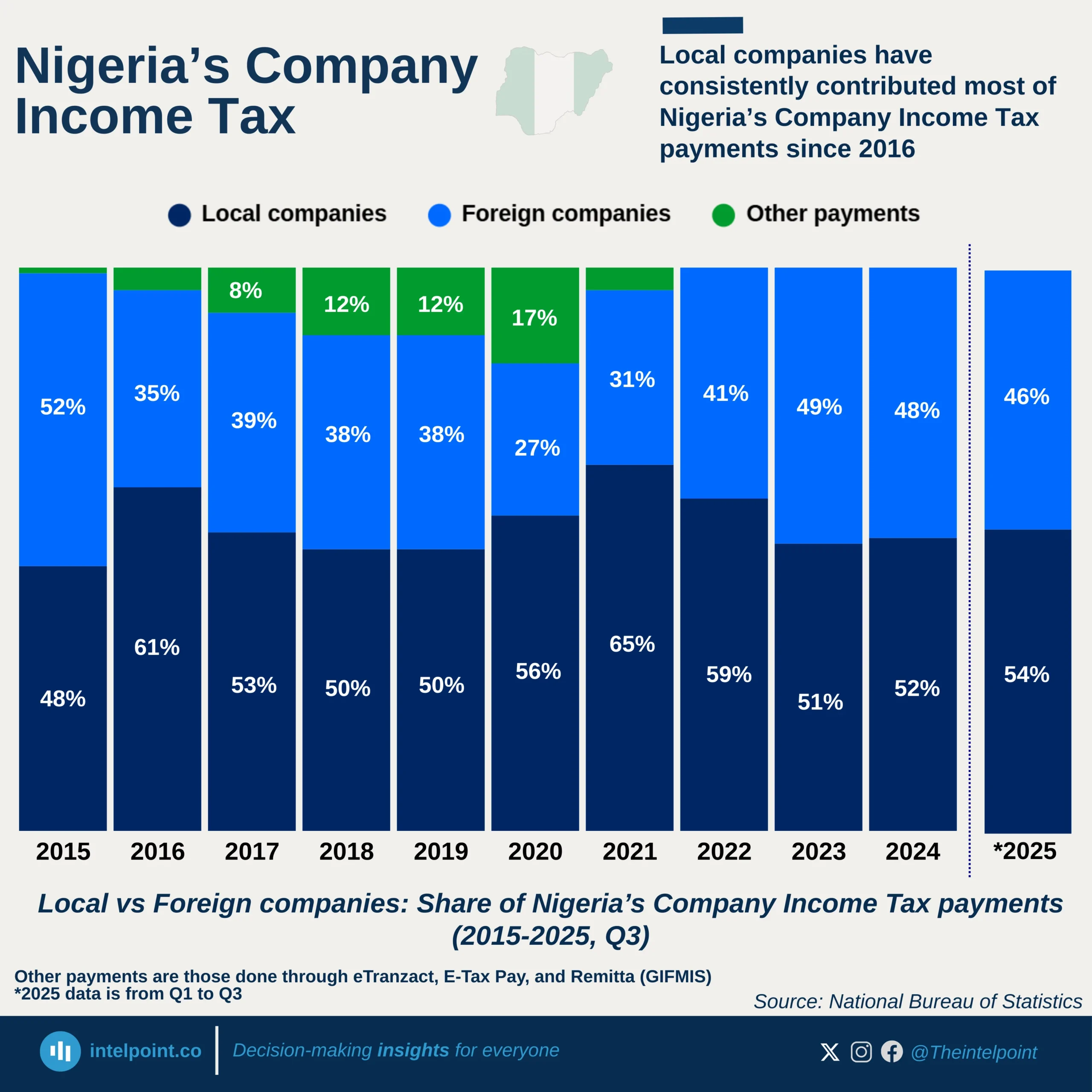
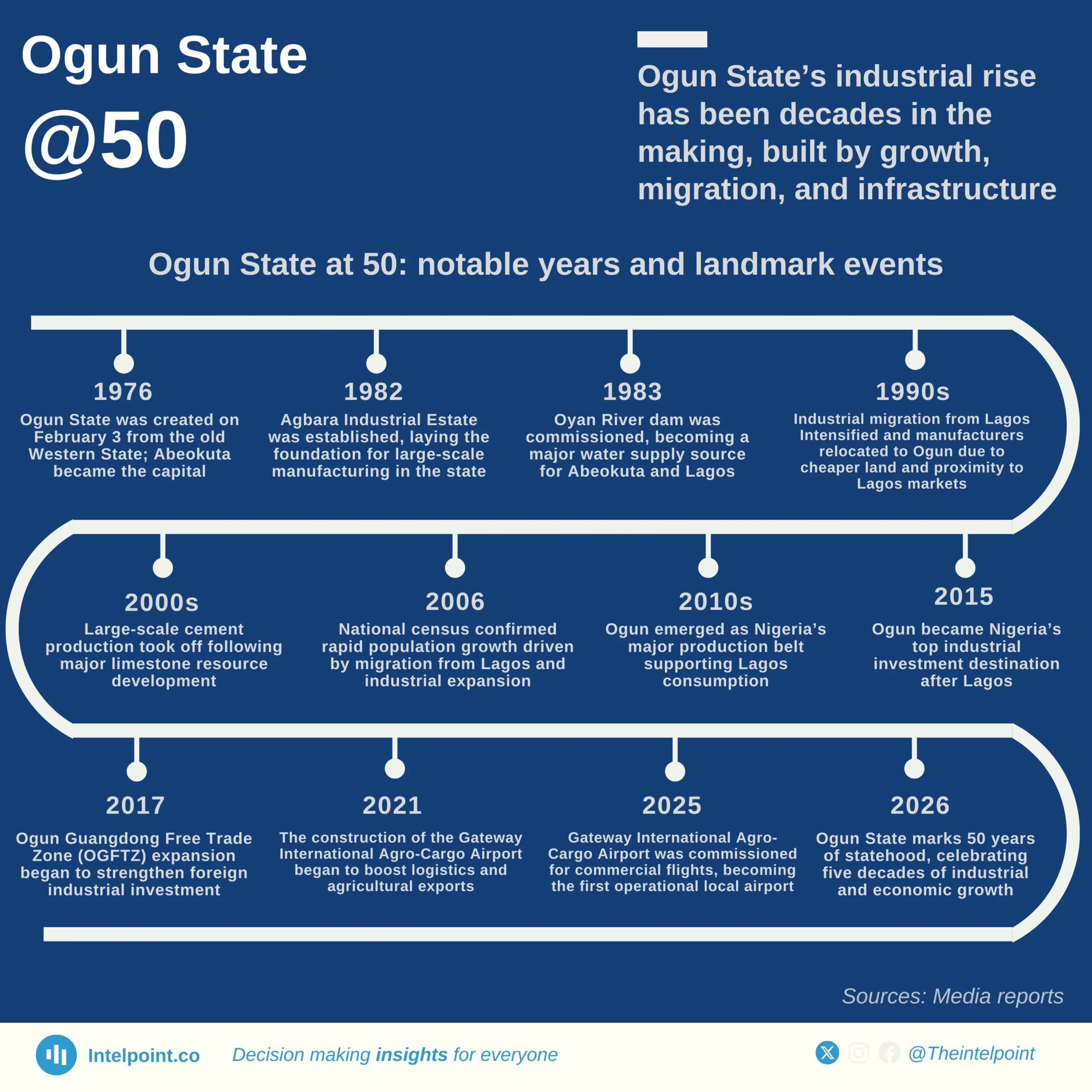
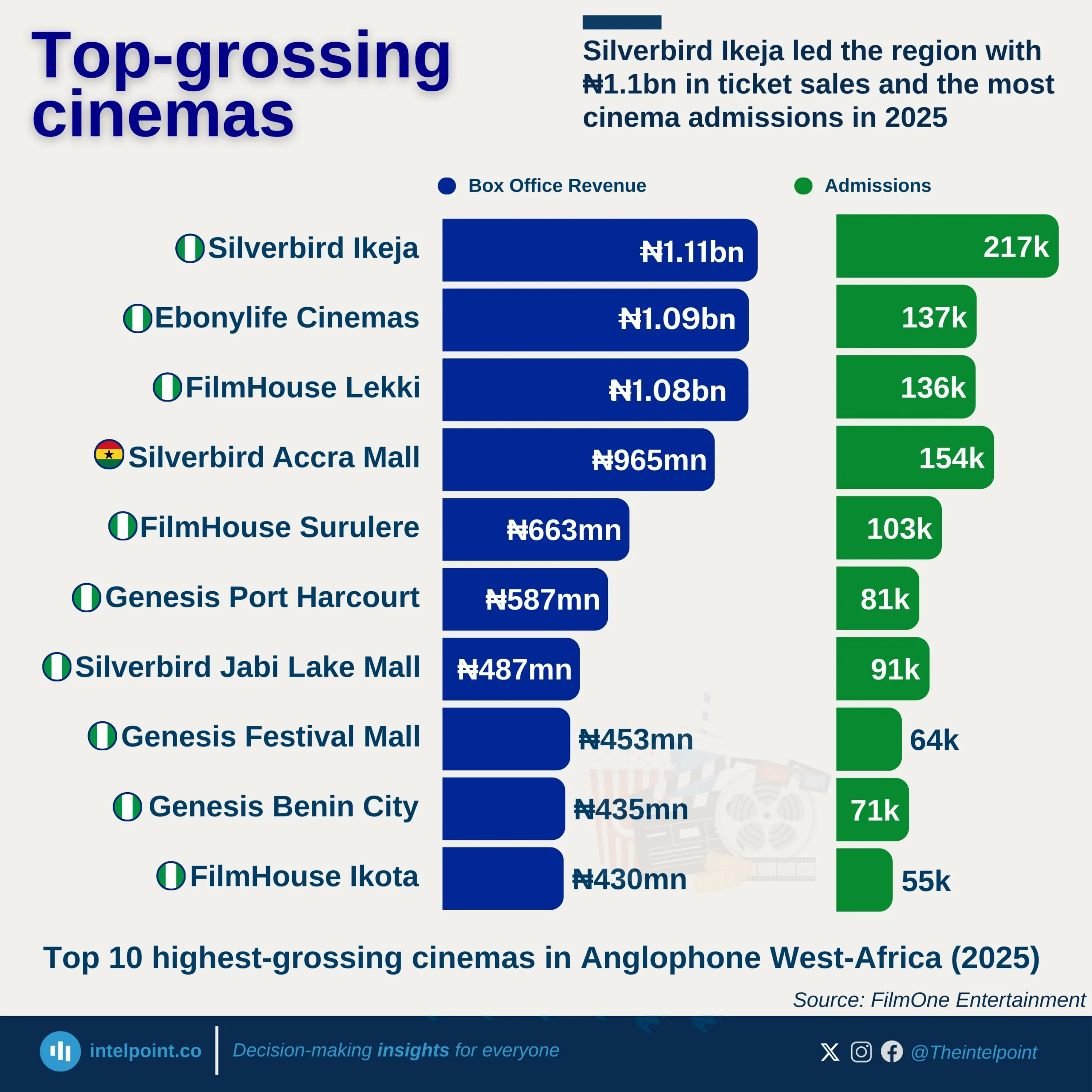
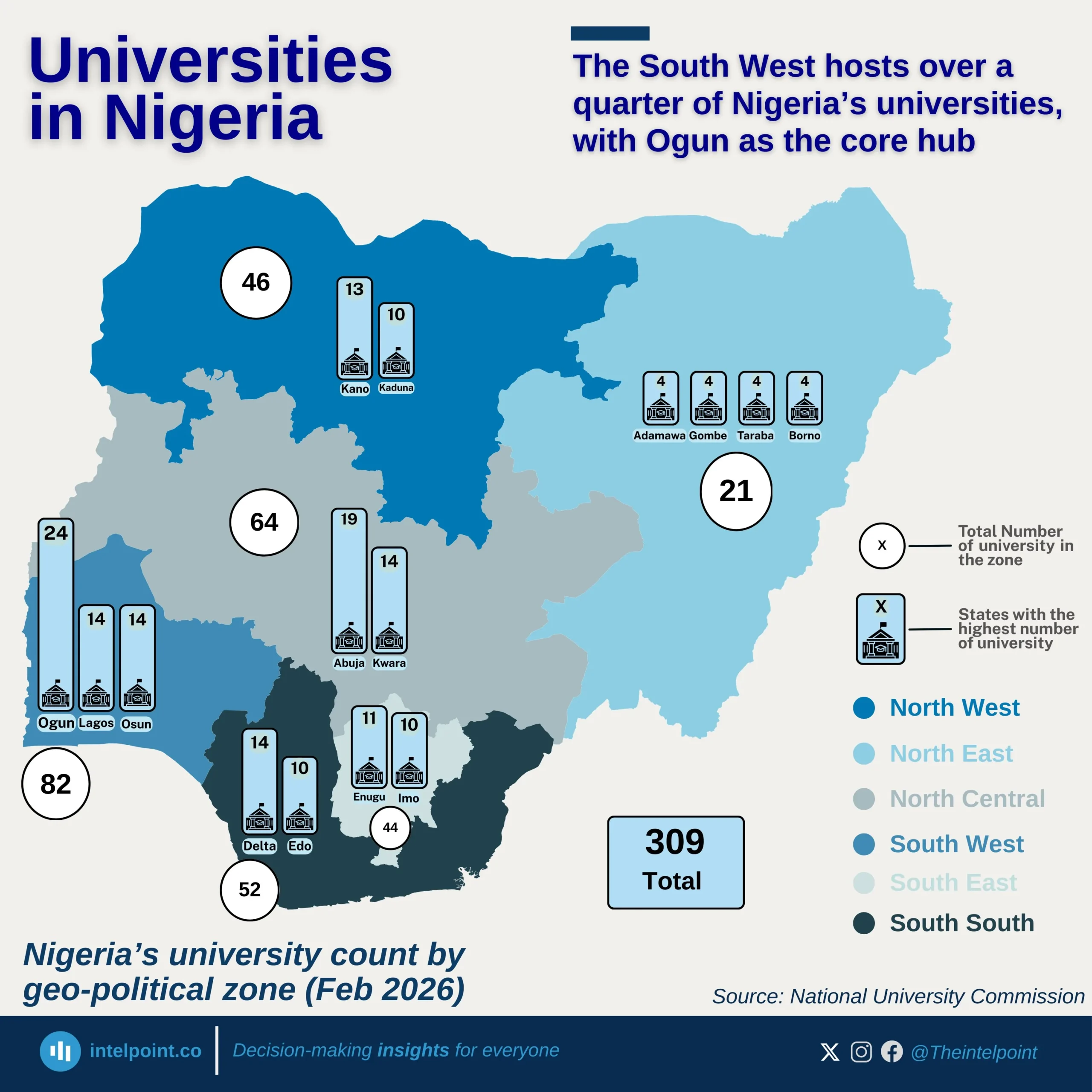
Gender disparities in Nigeria’s education loan fund are stark and numeric. Out of a combined 552,009 institutional loan applications as of May 2025, male students accounted for nearly 375K, significantly outpacing the 177K submitted by female students. That’s a 68 - 32 split, showing a two-to-one lead in favor of male applicants.
This gap could reflect underlying trends in enrolment rates, access to information, or even confidence in navigating application systems. What is certain, though, is the data: for every female student [who] accessed the fund, there were 2.1 male students right ahead, painting a clear picture of gender imbalance in educational financing demand.