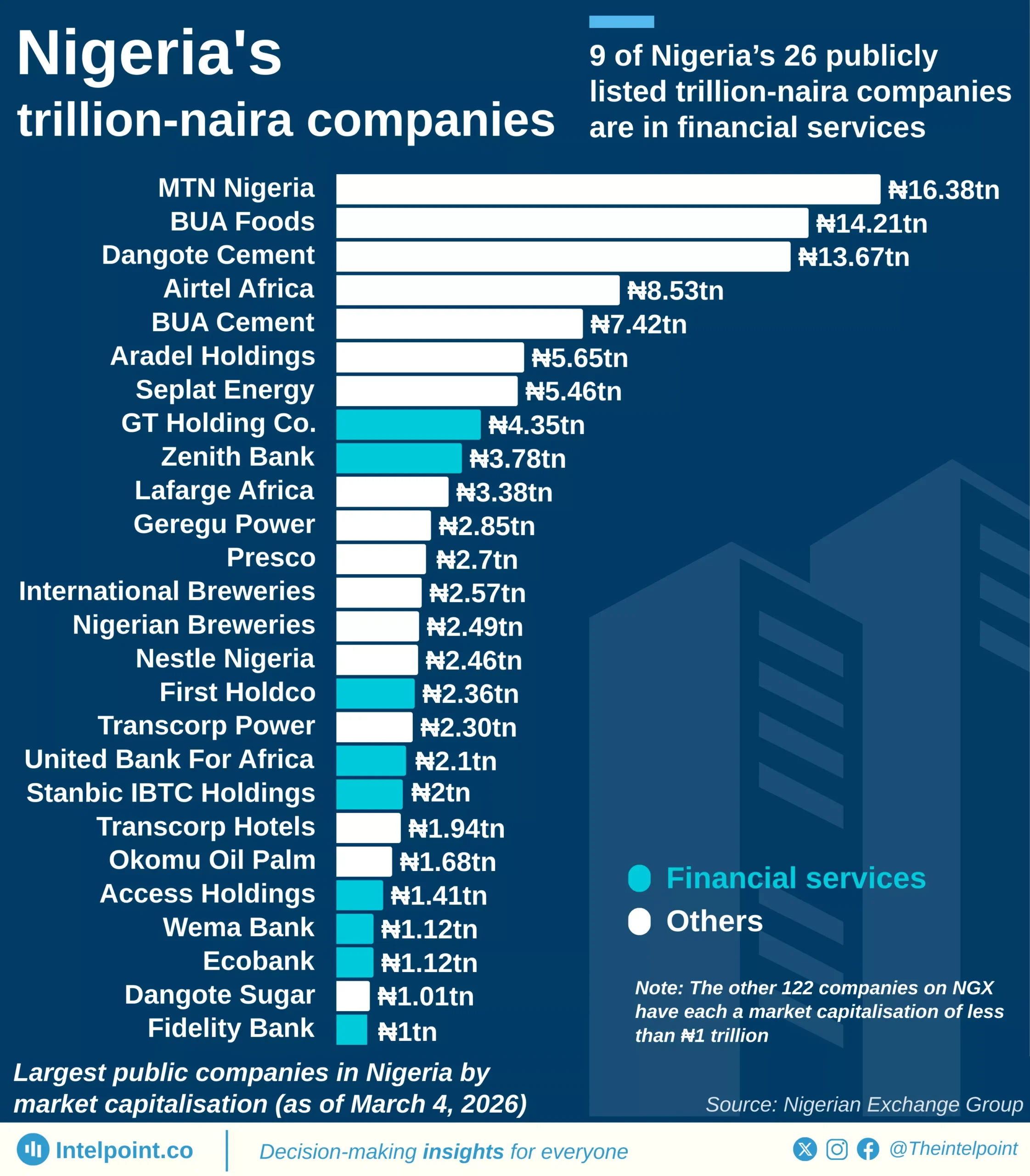
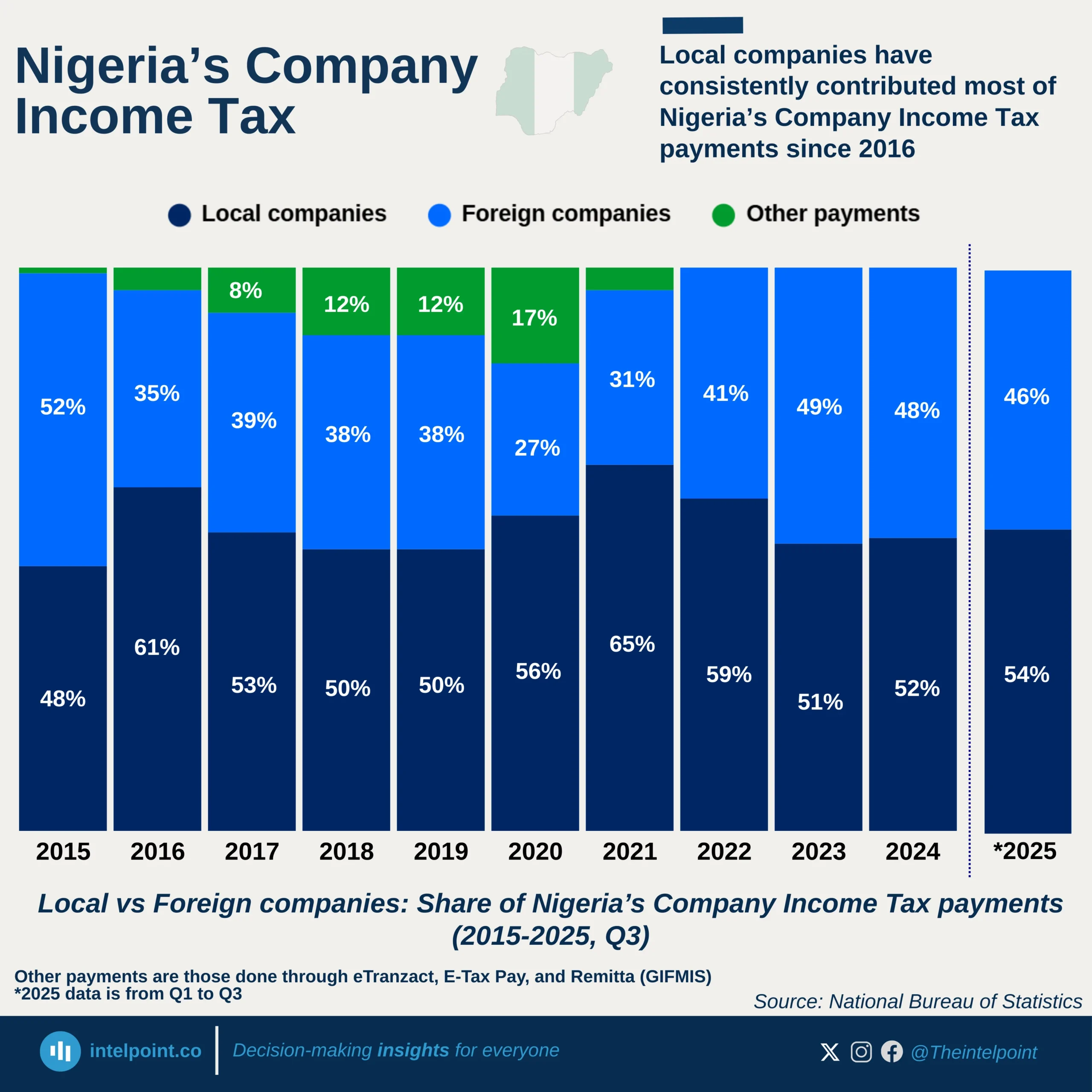
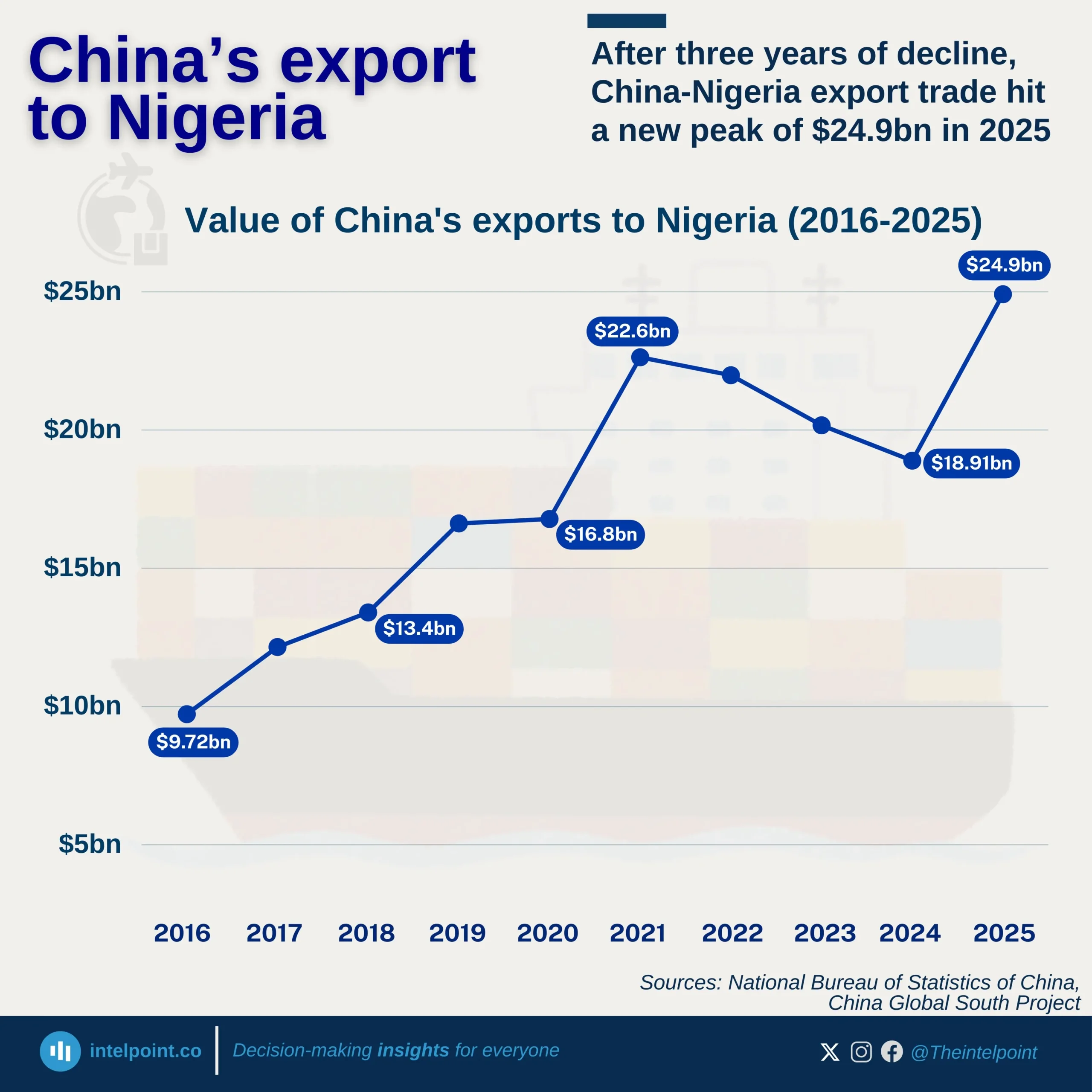
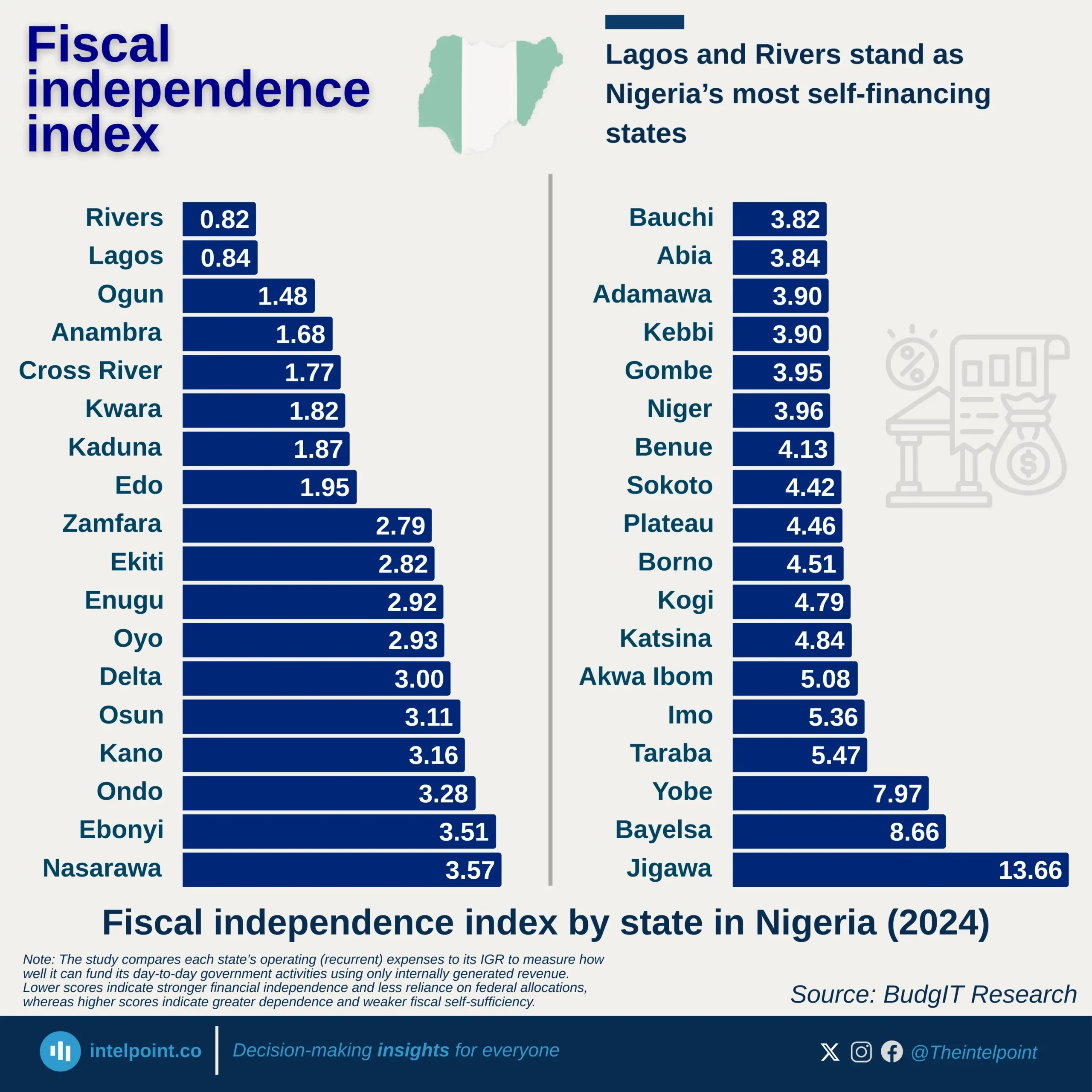
Ghana’s digital services trade between 2005 and 2024 showed a remarkable rise. Exports grew from just $78 million in 2005 to $5.18 billion in 2024. Over the 20-year period, Ghana accumulated $49.11 billion in exports. Imports, however, stood slightly higher at $53.00 billion, leaving the country with a trade deficit of $3.9 billion across the two decades. This deficit is relatively small when compared to the size of its economy. It also shows Ghana’s digital exports are expanding steadily, highlighting the country’s increasing role in the digital economy.
Compared to Nigeria, Ghana is performing stronger in balancing its digital trade. Its deficit is modest, and its exports are growing faster. Nigeria, though larger in population and economy, remains import-heavy. The contrast shows Ghana is better positioned to harness digital opportunities.