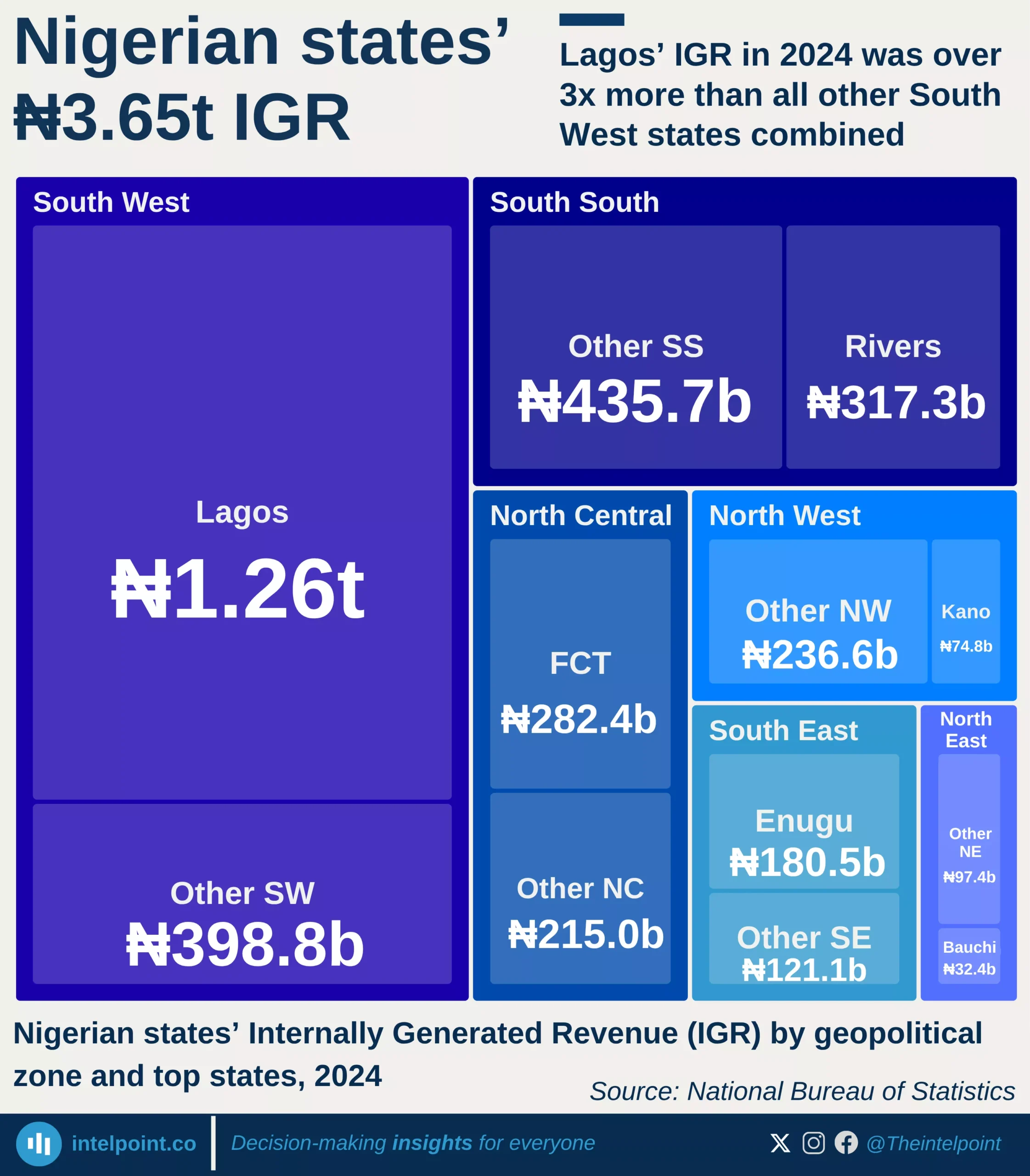
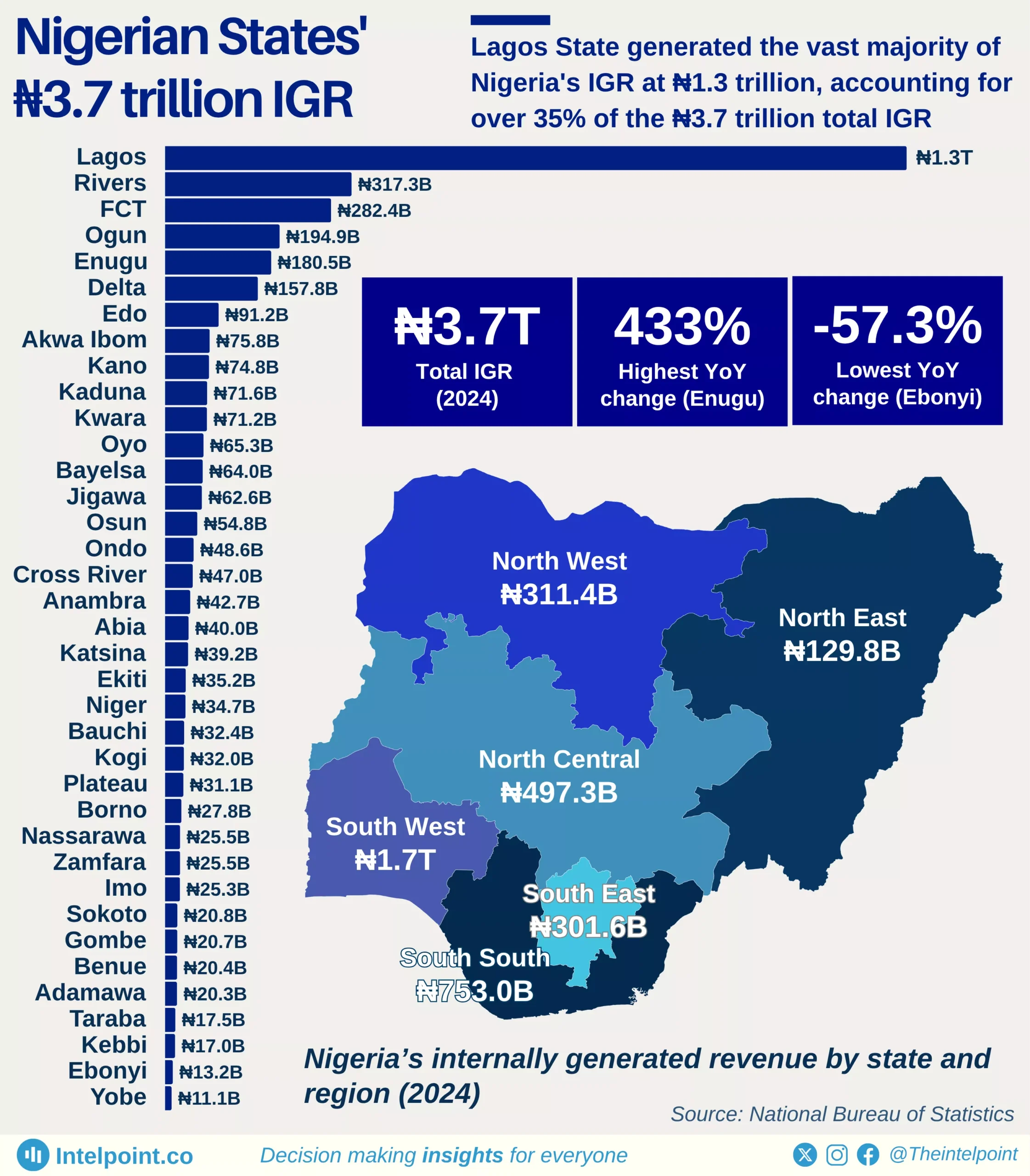
Lagos State’s Q1 2025 inflows highlight the state’s heavy reliance on internally generated revenue (IGR), which accounted for 61% of total funds. This dominance reflects Lagos’ strong tax administration capacity and its ability to sustain governance largely independent of federal allocations. The state’s total fund composition reveals a diversified yet uneven structure, with VAT contributing 22% and loans accounting for 8%, while other streams, such as statutory allocation (2%) and FAAC (3%), play minimal roles.
The reliance on IGR is significant because it highlights Lagos’ economic strength compared to many other Nigerian states that heavily depend on federal allocations. With a vibrant business ecosystem, a large population base, and stronger infrastructure, Lagos has positioned itself to thrive on its own funding sources. This financial independence not only strengthens the state's fiscal resilience but also gives it greater autonomy in executing development projects without being overly constrained by federal transfers.
The broader implication of this inflow structure is that Lagos has created room for a more predictable financial system, relying less on volatile oil-related allocations and more on a stable stream of internal taxes and levies. This not only supports long-term planning but also makes the state better equipped to withstand national economic shocks.