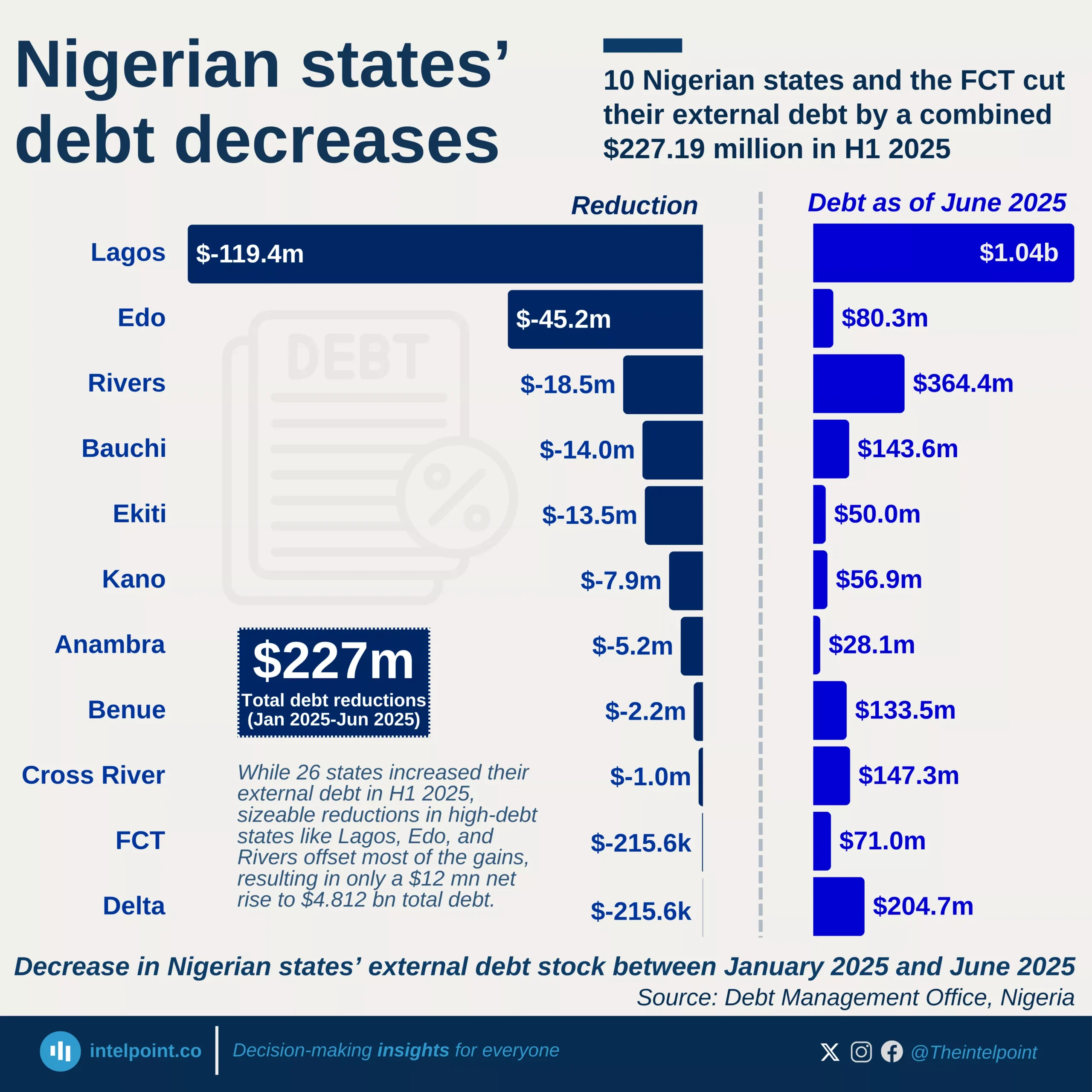
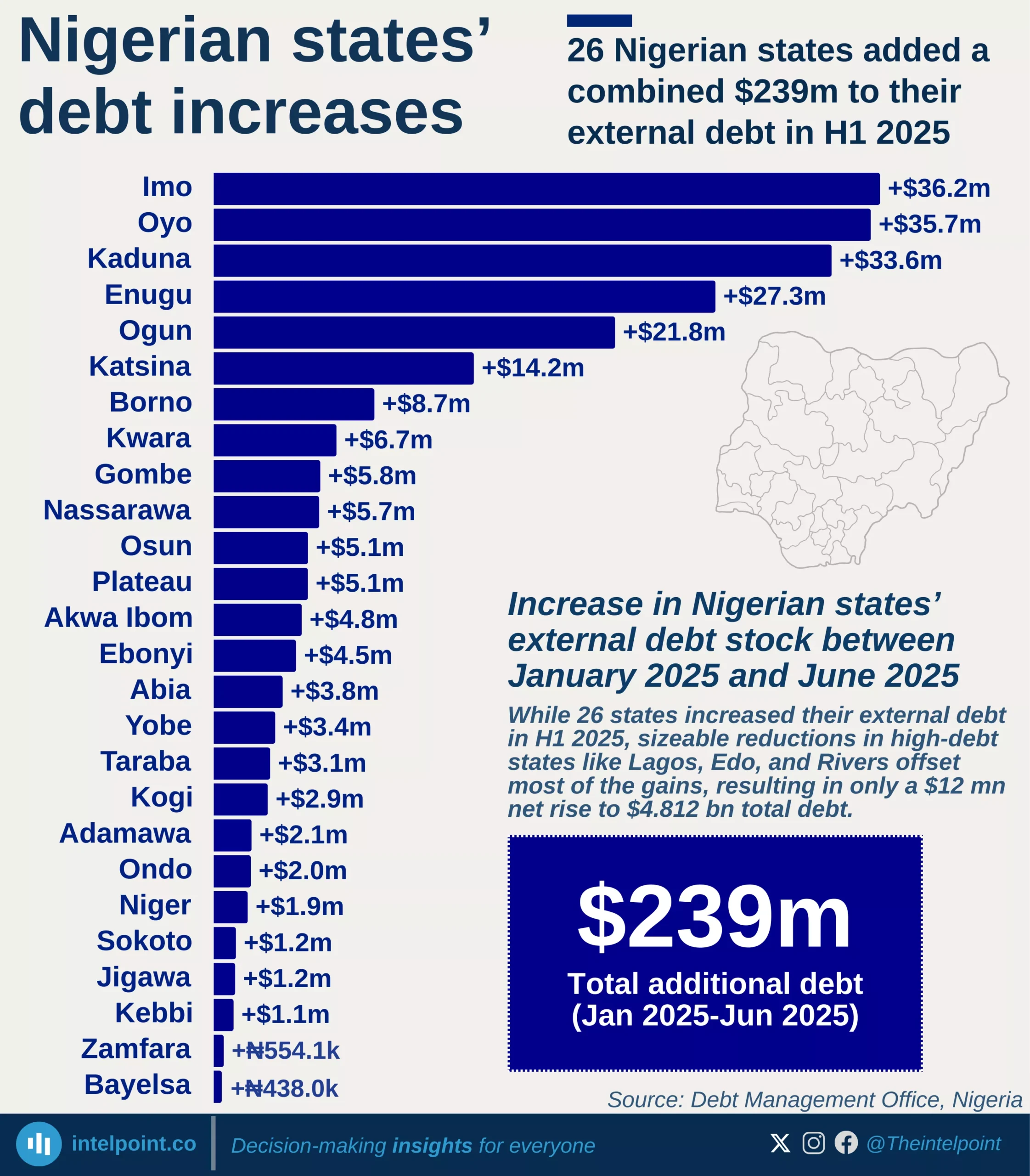
External debt across Nigerian states reveals significant financial disparities and fiscal reliance, with just three states—Lagos, Kaduna, and Edo—accounting for over $2.18 billion, nearly half of the total $4.80 billion external debt stock of all 36 states and the FCT as of December 31, 2024. Lagos alone, at $1.17 billion, owes nearly a quarter of the total, and more than double what any other state owes. These figures highlight the disproportionately large borrowing footprints of a few subnational governments compared to others.
The striking debt imbalance tells more than just a financial story—it reveals the extent to which some states rely on external financing, likely for infrastructure, health, education, or economic development projects. Lagos, as Nigeria’s commercial hub, likely incurs such high foreign obligations to fund its urban infrastructure and transportation network. Still, whether these debts translate into tangible economic returns remains a key question for future analysis.
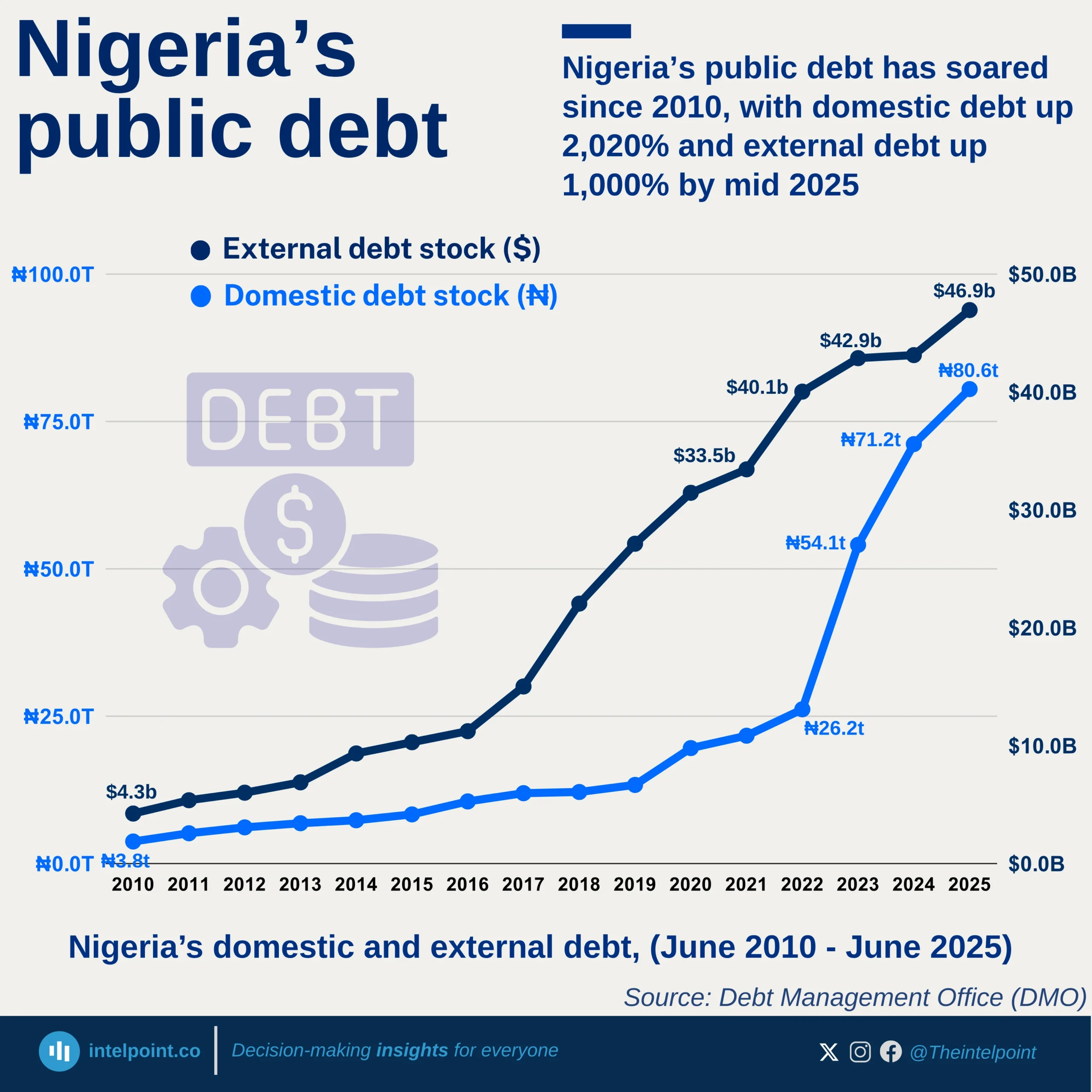
The federal government’s external debt, however, remains significantly larger at $40.98 billion, emphasising that states, though active, hold only a fraction of Nigeria’s total public debt obligations.