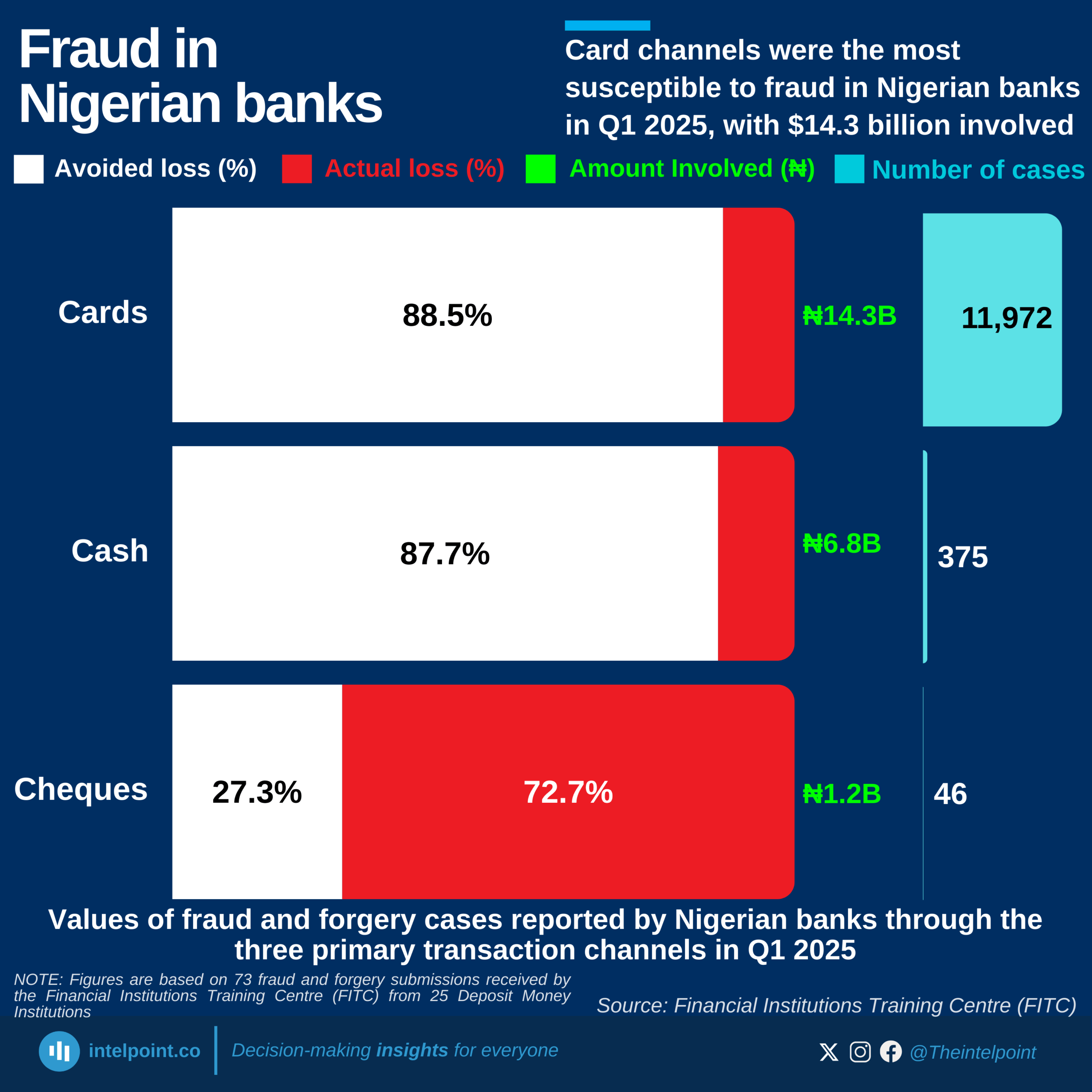
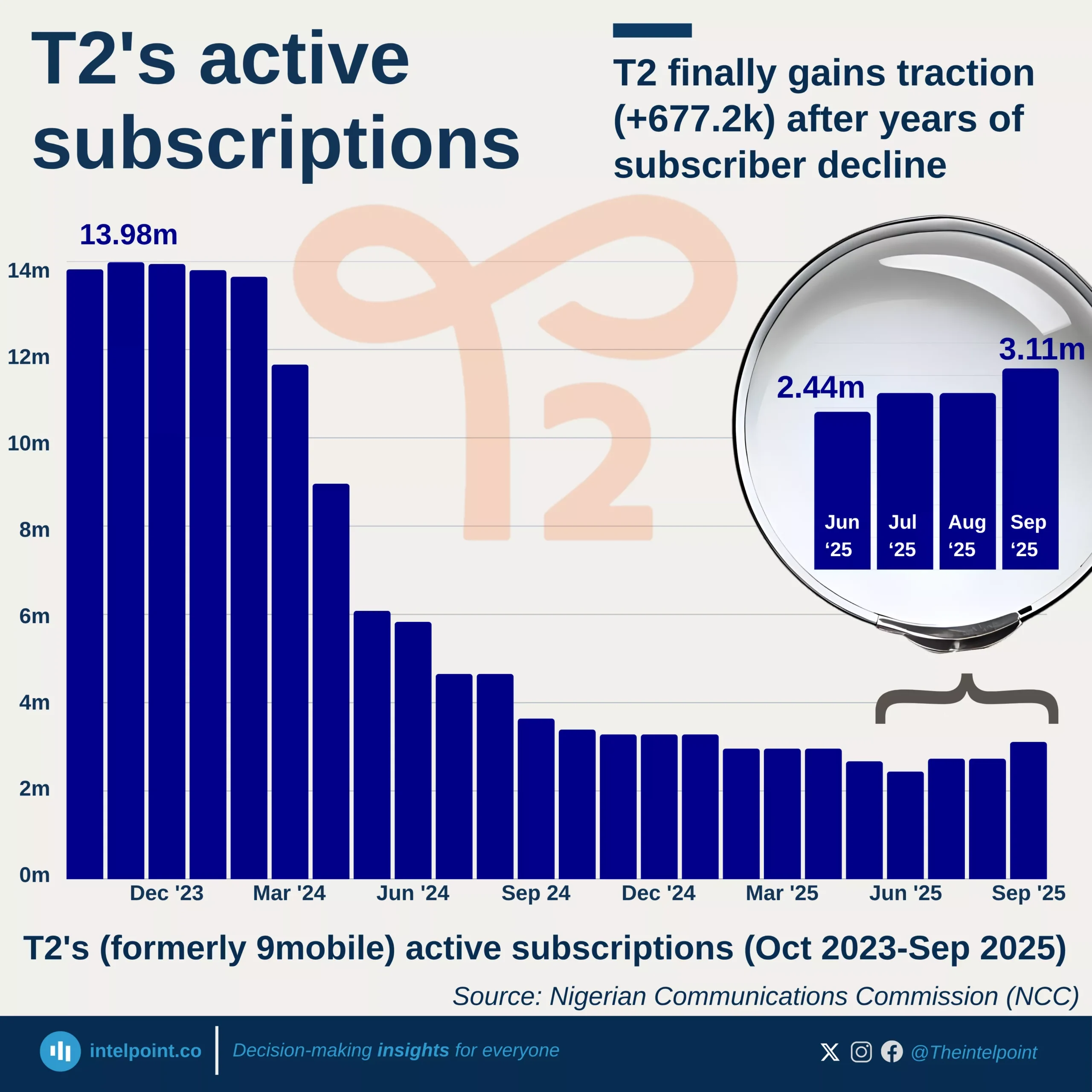
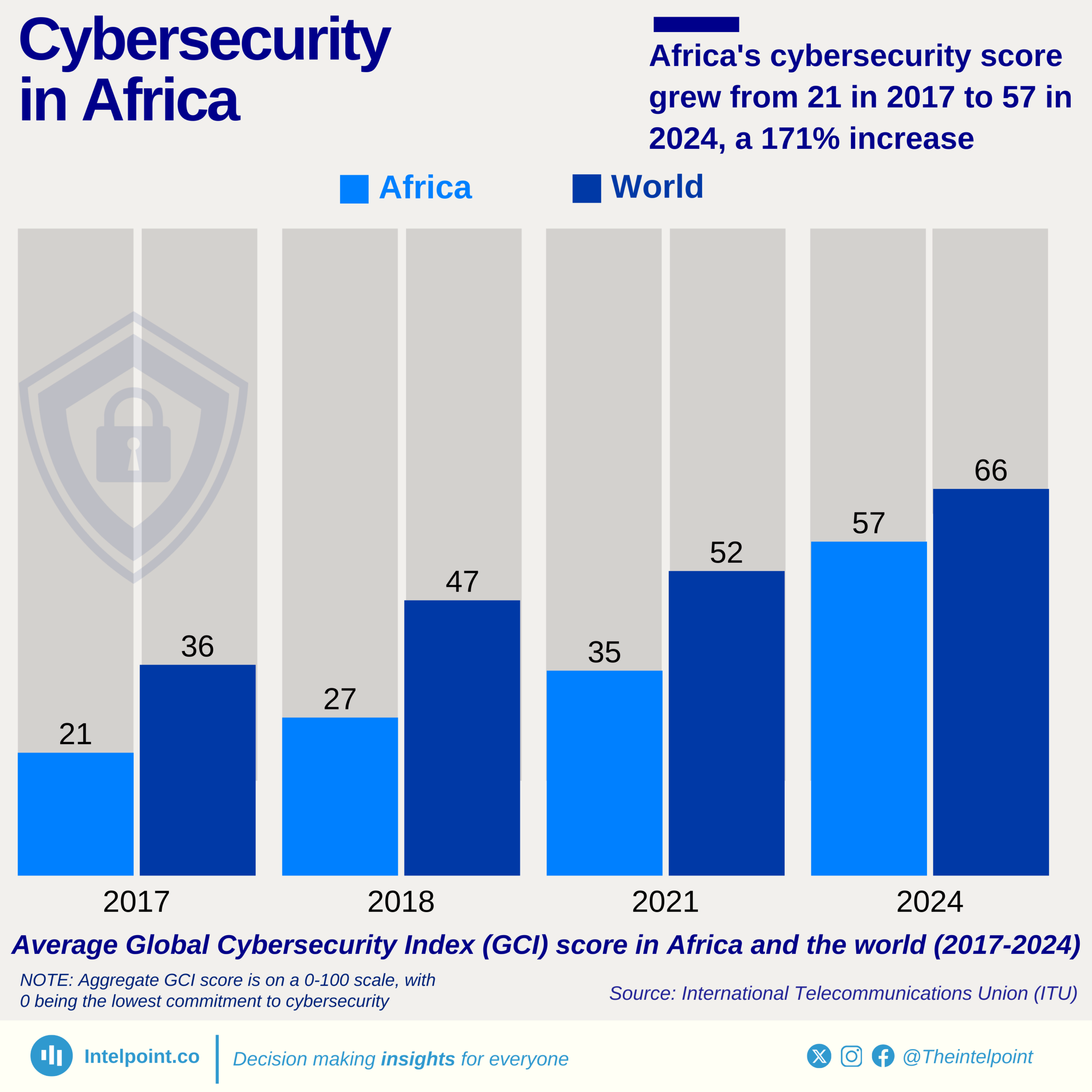
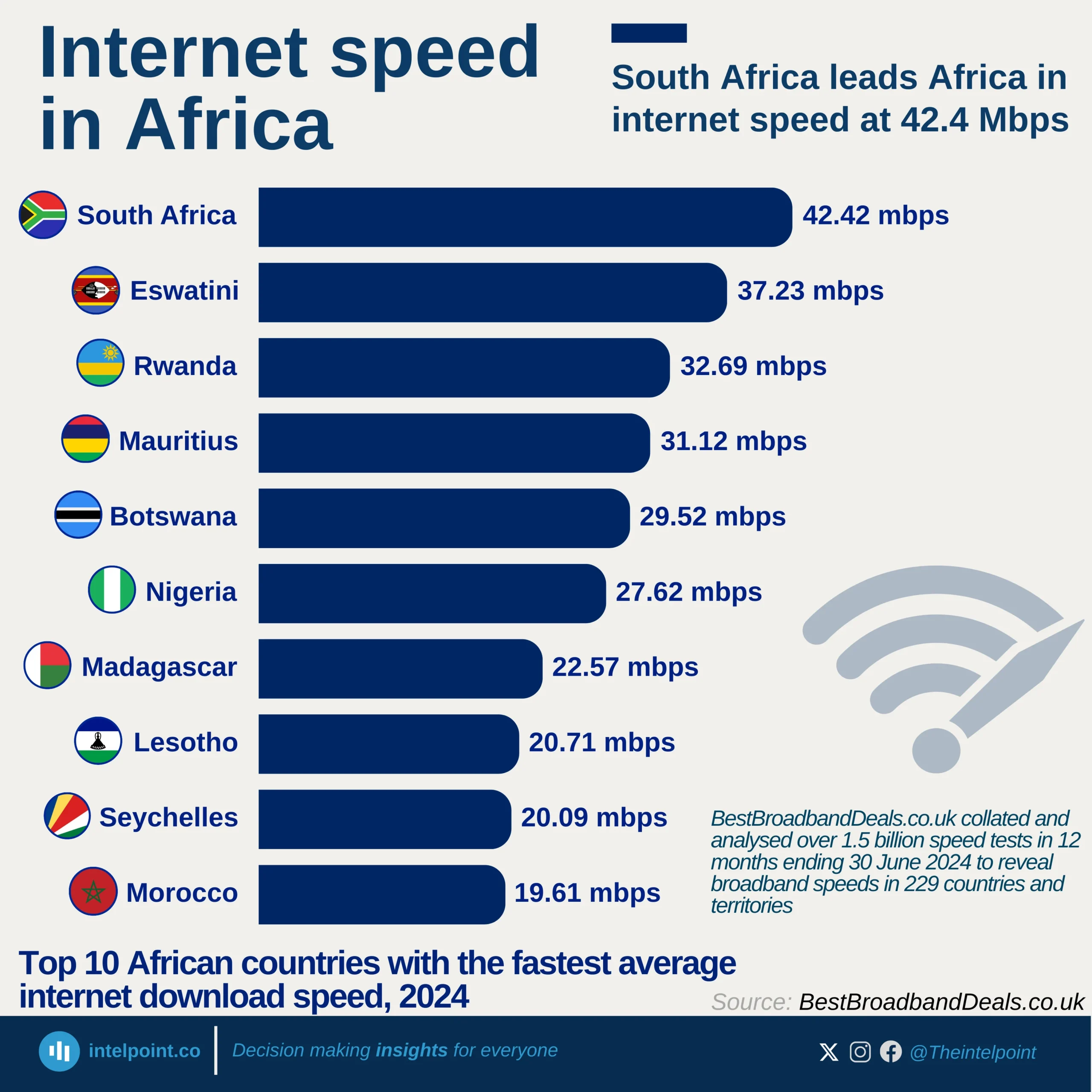
Over the past few years, the information and communications technology industry has been one of Nigeria’s fastest-growing industries. In Q4 2023, it was among the top three contributors to the real GDP with 14%. Between 2015 and 2024, the sector's quarterly GDP hit 15% thrice, ranging between 10.88% and 16.36% from Q1 2020 to Q2 2024.
An observable trend in the past five years of quarterly data indicates that the second quarter of each year consistently recorded much higher contributions than other quarters. In Q2 2023, the sector’s GDP contribution was 16.06%, while the Q2 2024 contribution rose to 16.36%, representing the highest contribution throughout the observed duration. However, in the third quarter of 2024, the contribution dropped to 13.94%, a 2.42% drop from the second quarter of 2024.