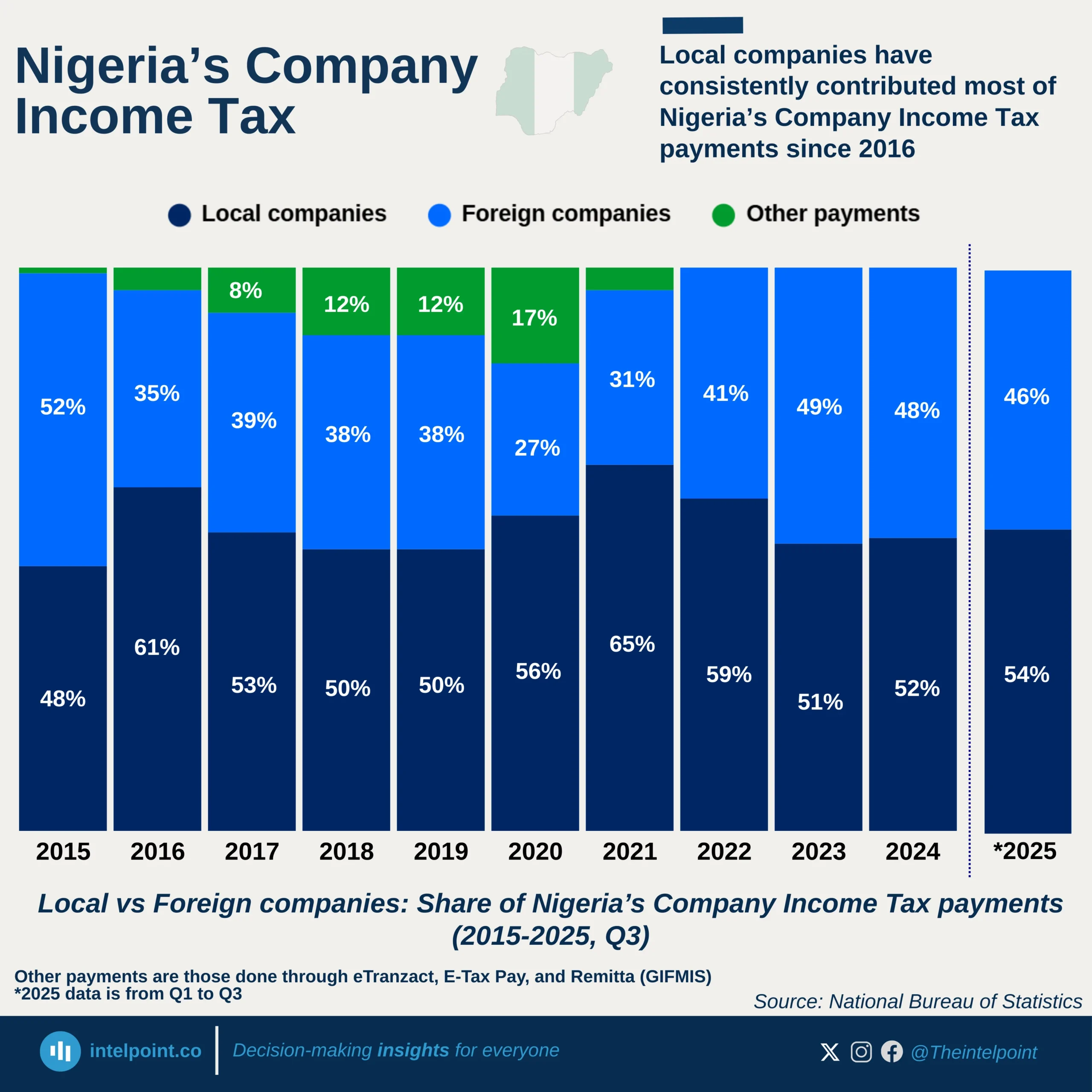
In the first quarter of 2025, Nigeria's total trade value reached a significant milestone of ₦36.03 trillion, reflecting the country’s continued engagement in global commerce. This figure comprises ₦20.60 trillion in exports and ₦15.43 trillion in imports, showcasing a trade surplus of ₦5.17 trillion, a positive indicator of stronger outbound trade compared to inbound. Nigeria's international trade dynamics reflect a strong reliance on commodity exports and imported manufactured goods. The country’s export activity was most heavily concentrated with India, receiving ₦2.84 trillion in goods, mostly attributed to crude oil exports, which continue to underpin Nigeria's trade economy. Following India are the Netherlands, the United States, France, and Spain, which reflect Nigeria’s enduring trade relationships with Western economies, especially in energy.
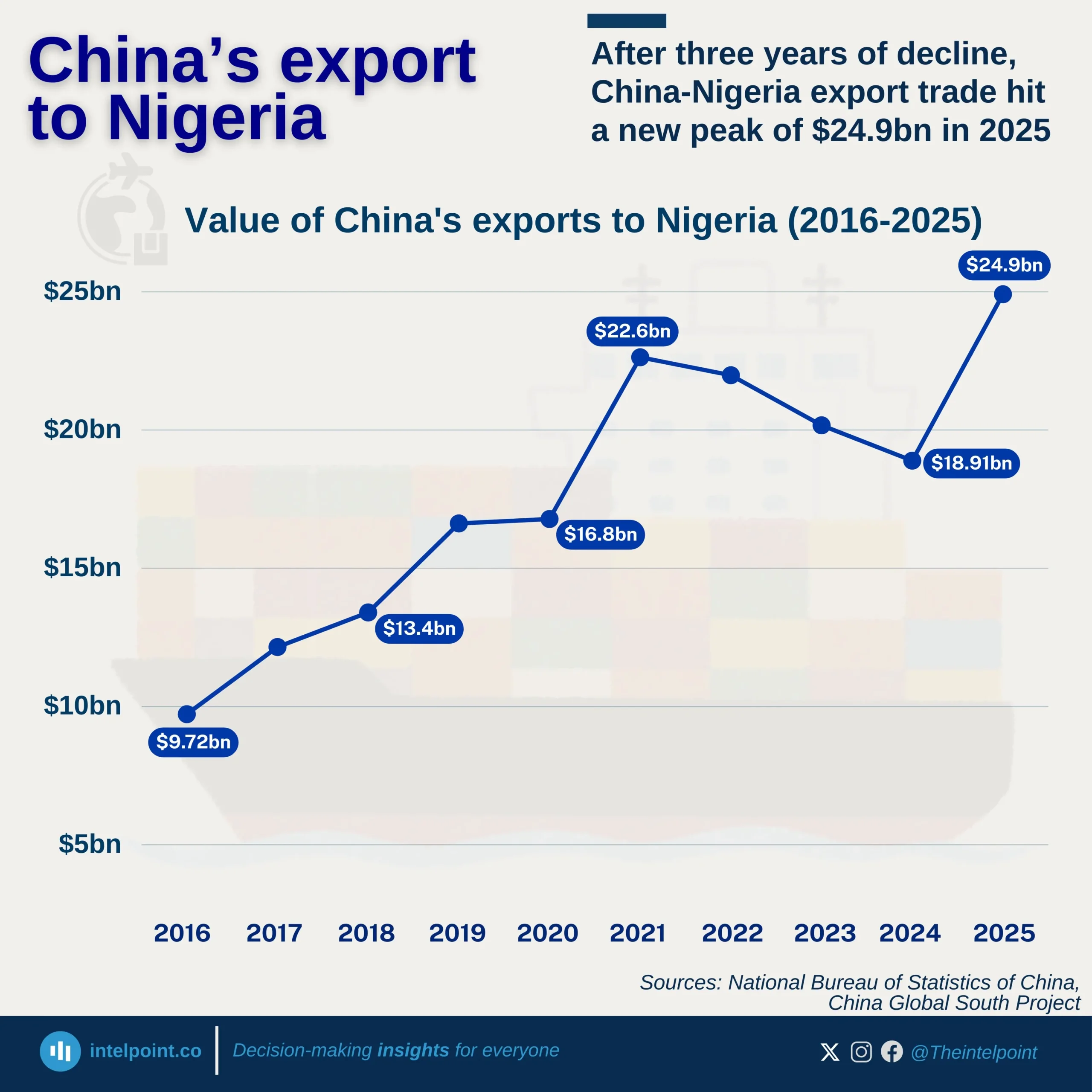
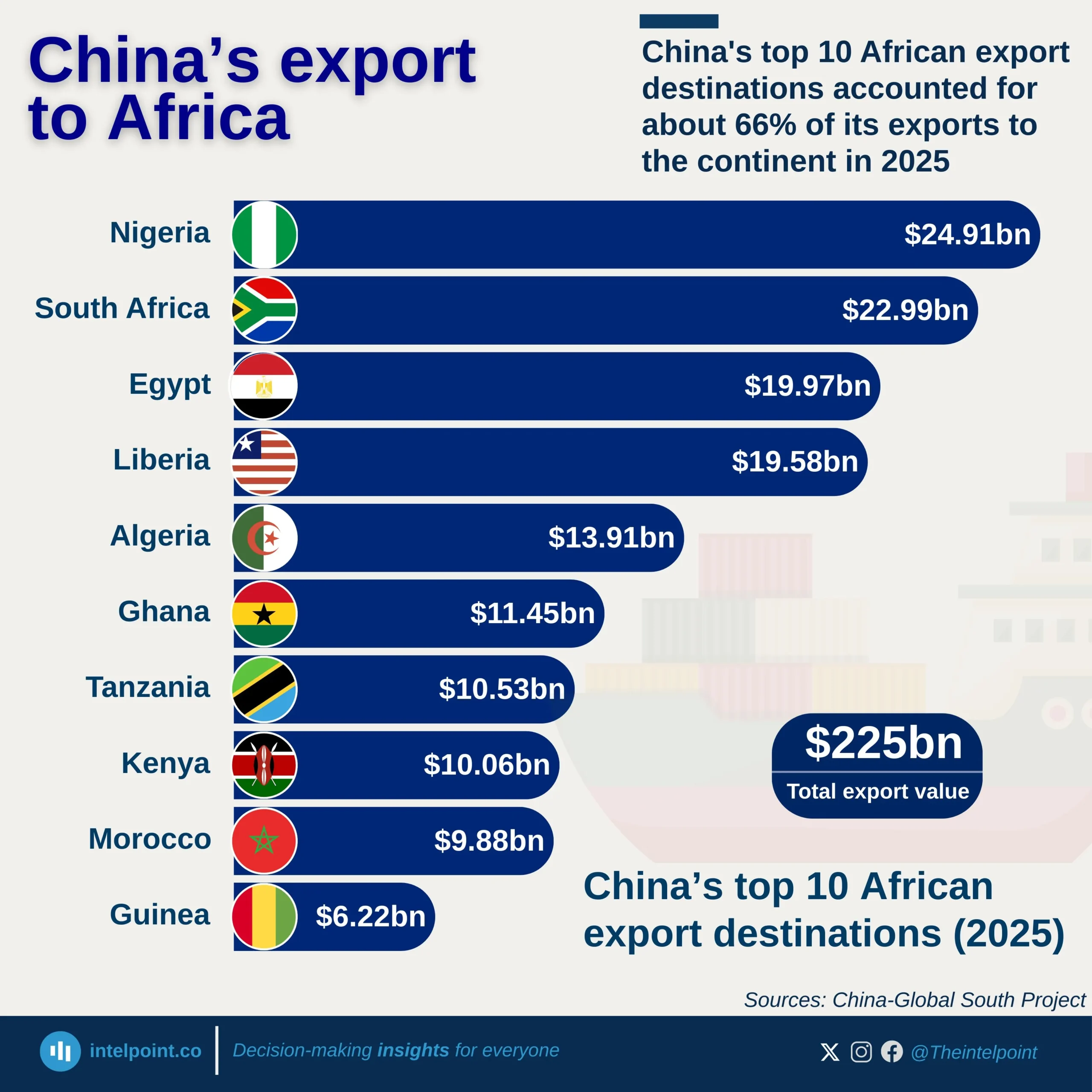
On the import side, China's dominance is notable, with ₦4.66 trillion in imports flowing into Nigeria. This is nearly three times the volume imported from India (₦1.71T), the second-largest source. China’s position illustrates its role as Nigeria’s primary supplier of machinery, electronics, and industrial goods. Other key import sources include the United States, Netherlands, and UAE, all of which maintain significant commercial ties.
Interestingly, the United States appears on both the top export and import lists, indicating a well-rounded trade engagement, rather than being skewed toward either inflow or outflow. This bilateral balance could be beneficial for both economies and may reflect growing diversification in traded products beyond oil.
While European countries dominate Nigeria’s export destinations, only the Netherlands appears among the top import sources. This might signal that Europe values Nigeria more as a supplier than as a buyer, maintaining a trade surplus.