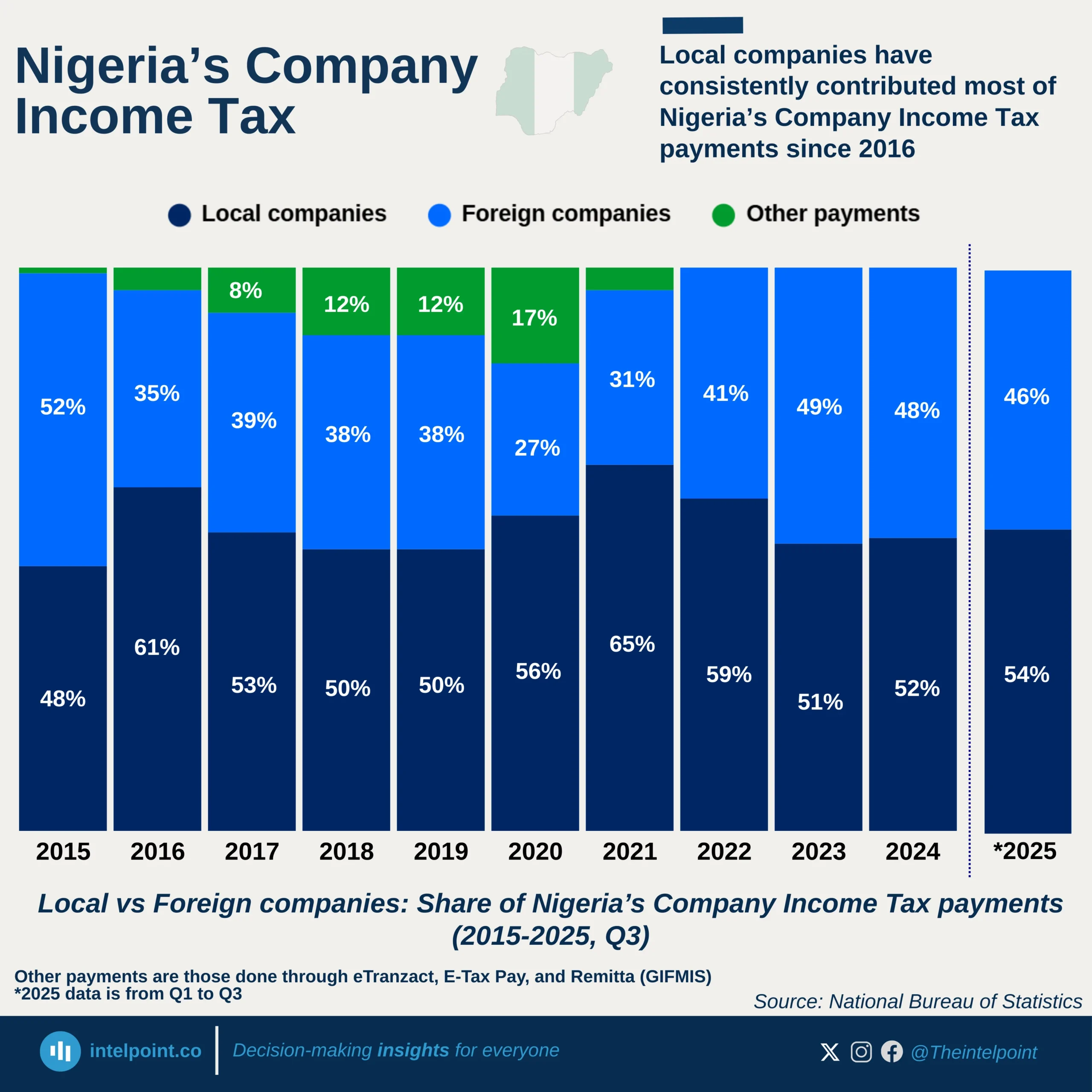
Nigeria's VAT system creates a deep financial imbalance across its regions. The South-West, despite remitting more than half of the nation’s VAT revenue (₦341.38B), receives only 29% of what it pays. Similarly, the South-South remitted significantly (₦121.84B), but most of it came from Rivers (₦90.21B), which barely got anything back.
Meanwhile, the three Northern zones collectively remitted ₦66.18B but received ₦161.11B, a staggering 240% return. This means that the North got back more than twice what it remitted, while the South-West and South-South are the biggest net losers.
Perhaps the most striking disparity is in the South-East, which remitted just ₦10.94B but received ₦39.13B, a return of over 357%. Similarly, the North-East enjoyed a 312% return, receiving ₦46.68B despite remitting just ₦14.94B.
This VAT redistribution formula favours lower-contributing regions while heavily taxing high-revenue states, raising critical questions about fairness and sustainability in Nigeria's revenue-sharing model.