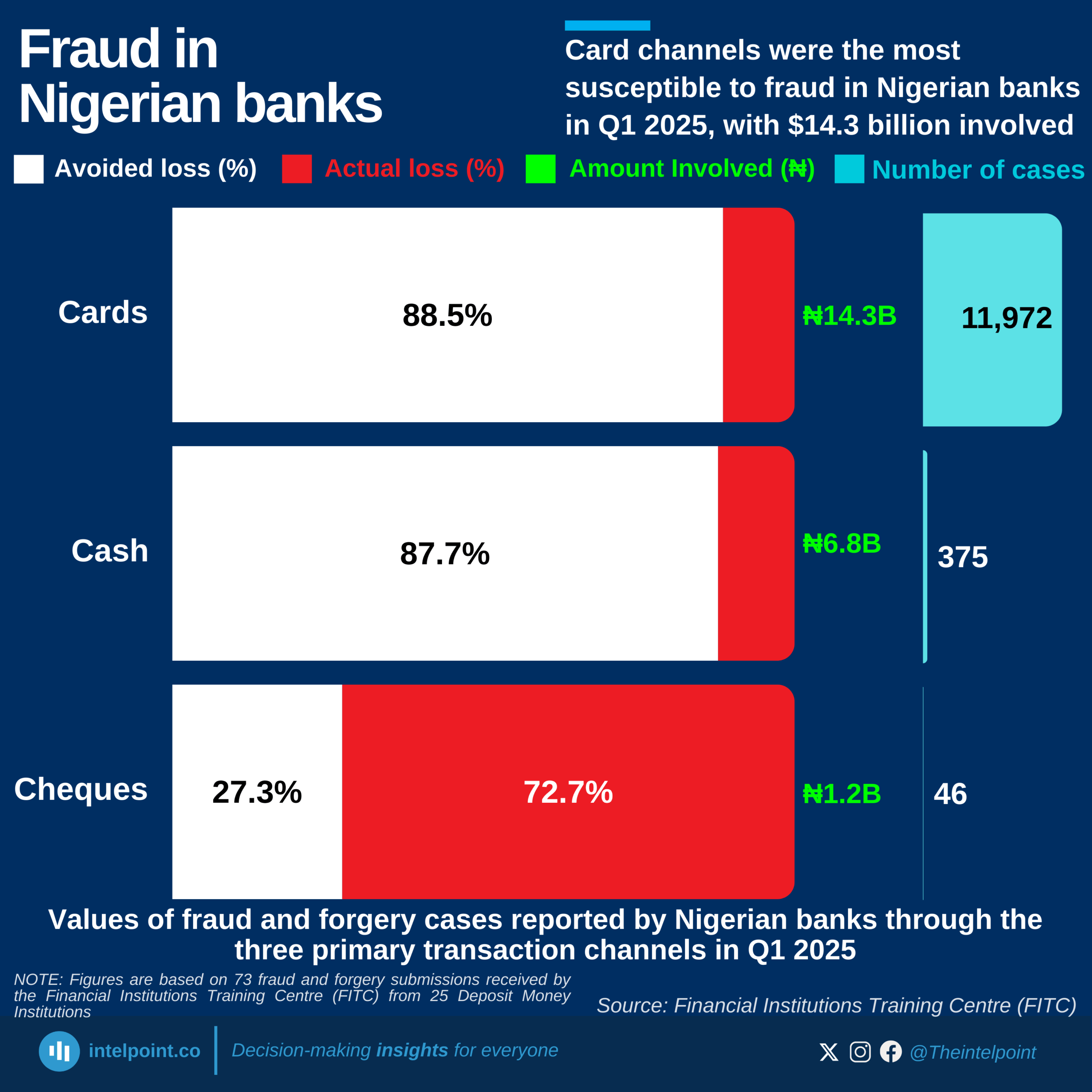
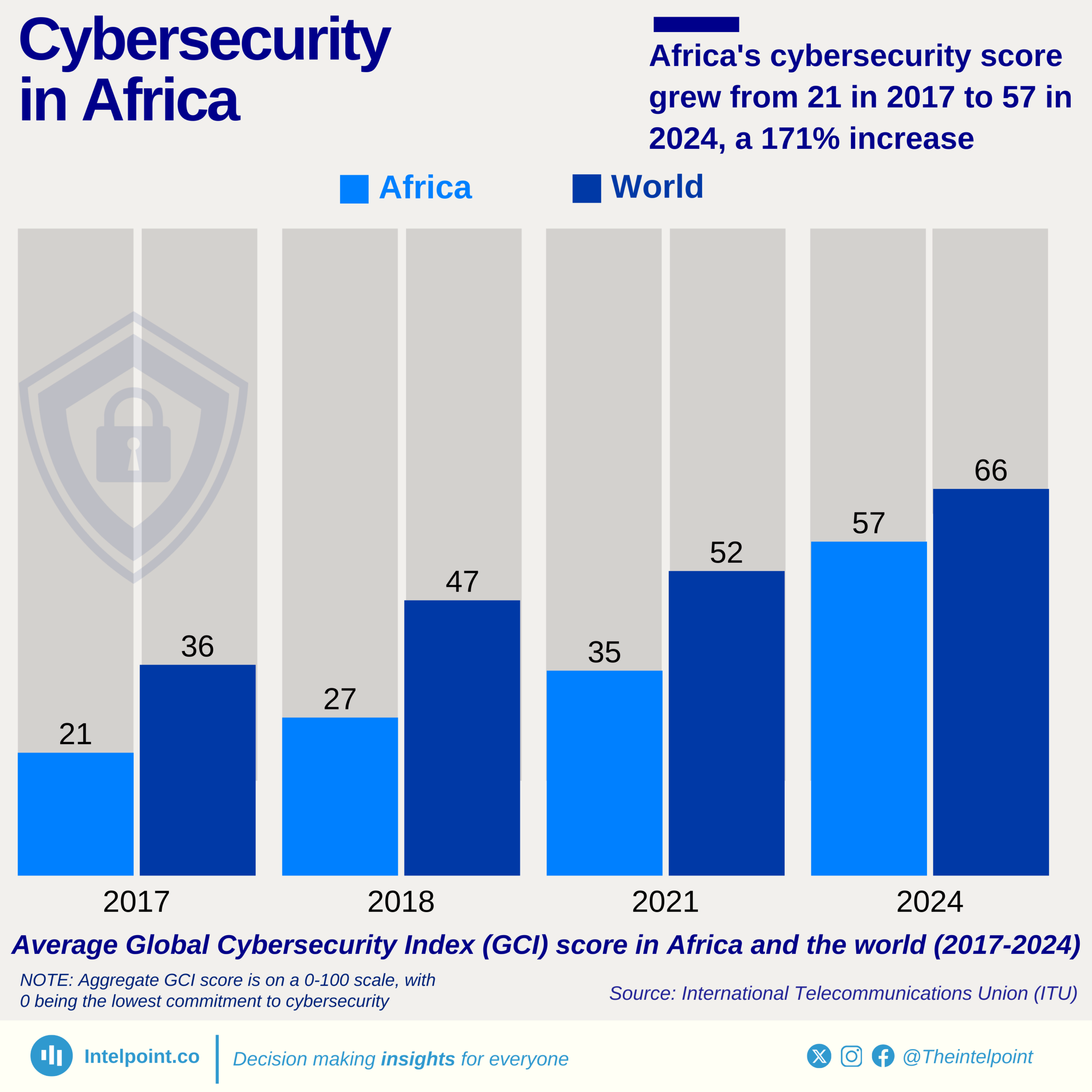
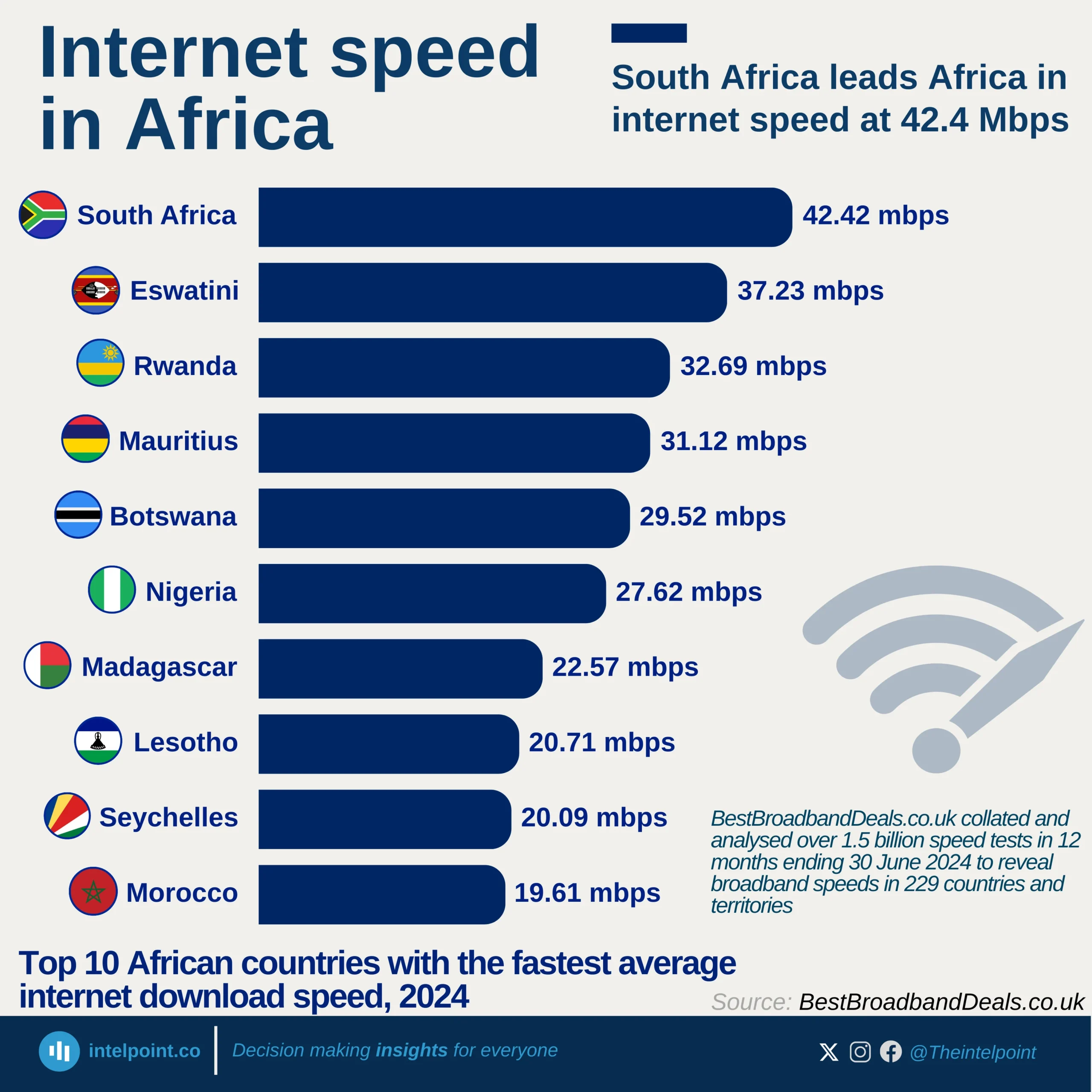
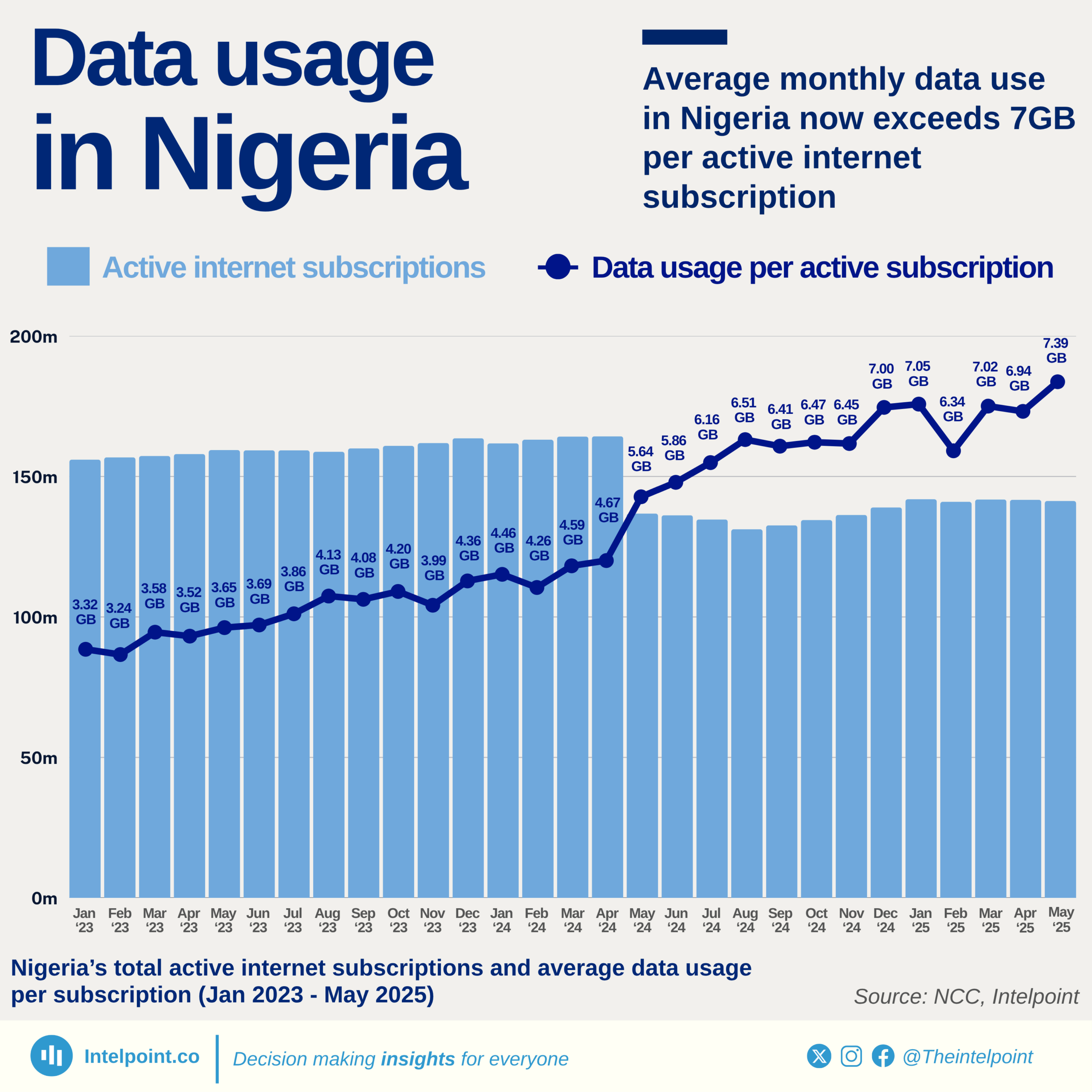
Despite being Africa's largest economy, Nigeria has 128.3 million people unconnected to the internet as of January 2025 — over 54% of the population. This ranks Nigeria 4th globally among countries with the highest number of unconnected individuals. The digital gap is no longer a future concern; it’s a present reality that affects how millions access education, health, jobs, and basic information.