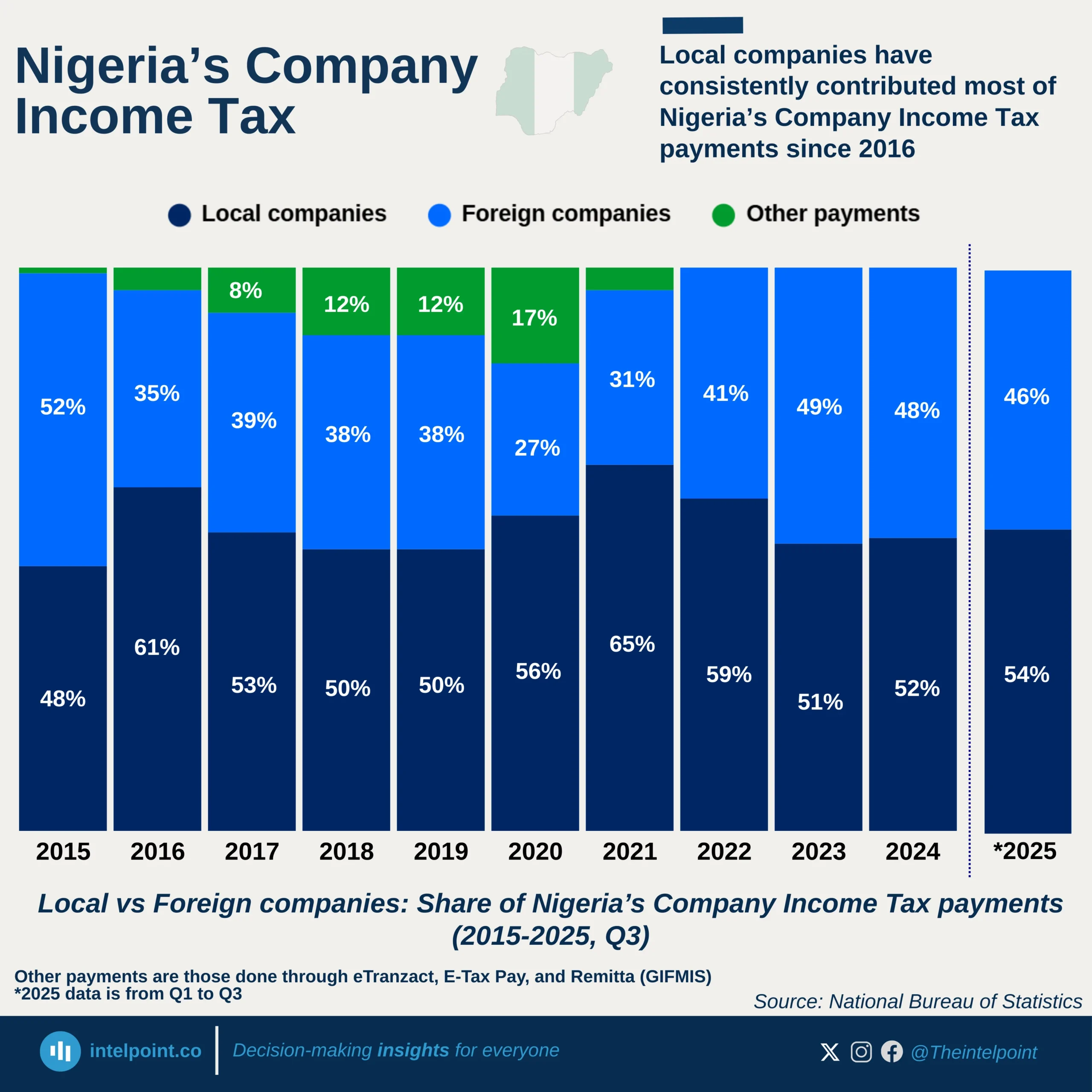
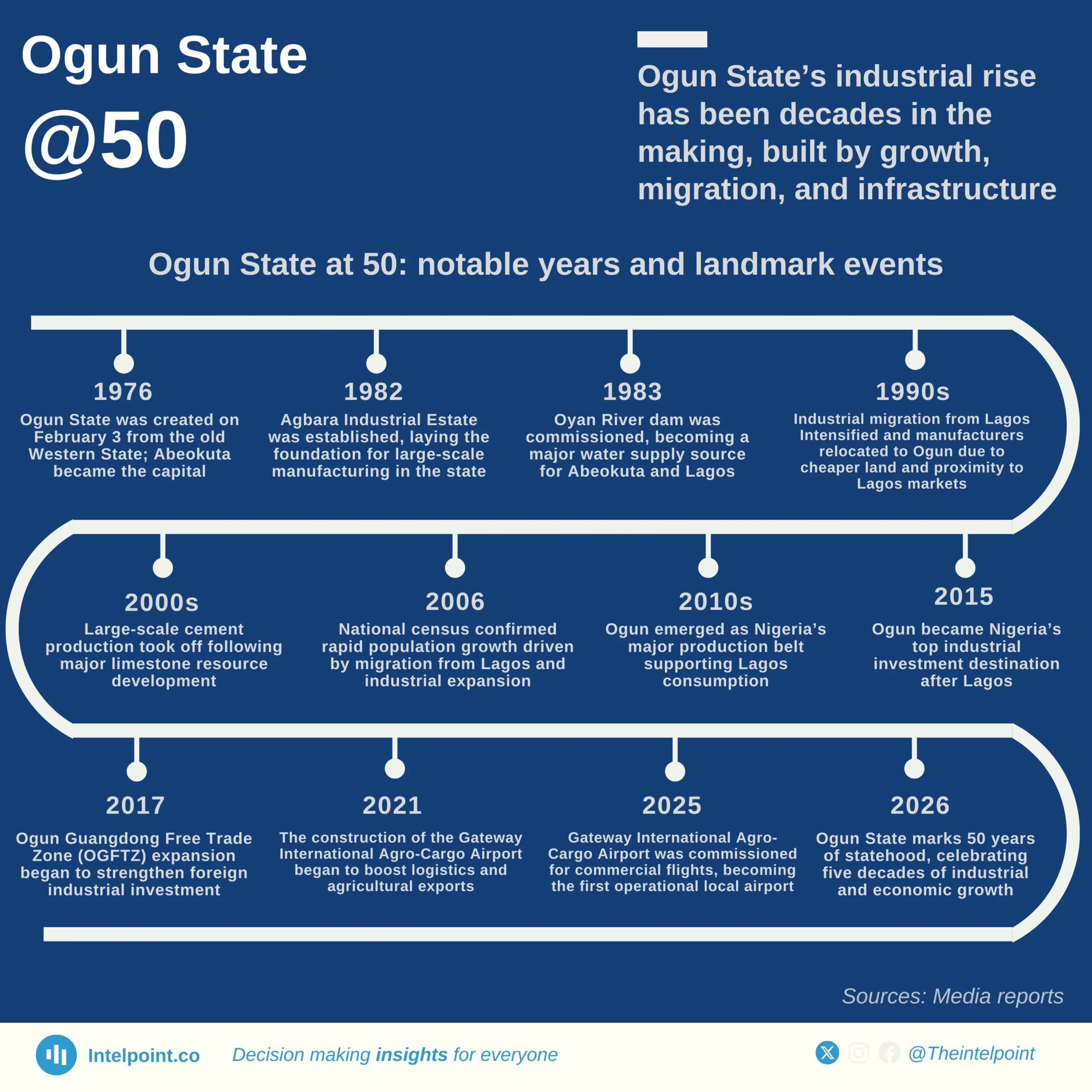
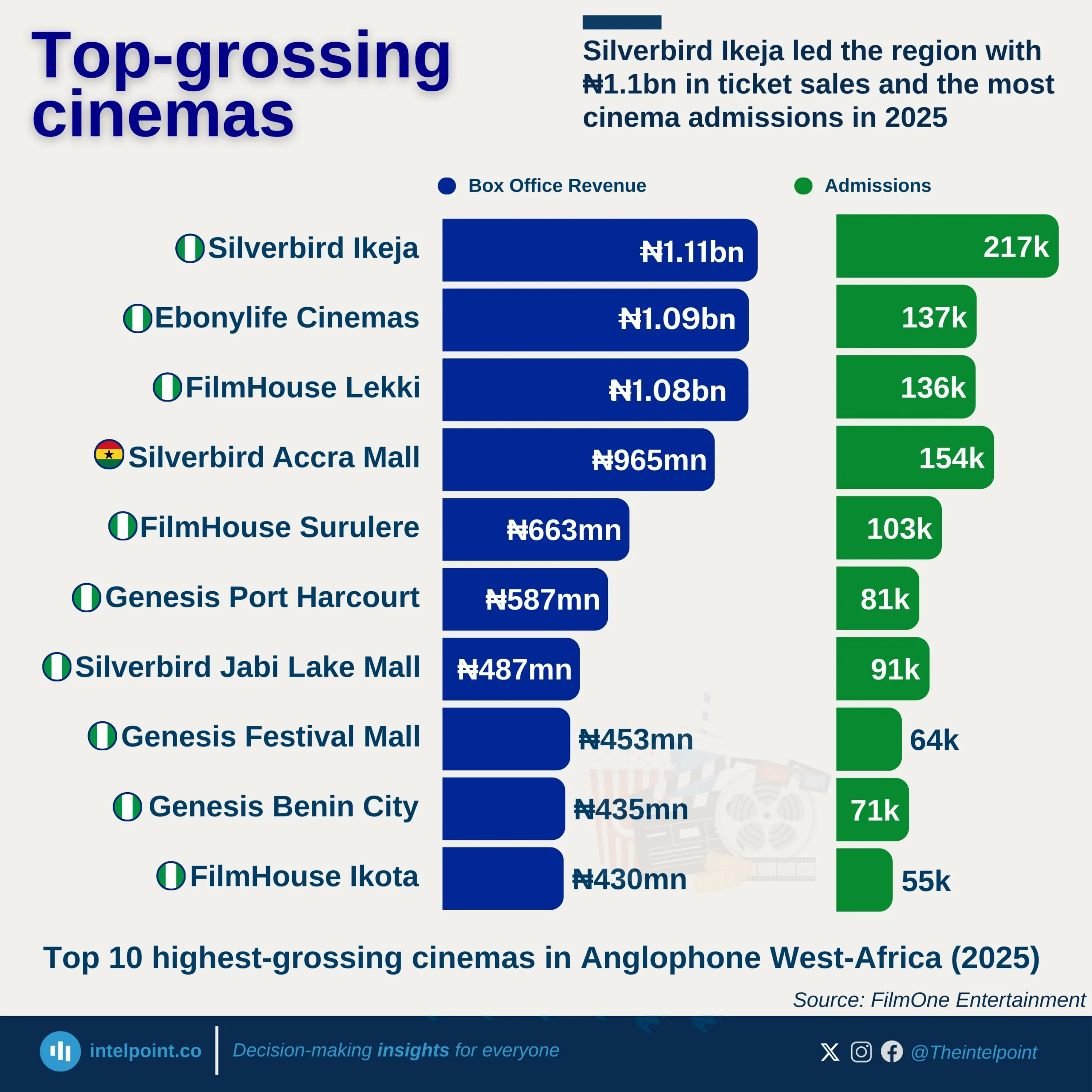
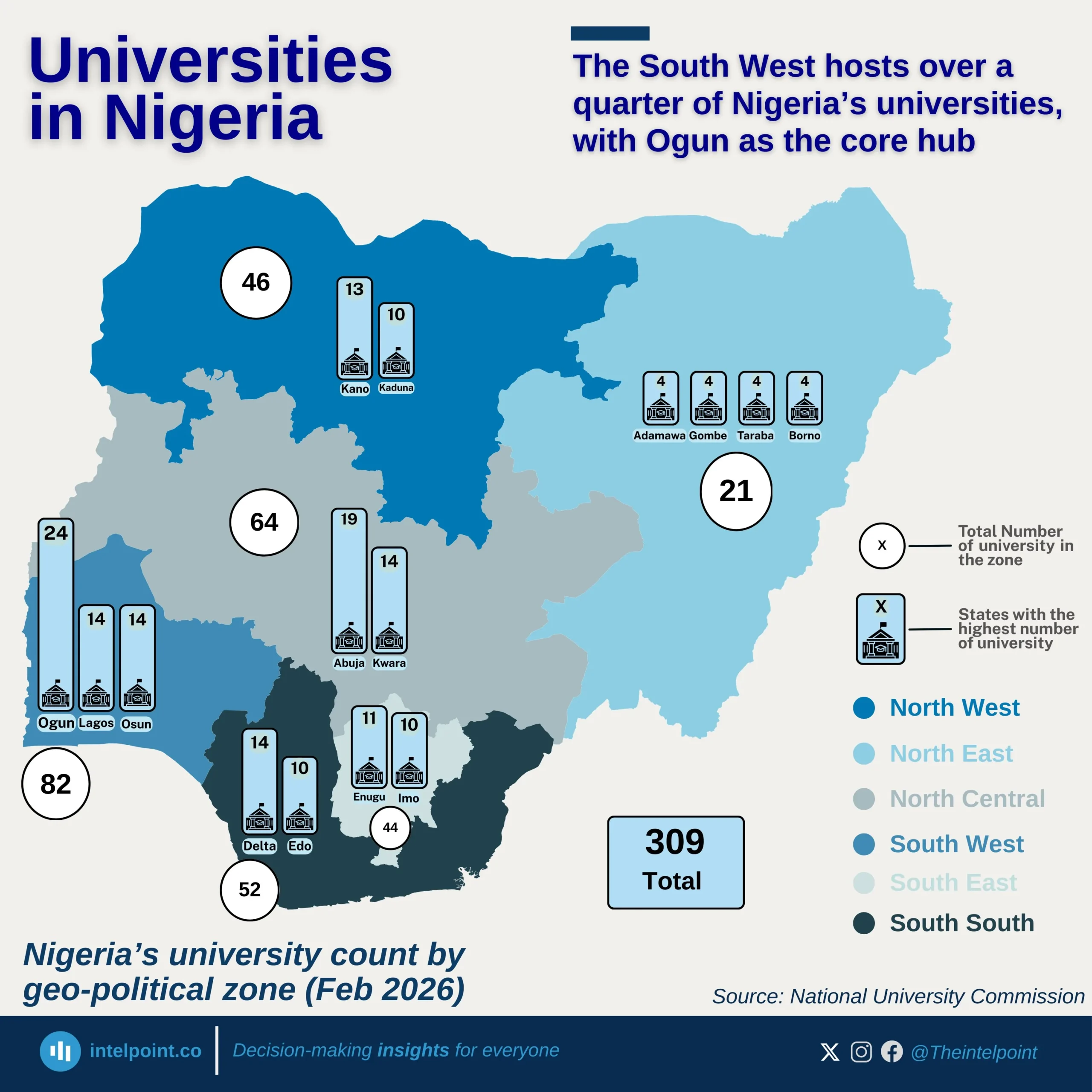
Nigeria’s economy expanded to ₦51.20 trillion in Q2 2025, with trade and agriculture leading as the top contributors. Trade added ₦9.36 trillion (18.28%), while crop production contributed ₦9.11 trillion (17.8%), together accounting for over one-third of national output. Real estate (₦6.55 trillion, 12.8%) and telecommunications (₦4.71 trillion, 9.2%) showcased the rising dominance of services, driven by urban growth and digital adoption.
In sharp contrast, crude petroleum and natural gas contributed only ₦2.07 trillion (4.05%), underscoring oil’s diminishing role in GDP despite its importance for exports and revenue. Other sectors, such as livestock, construction, food processing, finance, and public administration, collectively added over ₦8 trillion, signalling a broader diversification of the economy.