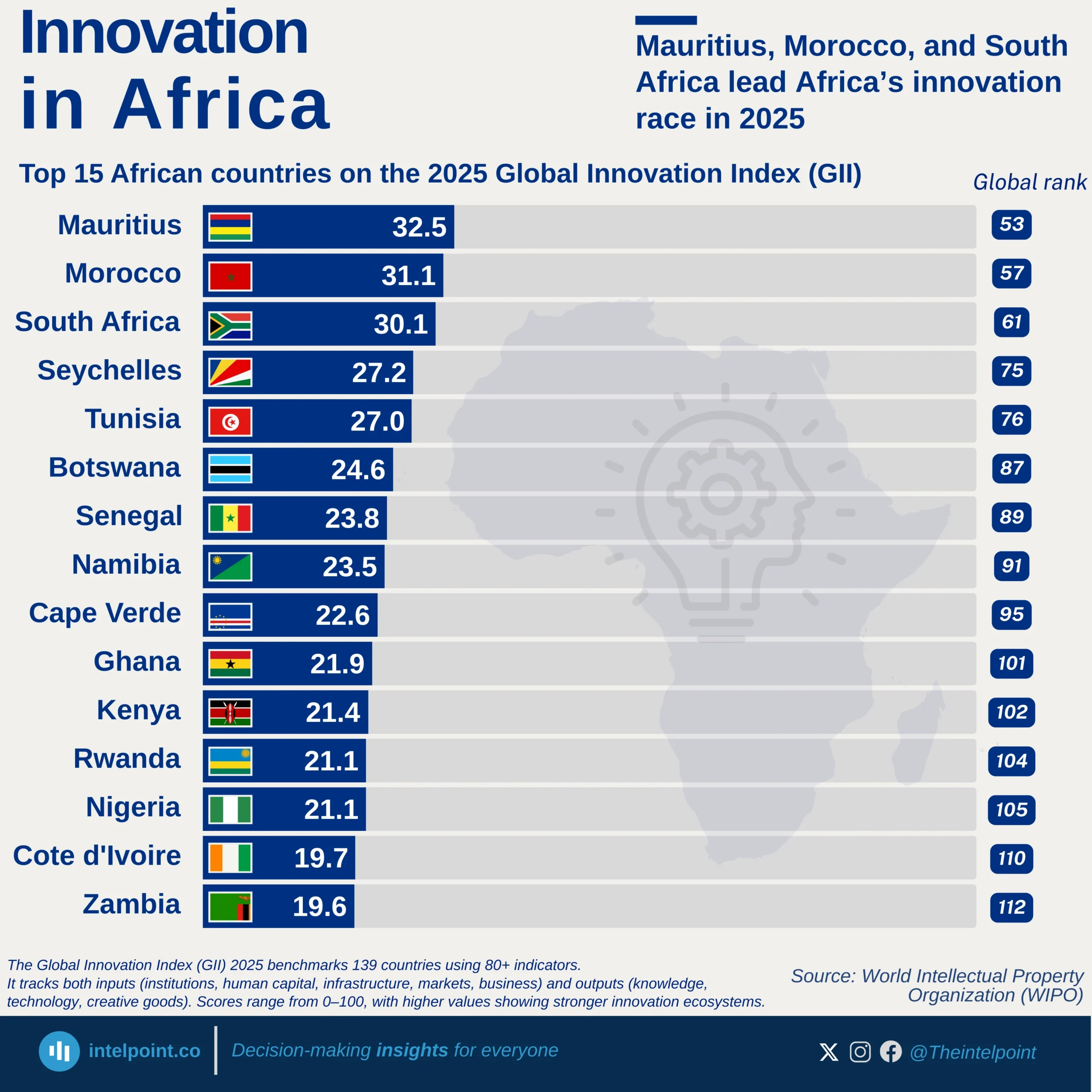
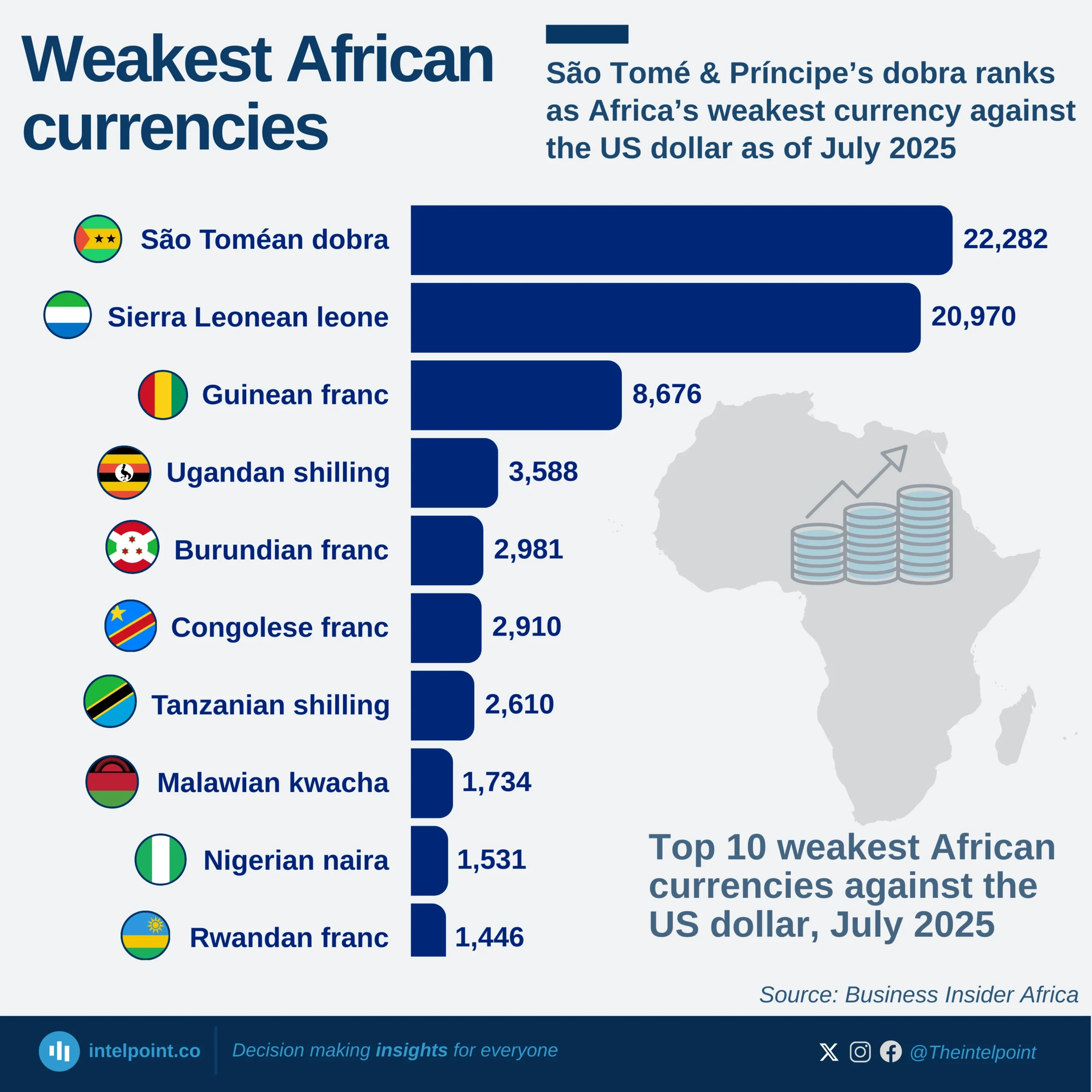
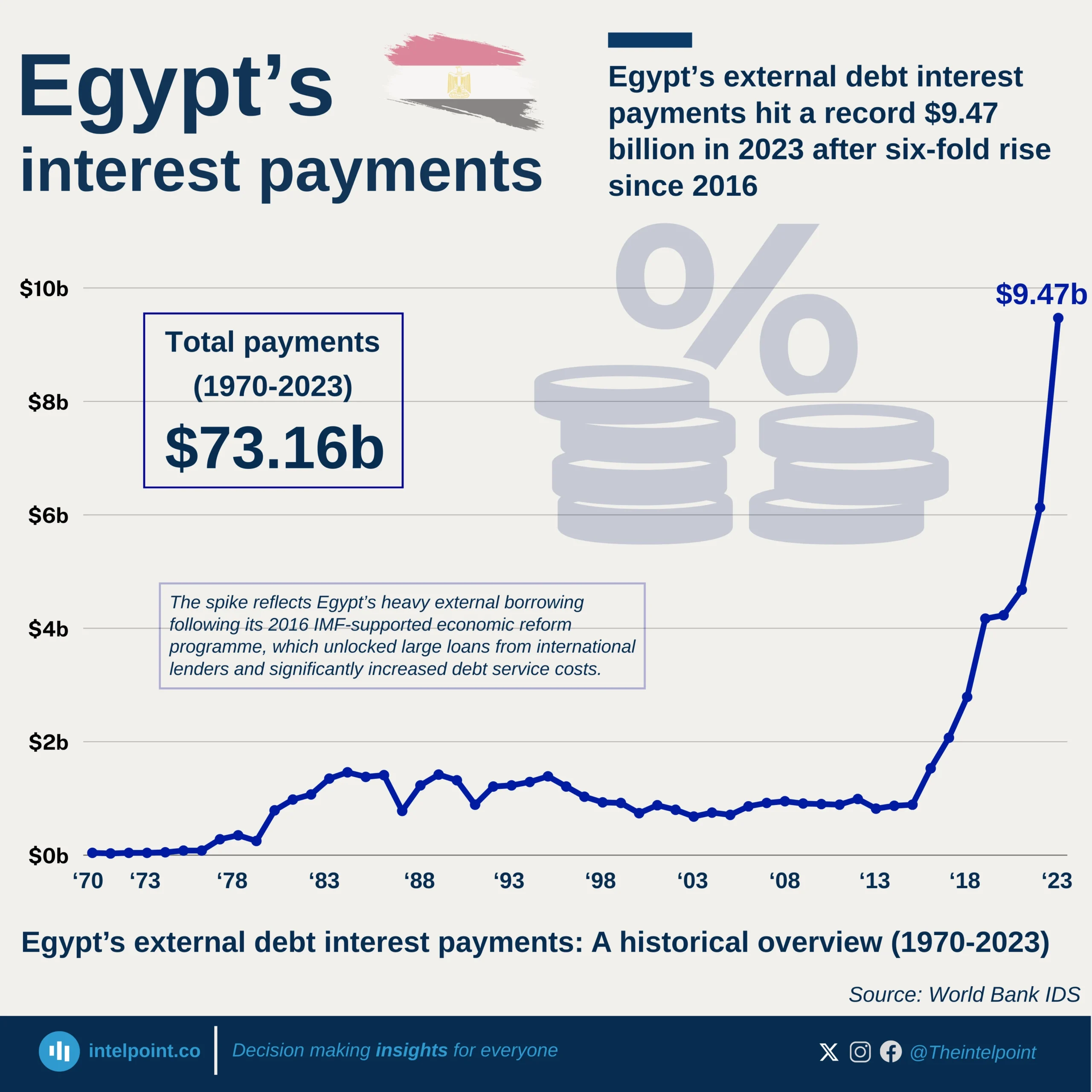
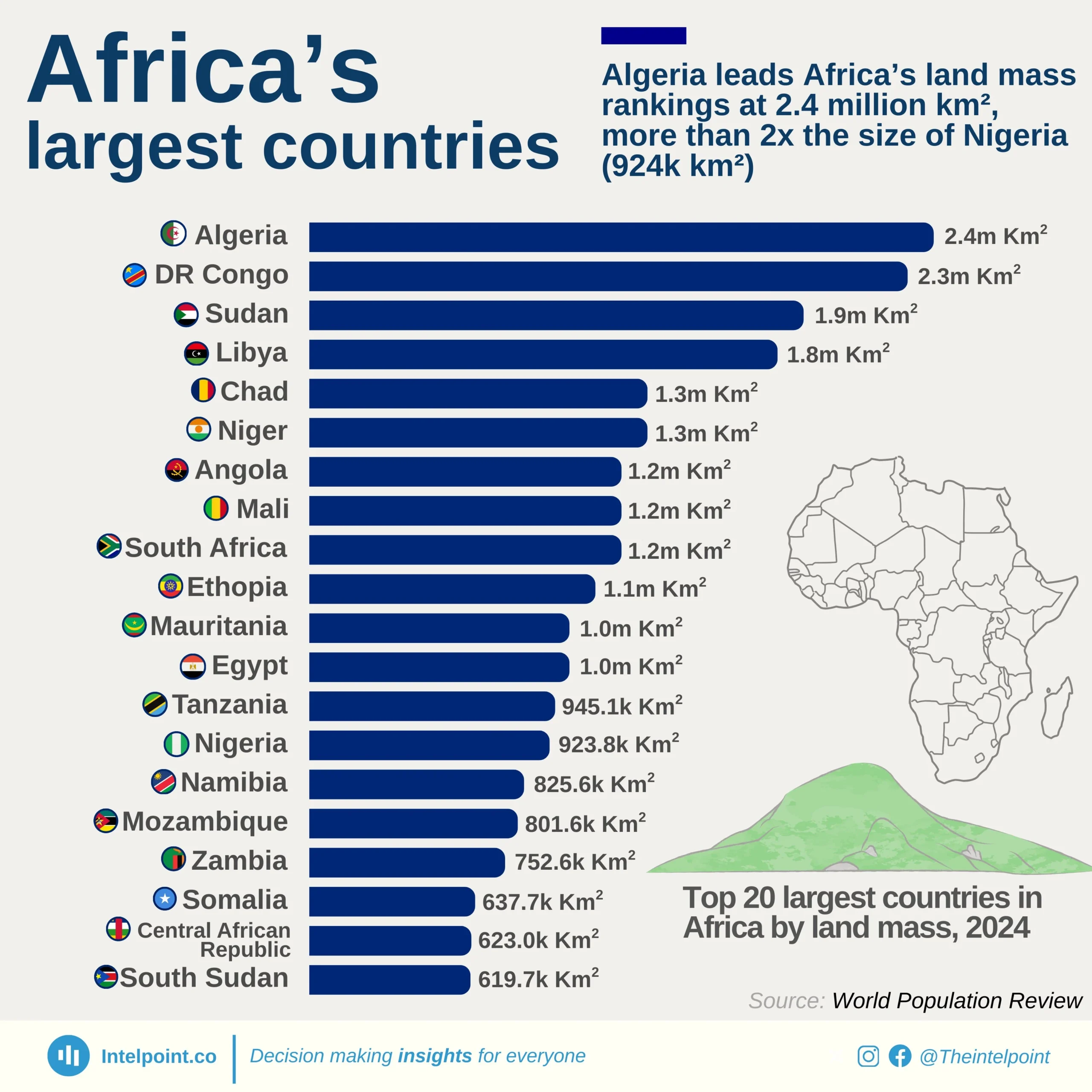
Nigeria’s infrastructure development trajectory has seen fluctuating growth across different administrations, with the most notable leap occurring during Goodluck Jonathan’s presidency. Between 2010 and 2015, Nigeria’s African Infrastructure Development Index (AIDI) score grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.84%, the highest among the administrations analysed. The index climbed from 11.96 in 2010 to 20.45 by 2015, signalling a focused and accelerated drive towards improving infrastructure during that period. In contrast, infrastructure growth slowed under Muhammadu Buhari’s administration, which posted a CAGR of 2.63%, taking the score from 20.60 in 2016 to 25.70 in 2024. Earlier still, Olusegun Obasanjo’s tenure saw modest growth (CAGR 2.59%), with the AIDI improving from 8.61 in 2003 to 9.78 by 2007.
Infrastructure influences everything from commuting time and electricity access to business costs and internet reliability. In cities like Lagos or Abuja, the strain on infrastructure is tangible, whether in daily traffic congestion or limited broadband access. So, when the AIDI score grows significantly, like it did under Jonathan, it signals more than just a number. It means more Nigerians likely had better access to basic infrastructure that shapes daily life and economic opportunity.