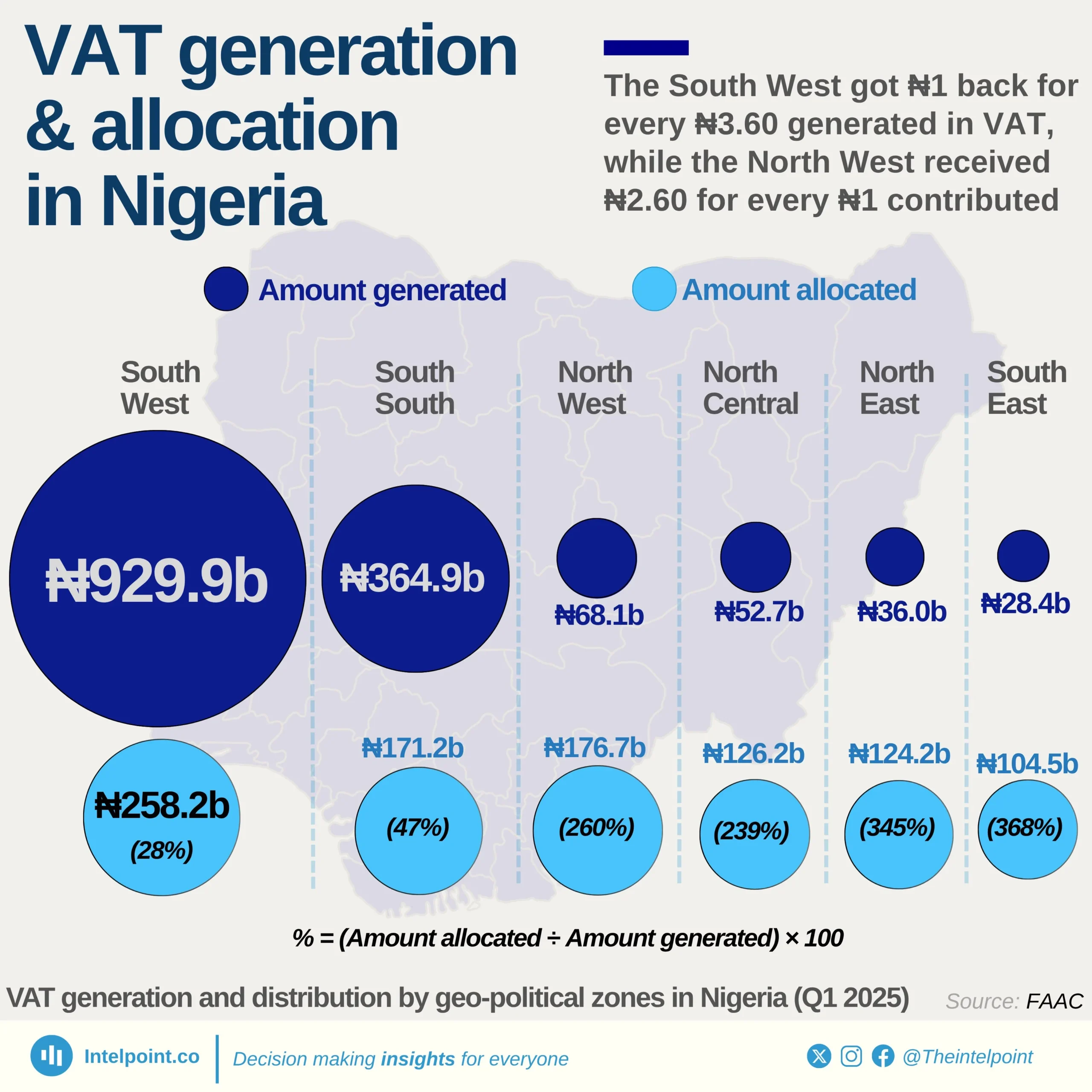
The VAT remittance vs. sharing in the South-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria reveals a system where some states receive significantly more than they generate. The region remitted ₦10.94 billion in VAT but received ₦39.15 billion, meaning it got back ₦3.58 for every ₦1 contributed—one of the highest sharing ratios in Nigeria.
A striking disparity is seen in Abia, which remitted the least (₦0.73 billion) yet received ₦7.29 billion, nearly 10× its remittance, making it the biggest relative gainer in the South-East.
Similarly, Imo and Enugu, which remitted ₦1.59 billion and ₦1.75 billion respectively, received ₦8.26 billion and ₦7.76 billion, further emphasising how VAT allocation prioritises equalisation over economic output. Despite varying contributions, every South-Eastern state received at least double its VAT remittance, with the region’s average allocation per state standing at ₦7.83 billion, compared to an average remittance of just ₦2.19 billion.