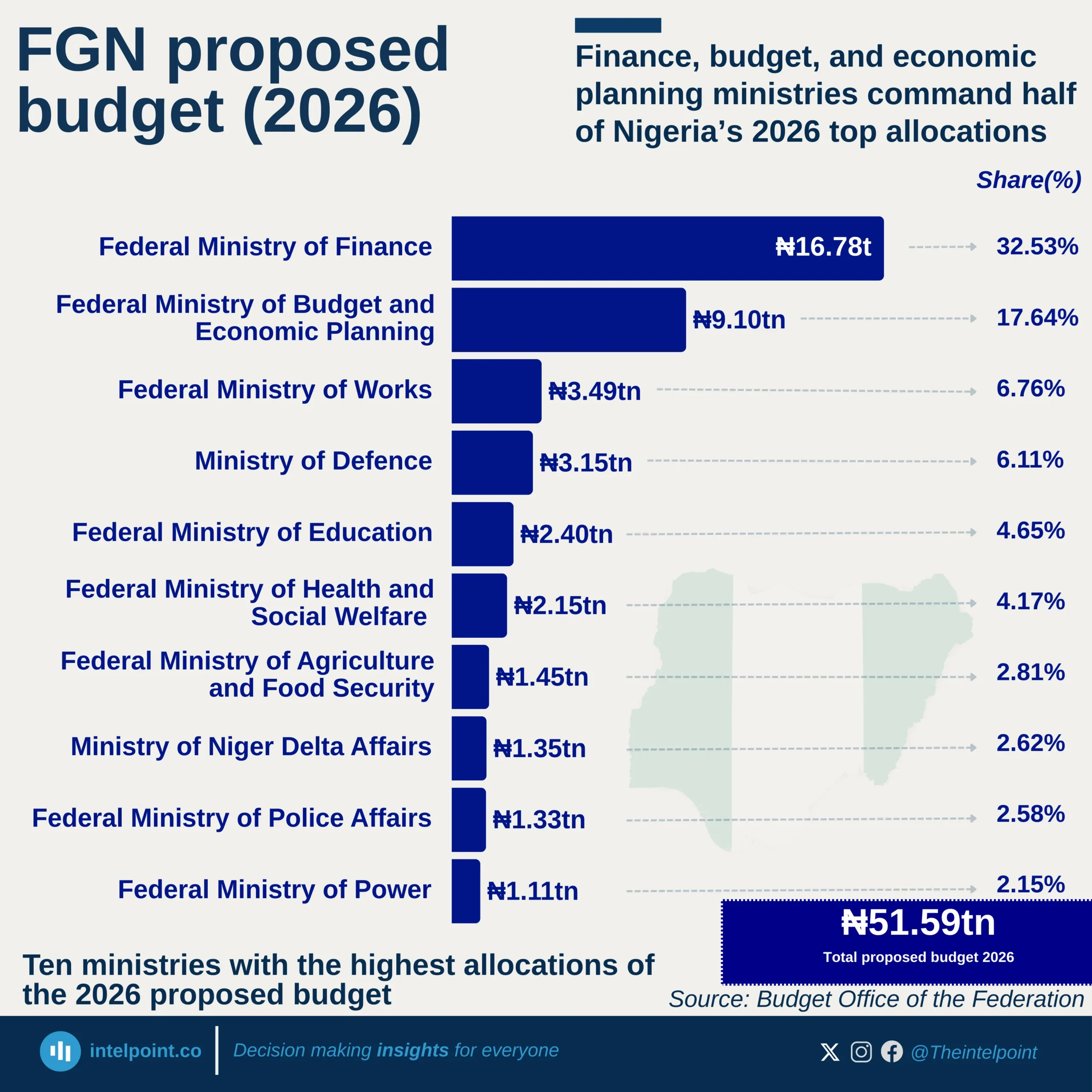
Apple dominates as the most valuable brand in 2025, boasting a staggering $574.6B valuation, surpassing Microsoft by $113.5B. Google follows in third place with $413B, trailing Microsoft by $48.1B, while Amazon secures fourth place with $356.4B, reinforcing its e-commerce dominance. Tech brands collectively account for 88% of the Top 10 brand value, underscoring the sector’s unparalleled influence.
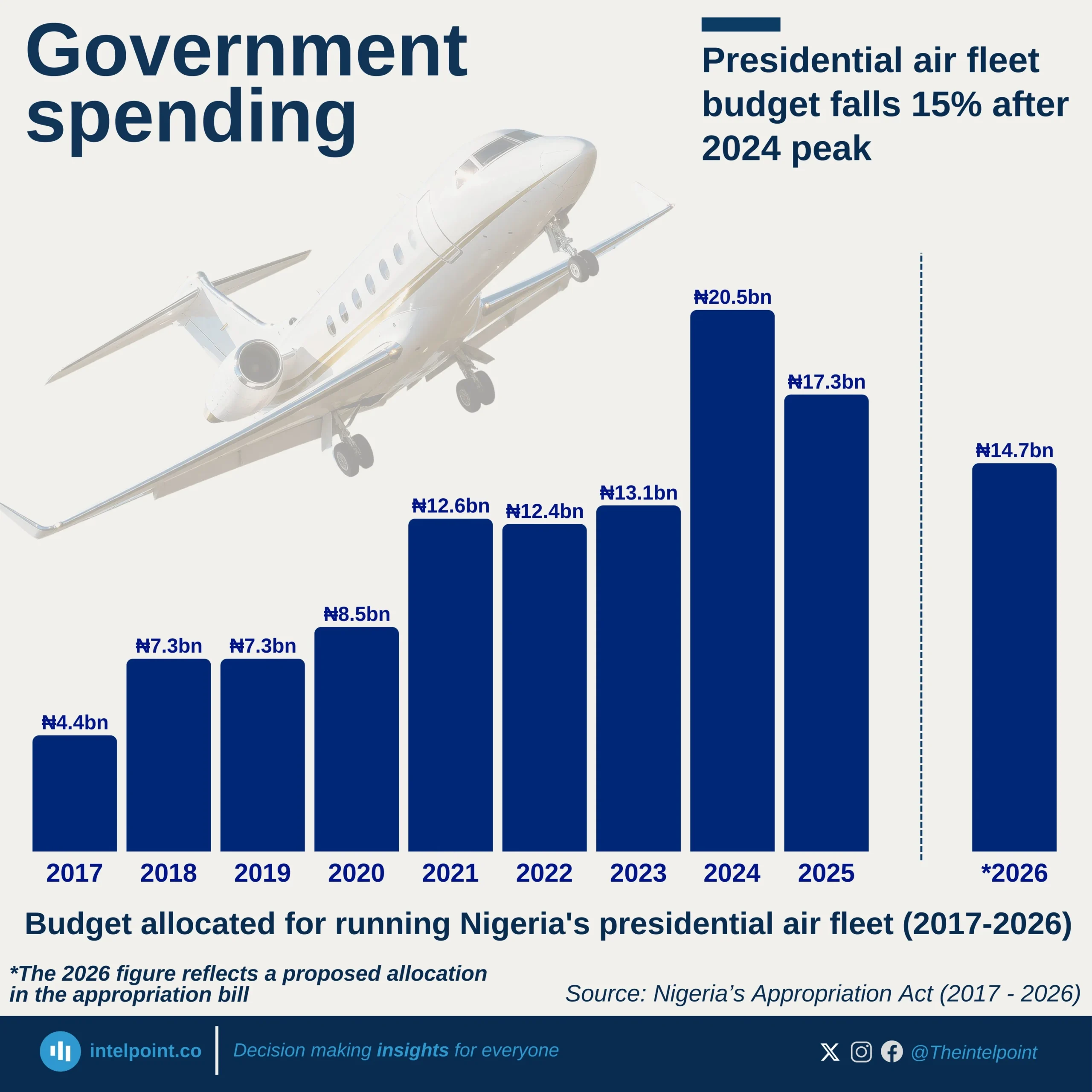
TikTok, now valued at $105.8B, overtakes Facebook at $91.5B in the social media race, marking a significant shift in platform dominance. Instagram, at $79.9B, maintains its position but continues to trail TikTok. Meanwhile, NVIDIA surges to $87.9B, solidifying its role in AI and GPU advancements, while Samsung leads non-U.S. tech brands at $110.6B.
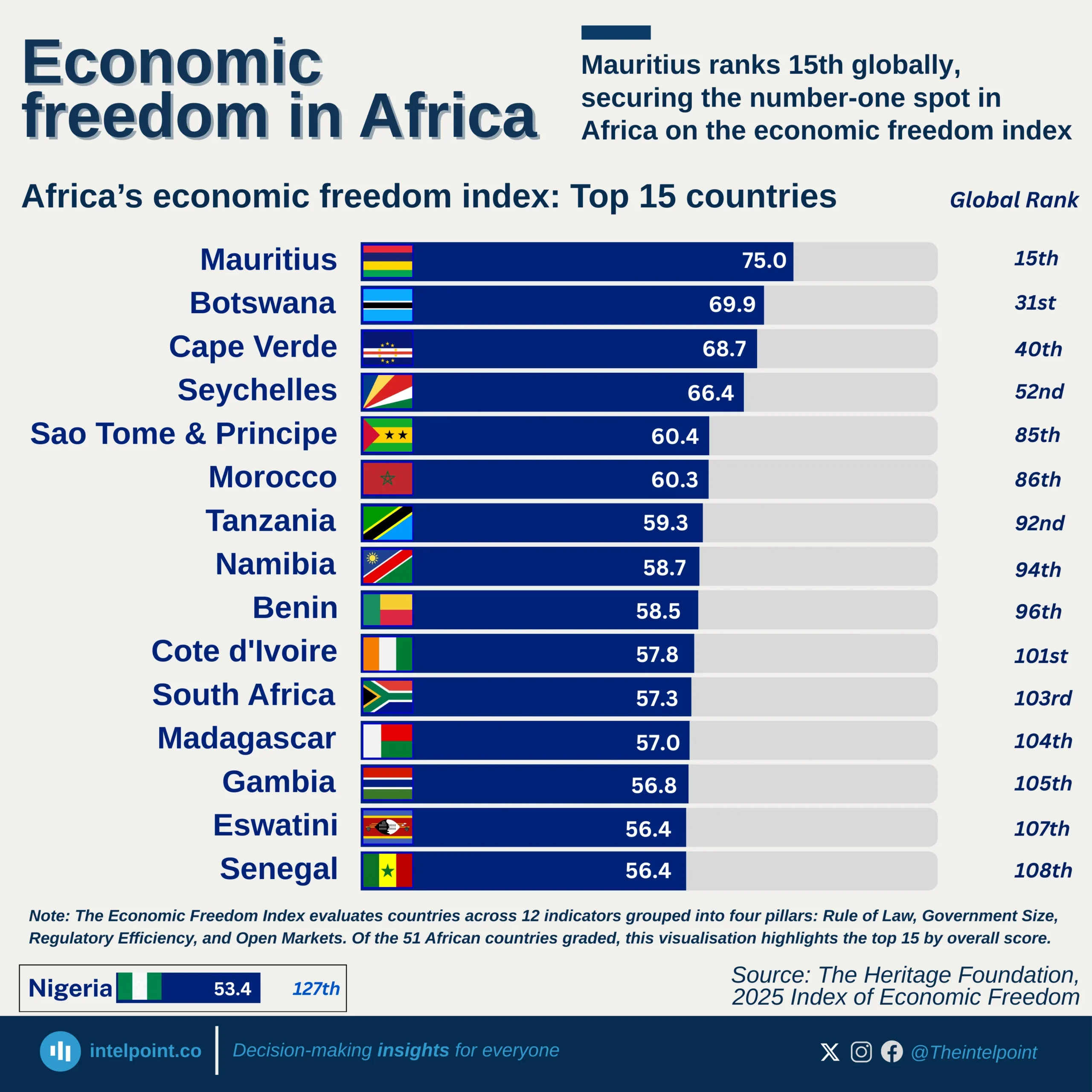
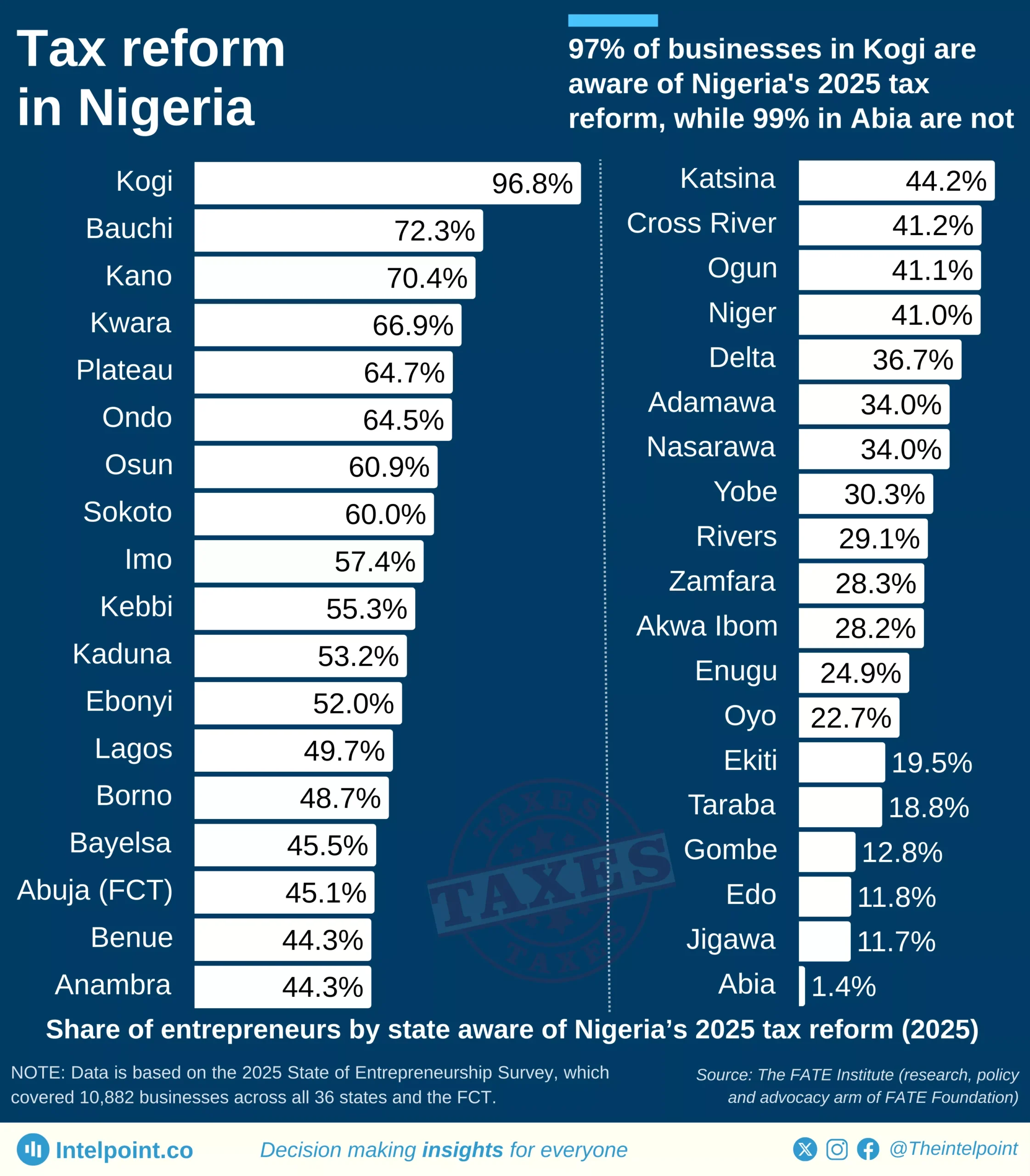
China’s State Grid emerges as the most valuable energy brand at $85.6B, just ahead of T-Mobile at $85.3B. Banking powerhouses from China, including China Construction Bank ($78.4B), ICBC ($78.1B), Agricultural Bank of China ($70.2B), and Bank of China ($63.8B), reinforce Asia’s growing presence in global finance. Oracle, at $57.4B, surpasses Mercedes-Benz ($53B) and AT&T ($52.5B), highlighting the rising strength of enterprise tech. With TikTok’s rise over Facebook, Asian brands gaining ground, and technology dominating global brand value, the landscape of industry leadership continues to evolve.