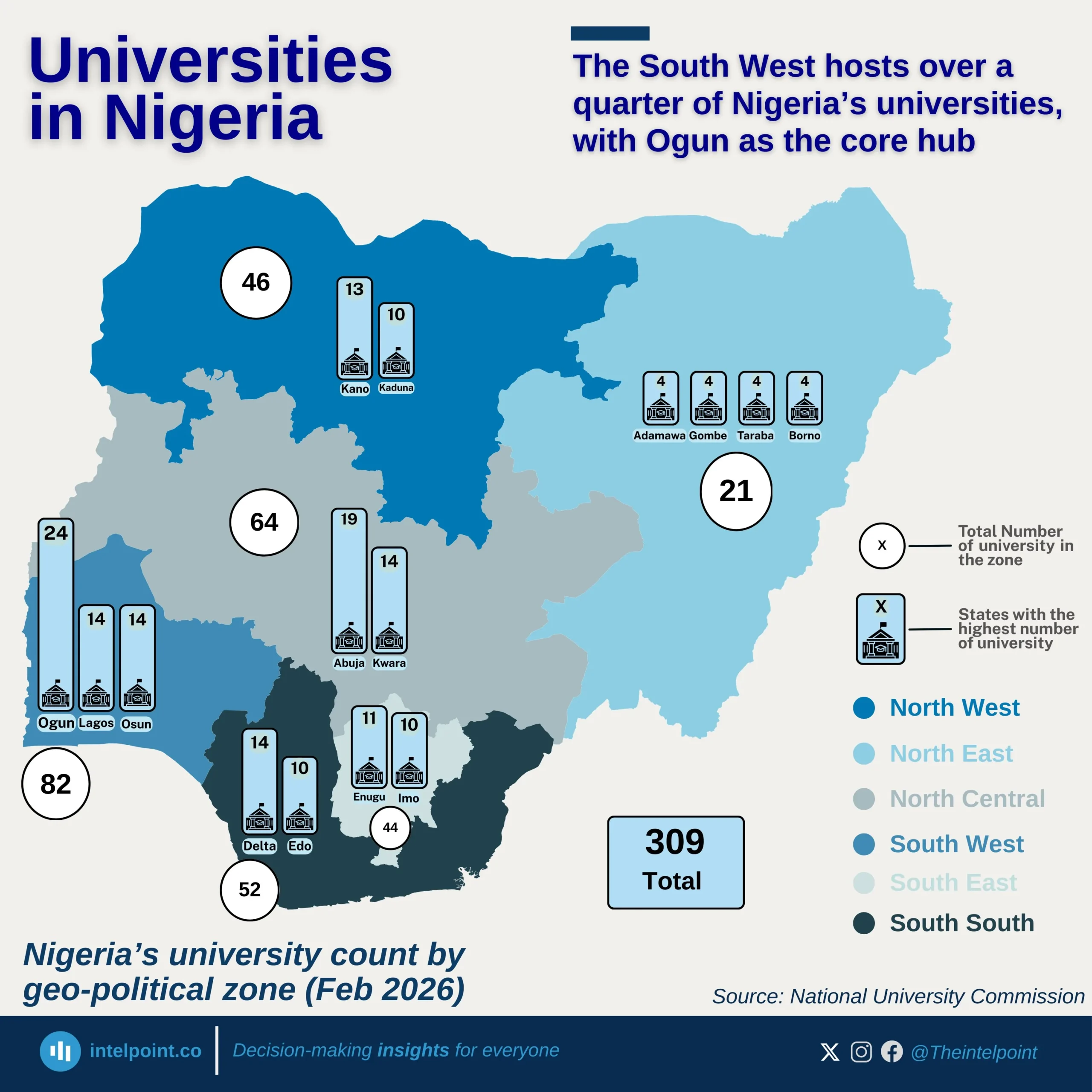
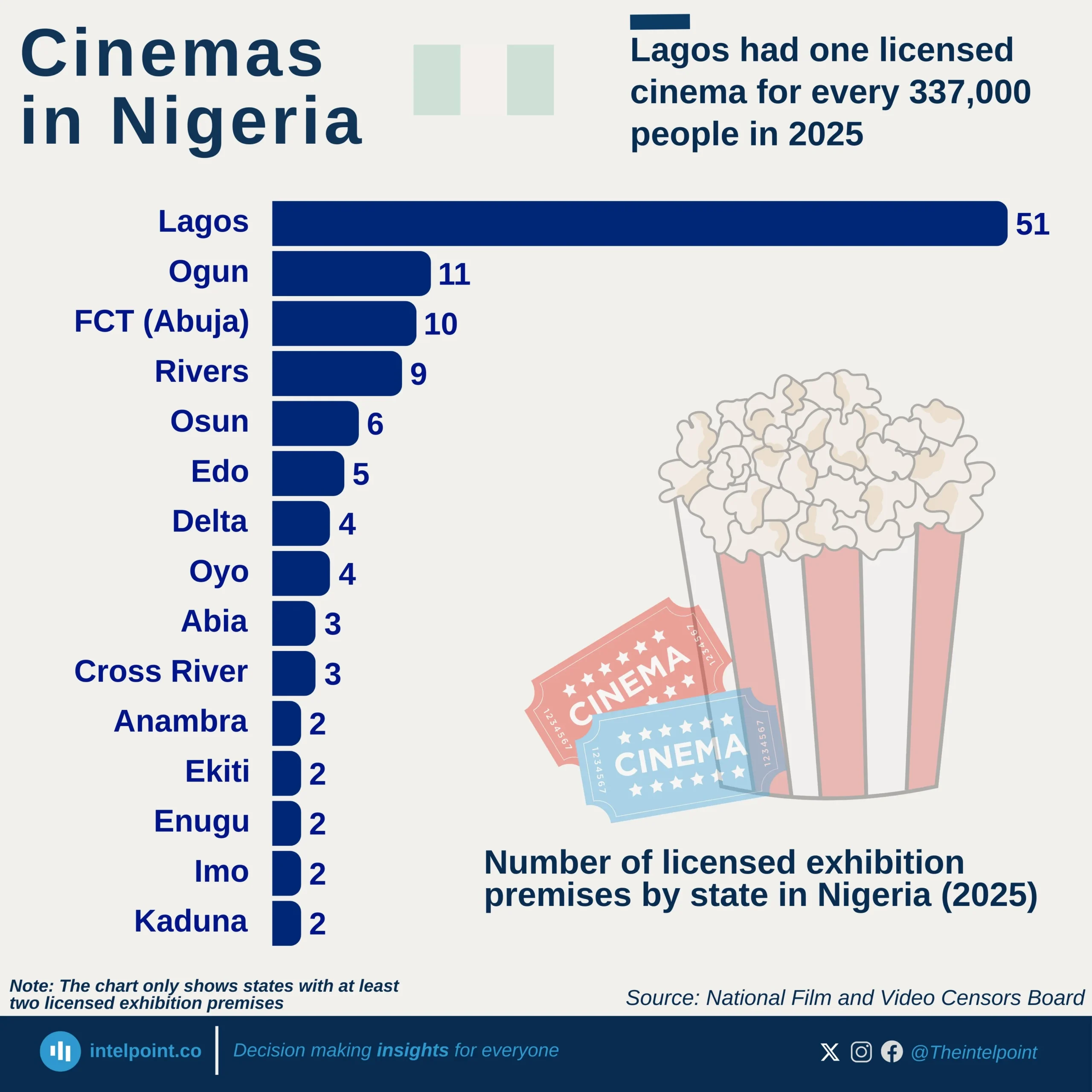
Nigeria’s passport mobility has seen notable shifts over the past decade, reflecting changes in global travel dynamics and diplomatic efforts. In 2015, the mobility score stood at 42, experiencing a slight dip to 41 in 2016 before climbing steadily to 50 by 2019. However, the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 led to a sharp decline, dropping the score back to 44 as global travel restrictions tightened.
Post-pandemic recovery began in 2021, with the score rebounding to 48, followed by a strong surge to 54 in 2022. This upward momentum peaked in 2023 at 56, marking the highest recorded mobility score in the dataset. Despite a slight stabilisation at 55 in 2024 and 2025, the overall trend shows a significant improvement, with Nigerian passport holders gaining access to more destinations over time.
From 2015 to 2025, the mobility score increased by 31%, underscoring enhanced international partnerships and improved visa agreements. While challenges such as global crises can impact travel freedom, Nigeria’s steady recovery highlights progress in global mobility access for its citizens.