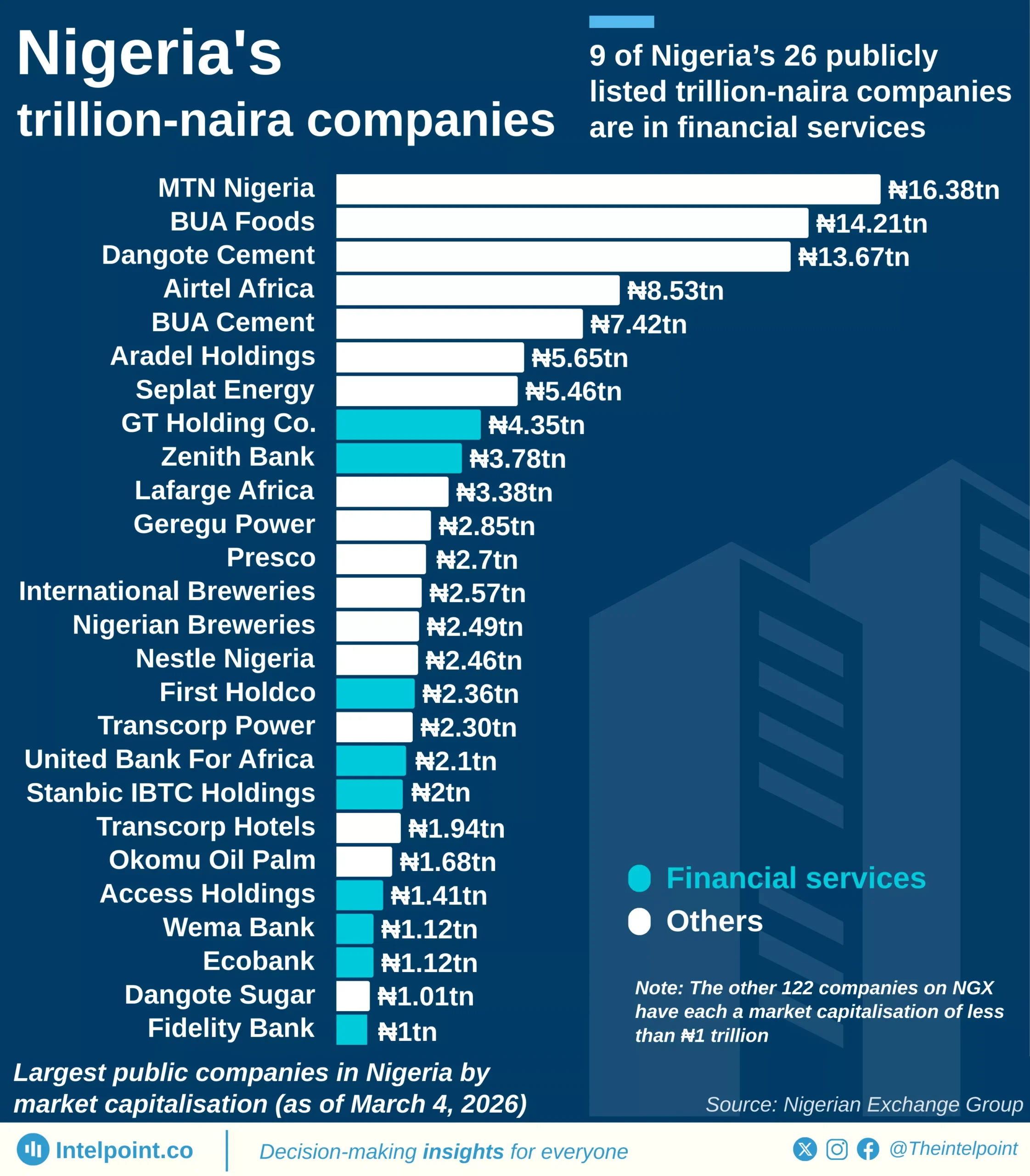
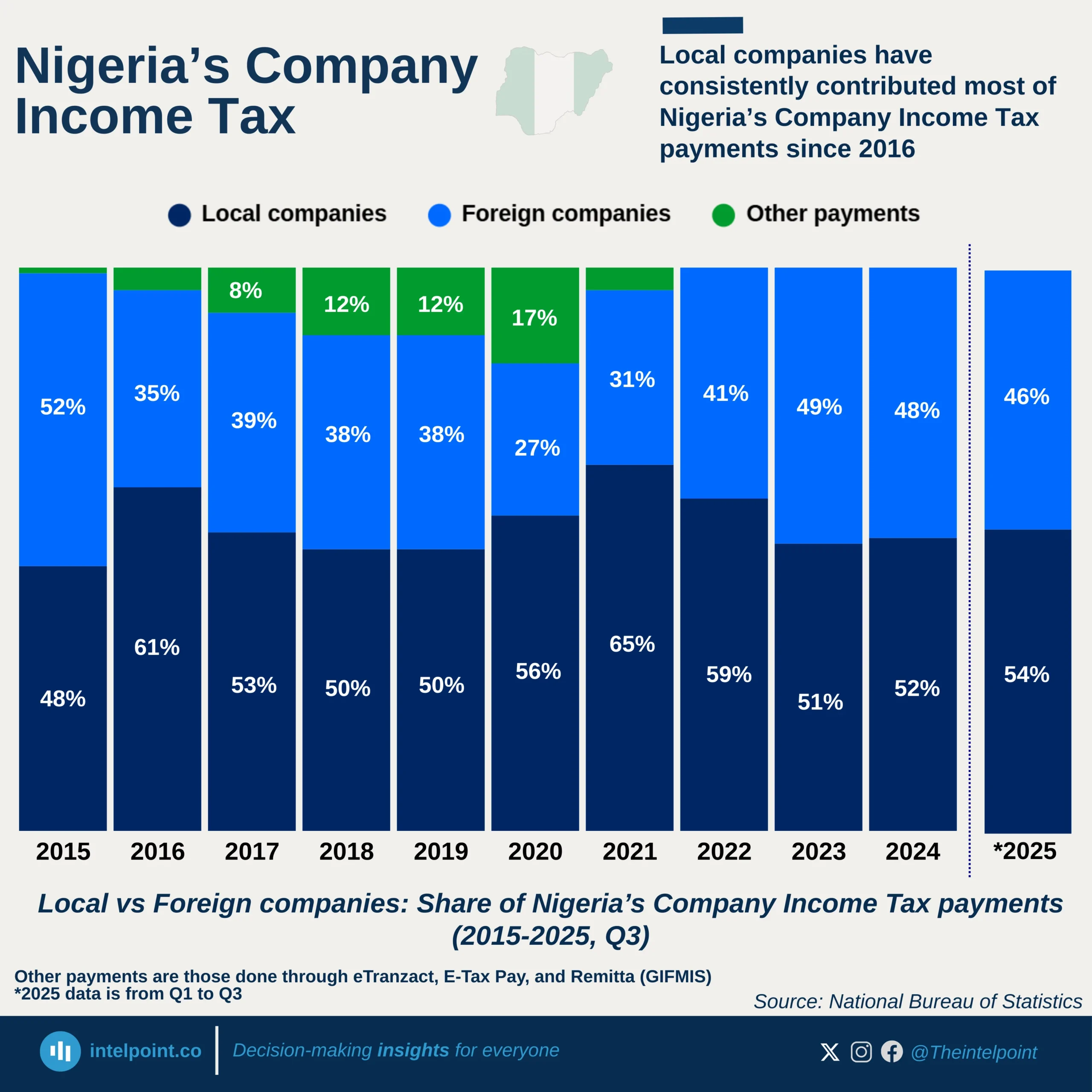
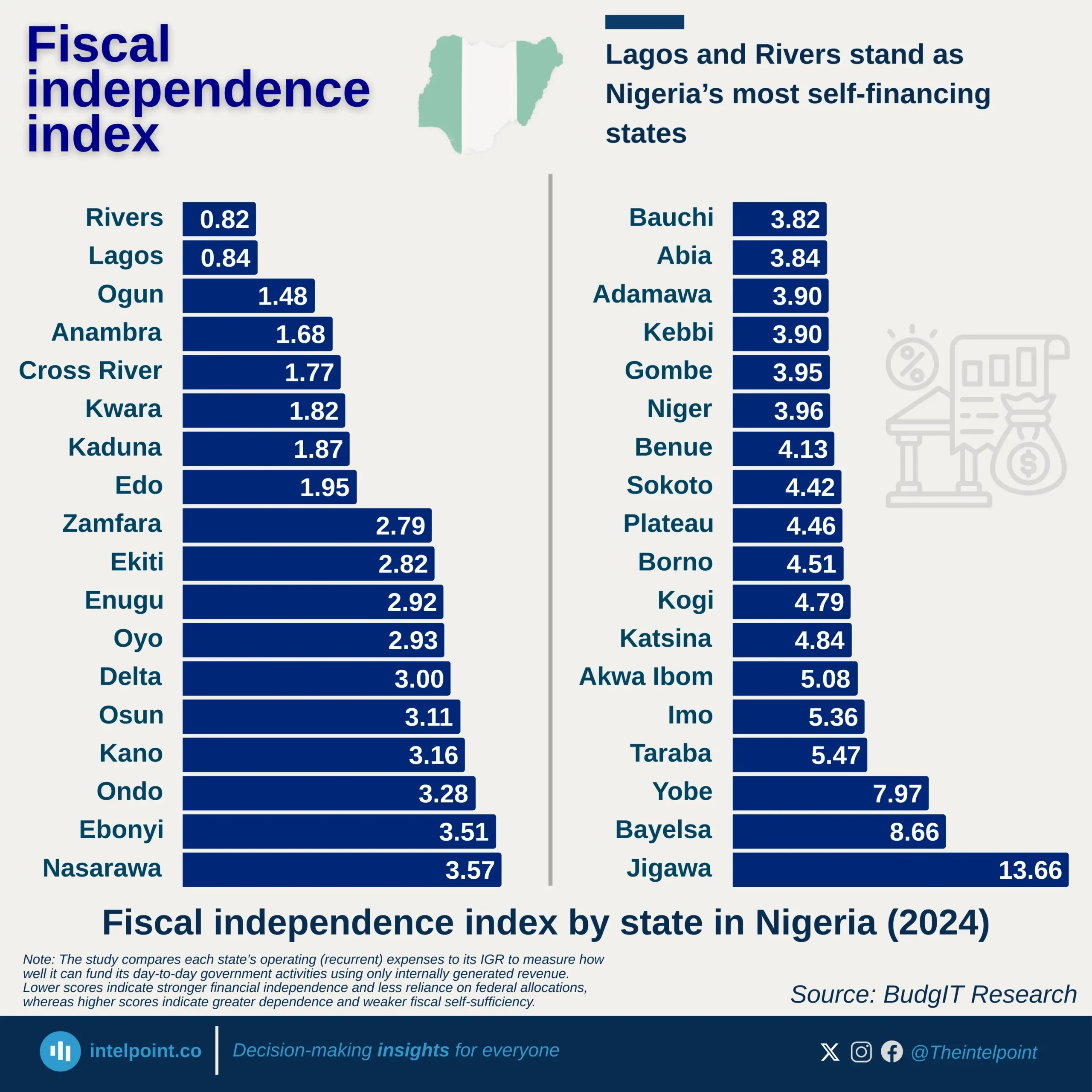
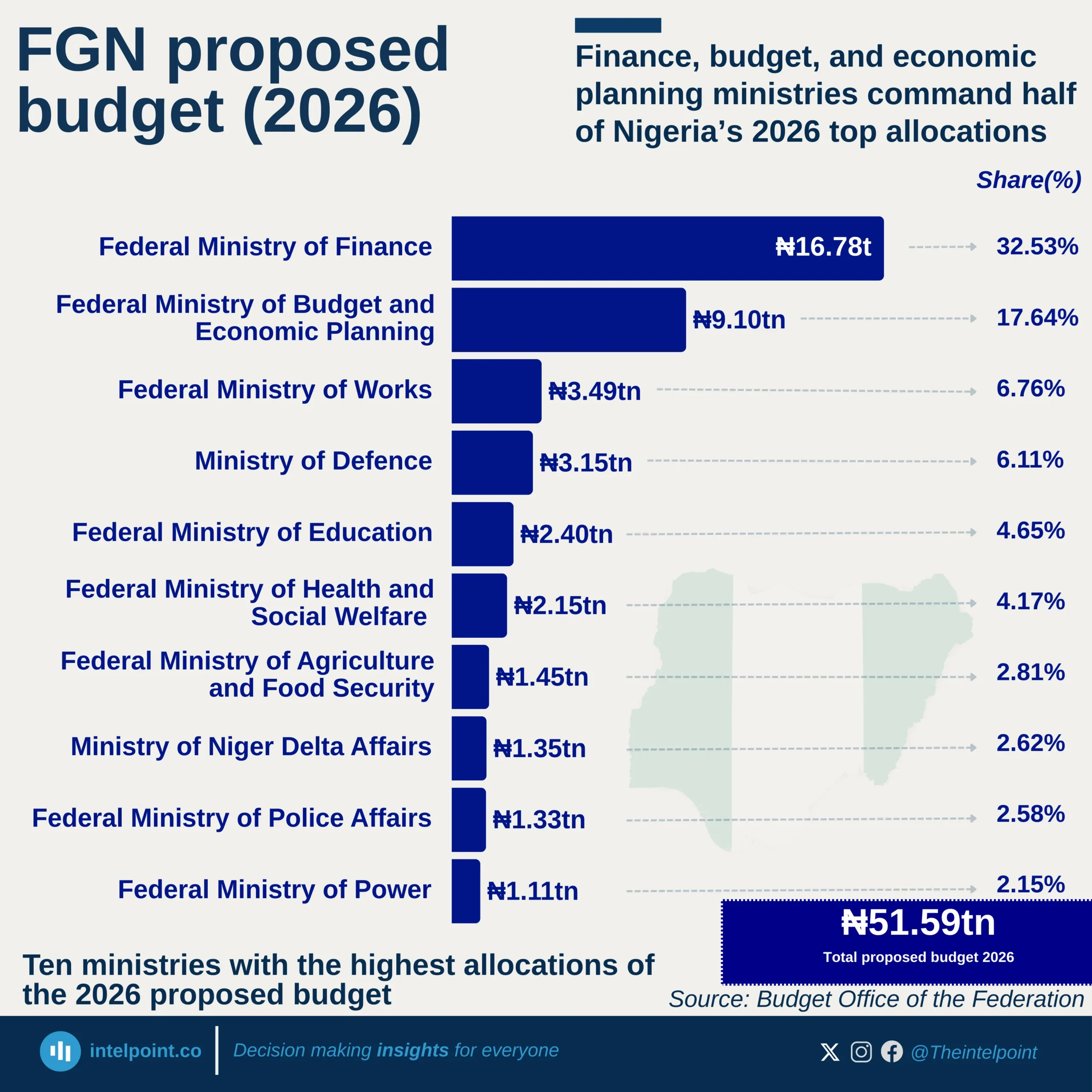
Since 2011, over ₦32.8 trillion has gone to Nigeria’s state governors from the Federation Account Allocation Committee (FAAC). States from the South East have received ₦3.3 trillion combined, the least nationwide.
This fund allocation is to ensure that all levels of government have the necessary funds to meet their financial obligations and to provide public services.