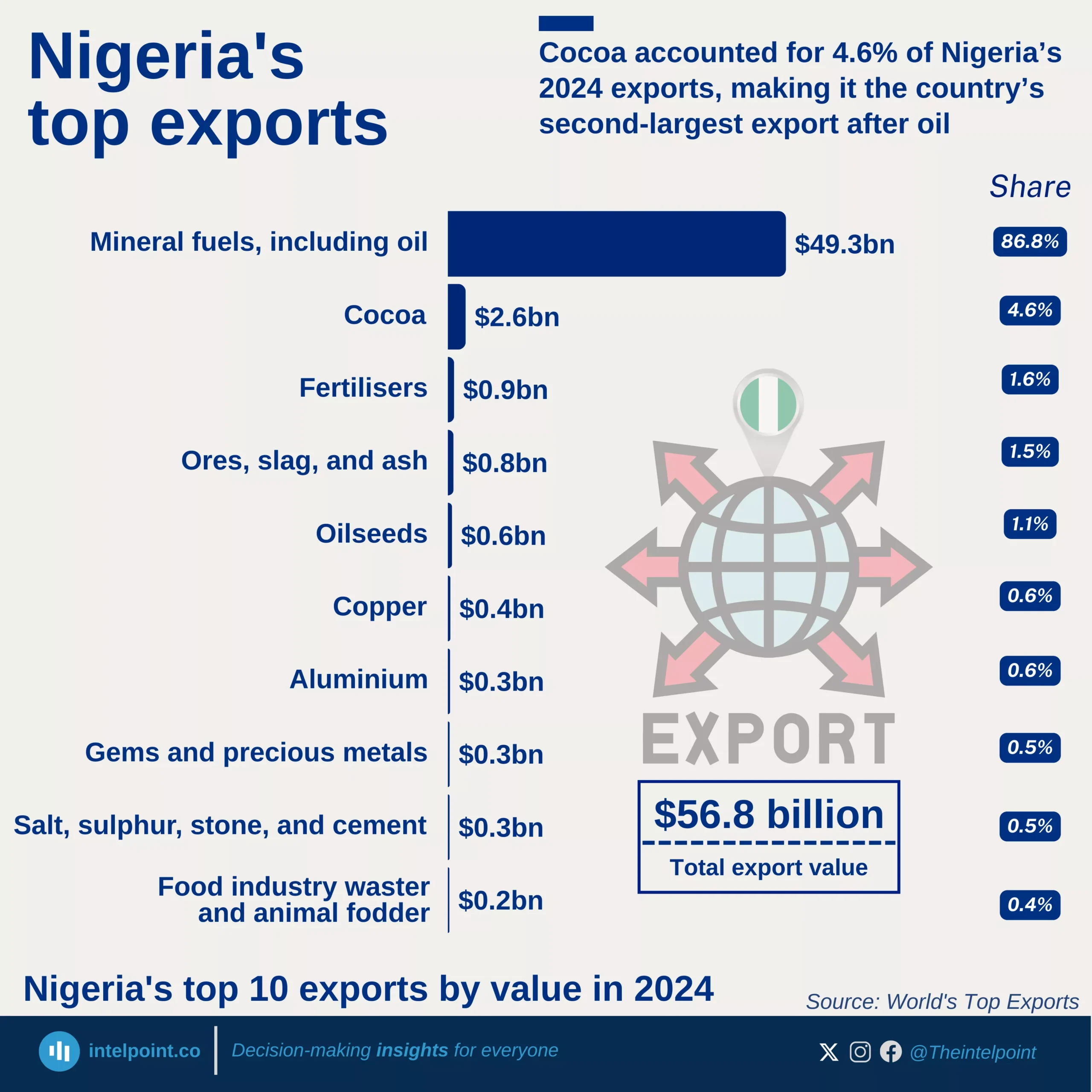
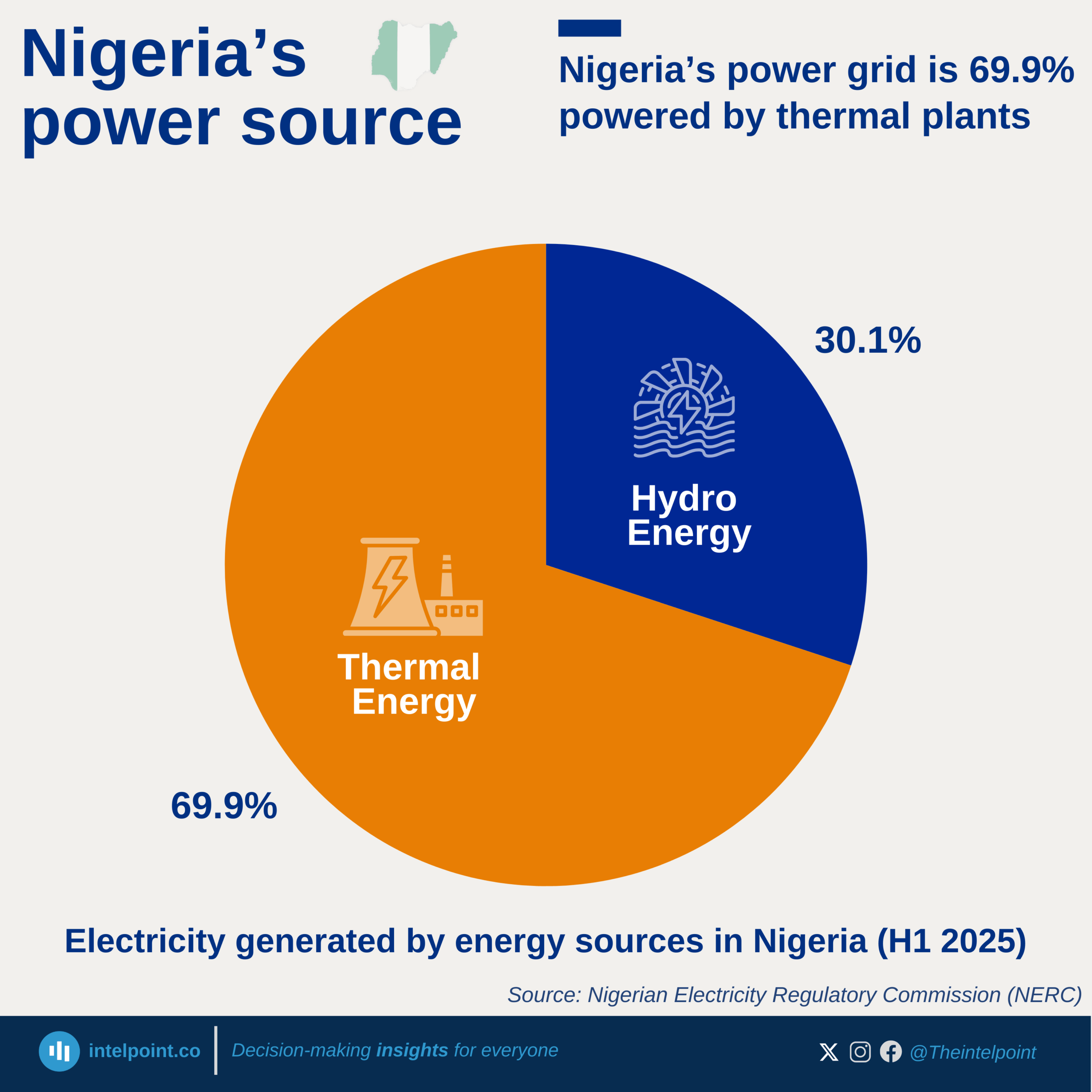
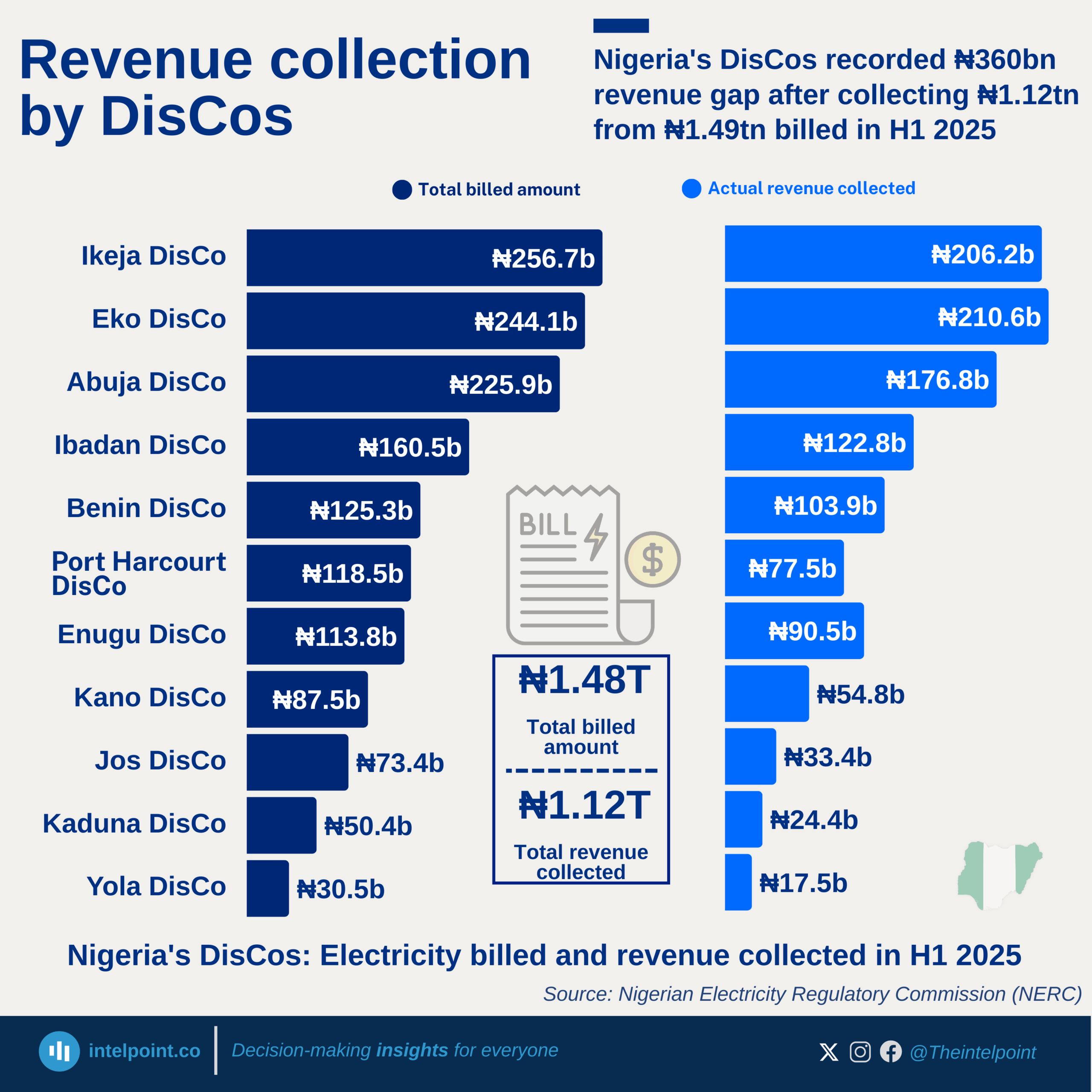
Nigeria’s import profile in Q2 2025 highlights a strong dependence on manufactured goods, which accounted for more than half of the total ₦15.29 trillion import bill. Despite being an oil producer, the country still imported ₦2.79 trillion worth of petroleum products and ₦1.64 trillion worth of crude oil, reflecting deep infrastructure gaps in refining and broader energy security challenges.
The reliance on raw material imports (₦1.72 trillion) also points to underdeveloped domestic industries that could otherwise add value locally. Meanwhile, categories like solid minerals (₦70.9 bn) and energy goods (₦150 mn) contributed little to the overall import basket.
Overall, the data paints a picture of an economy still heavily reliant on external markets for manufactured and refined goods, signalling opportunities for industrial growth, local refining capacity, and raw material processing as pathways to reduce the trade imbalance.