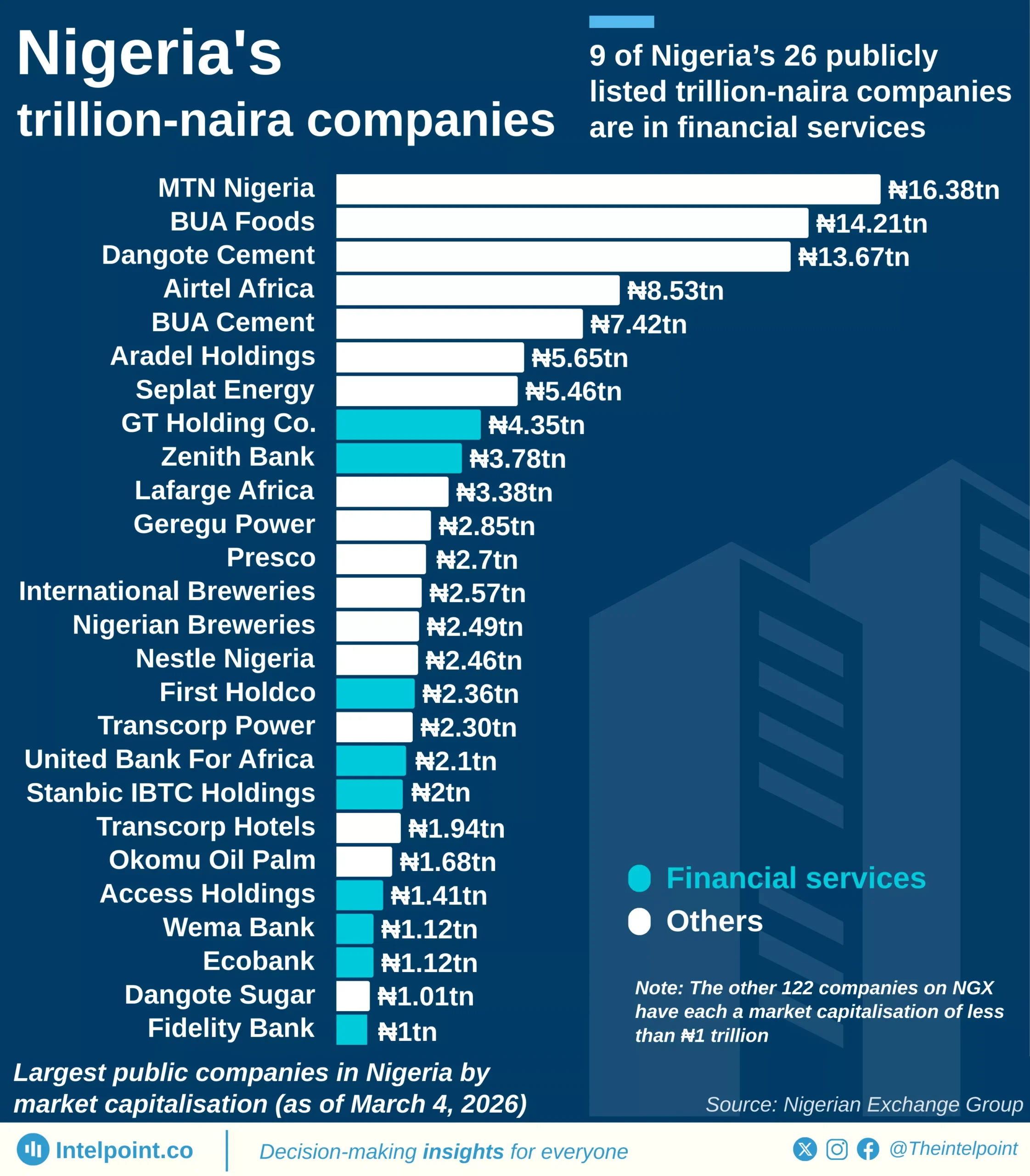
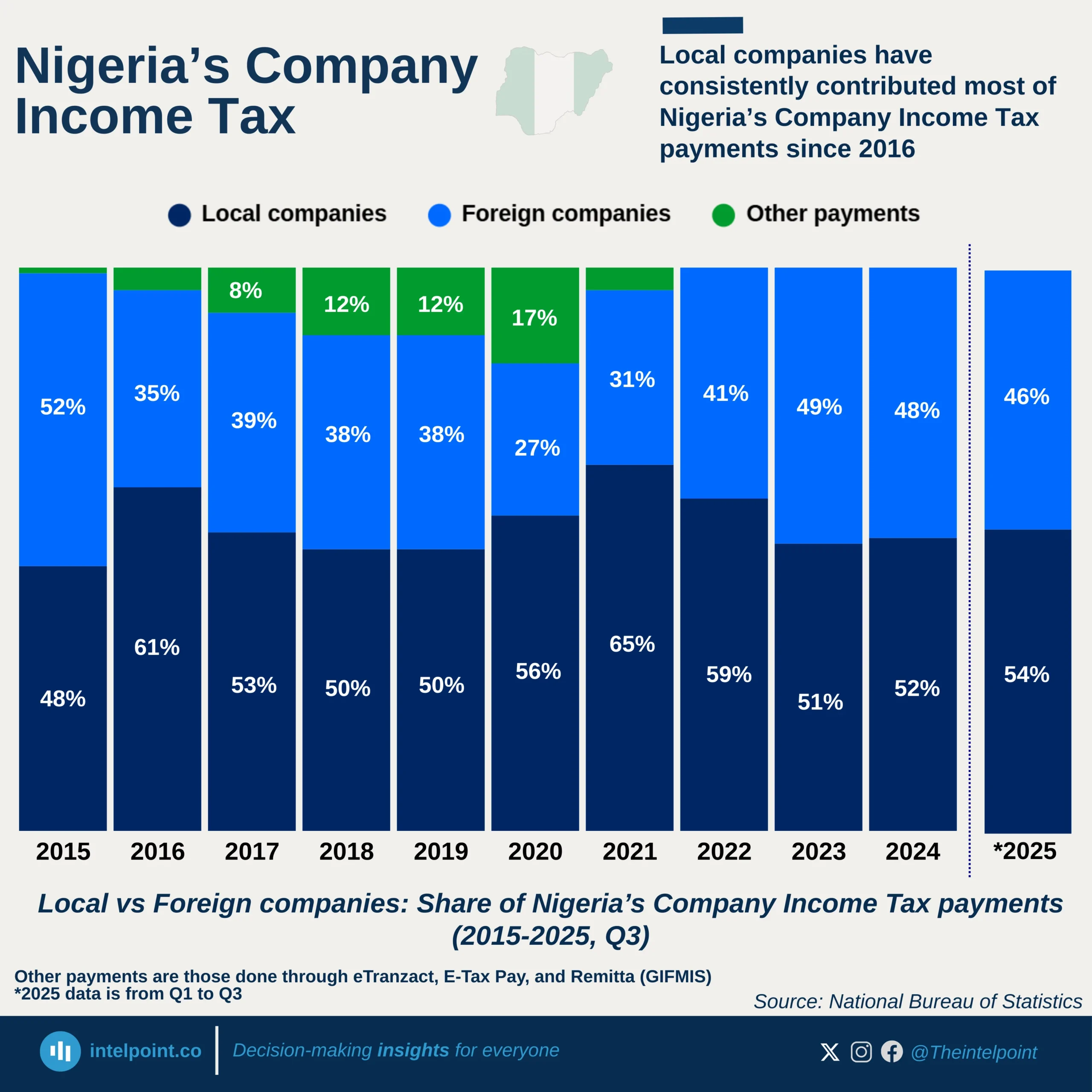
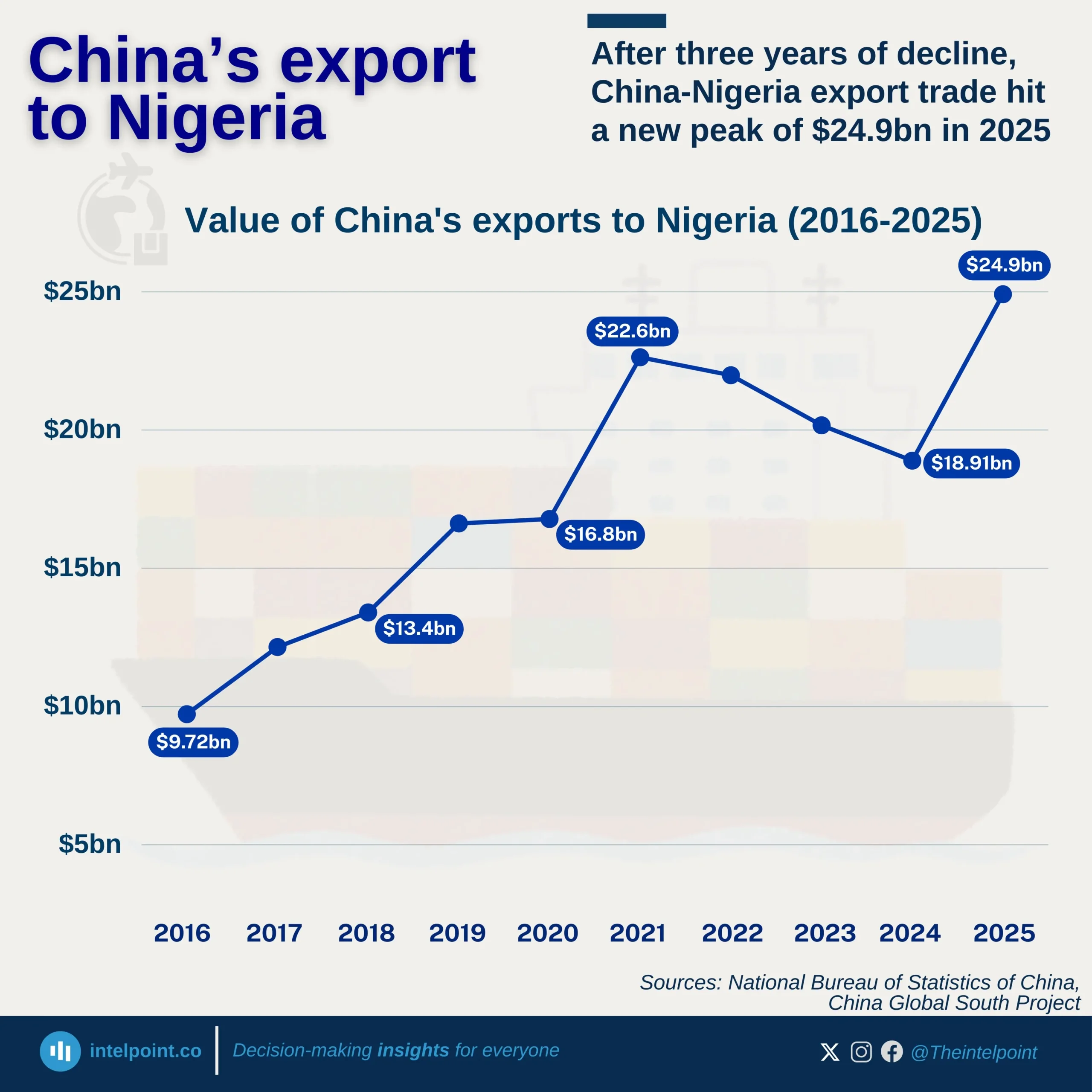
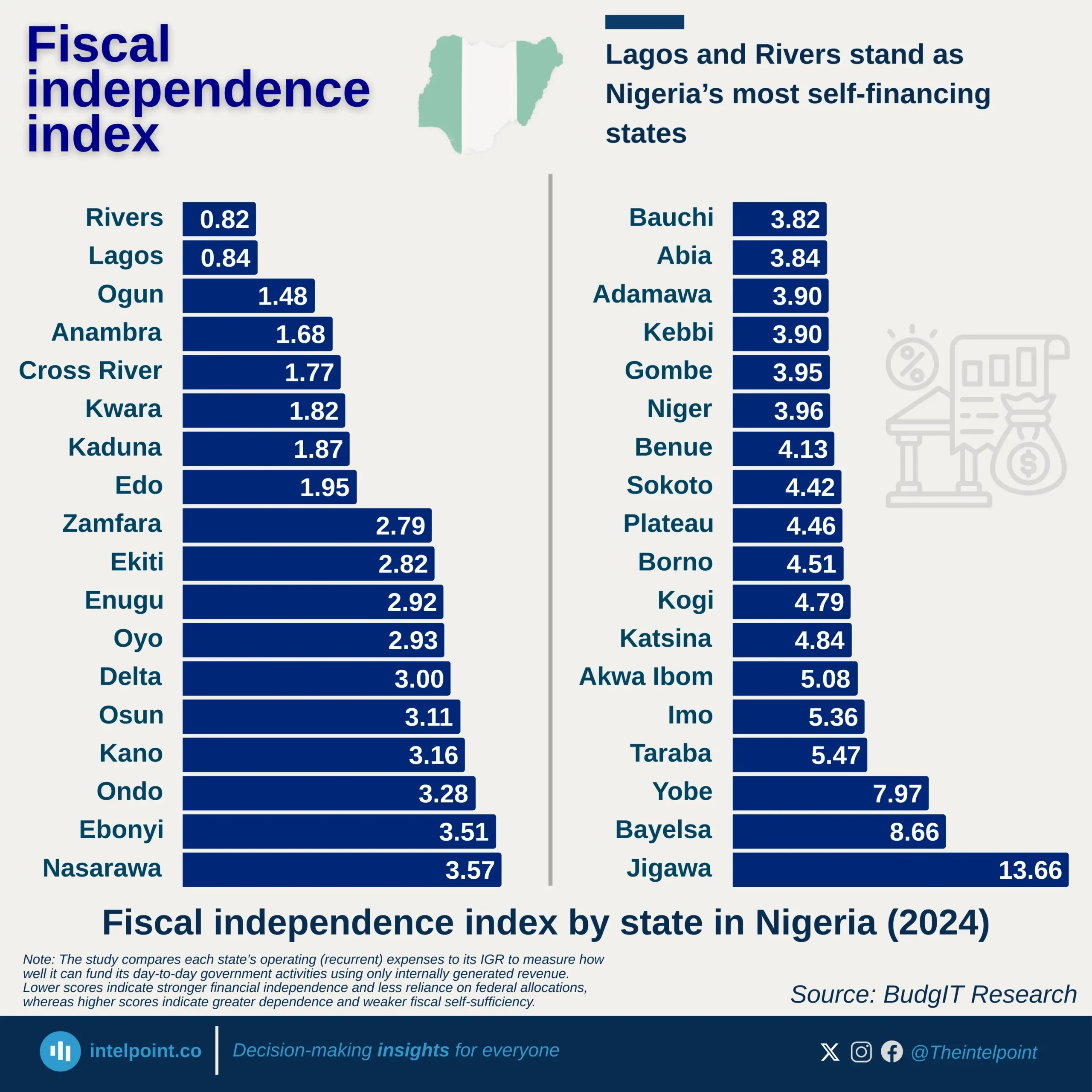
From 2005-2024, Egypt exported a total of $46.007 billion in digital services. During the same period, imports were much higher, amounting to $101.98 billion, resulting in a substantial trade deficit of $55.973 billion. In 2005, Egypt’s exports in digital services stood at just $1.91 billion. By 2024, exports had more than doubled to $4.03 billion, reflecting upward momentum. However, imports in 2024 alone was $8.31 billion, more than twice the export value. This ratio illustrates Egypt’s heavy reliance on foreign digital solutions and platforms.
The rising demand for imports reflects the strength of Egypt’s domestic digital consumption. Yet, the slower pace of export growth highlights structural weaknesses in the competitiveness of local providers. The trade deficit of $55.973 billion represents a significant outflow of value over two decades. This imbalance raises concerns about Egypt’s ability to capture value in the global digital economy.