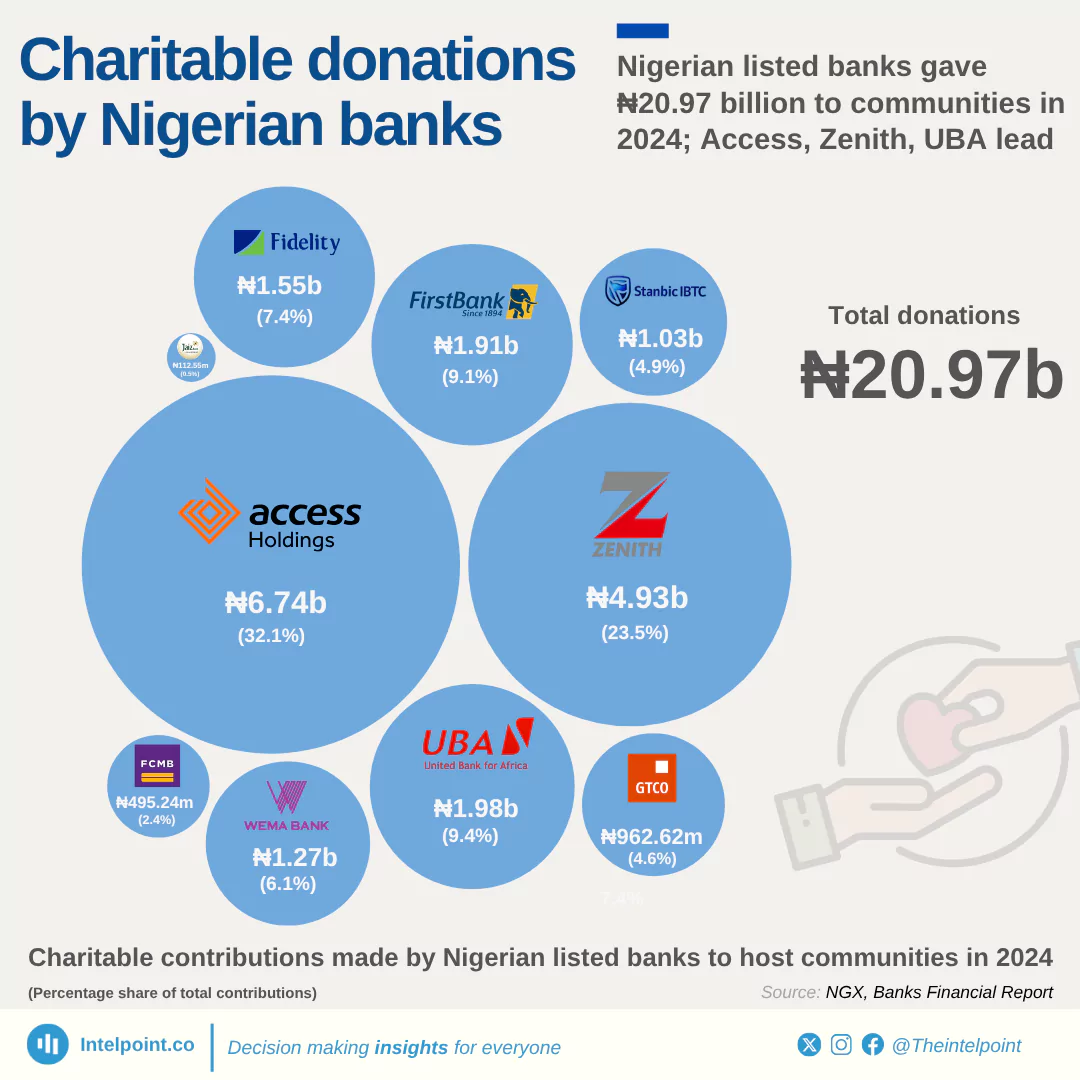
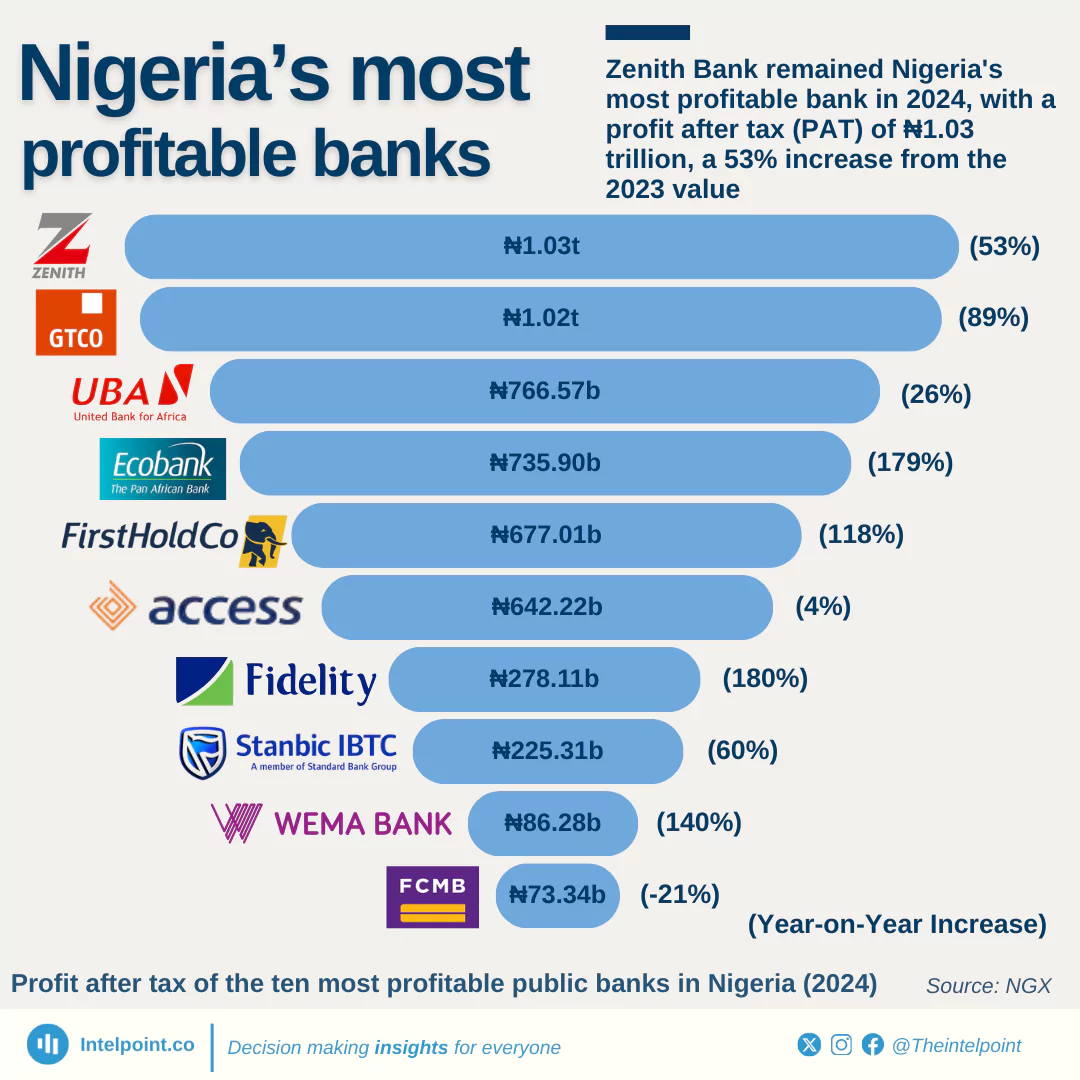
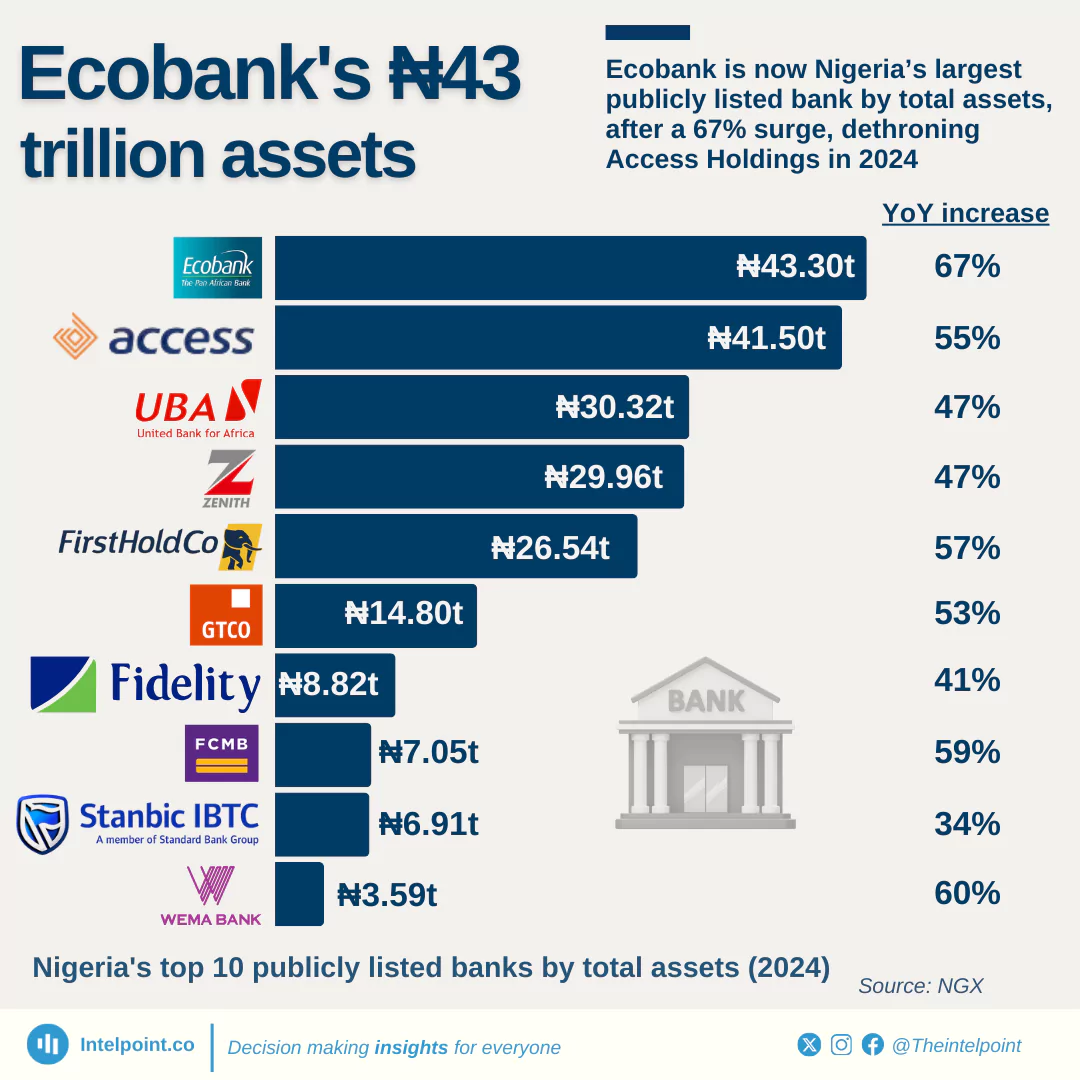
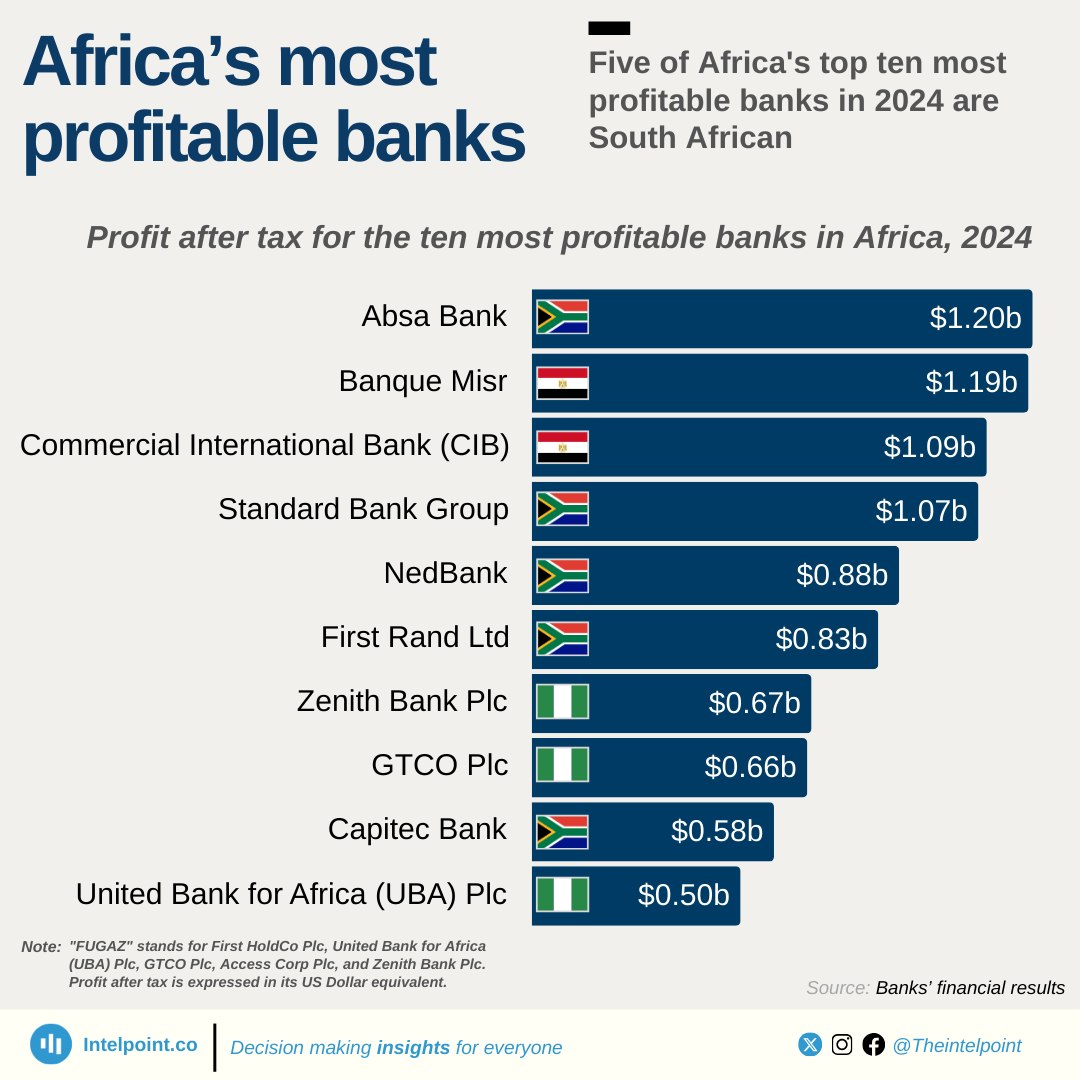
ATM operations in Nigeria have evolved significantly, shaped by regulatory changes and technological advancements. A recurring theme has been the regulation of withdrawal charges, with the CBN revising fees five times since 2012, including the latest increase, effective March 2025. Recent developments also indicate stricter oversight, as the CBN has sanctioned banks that fail to stock their ATMs. With rising fees and evolving policies, the future of ATMs in Nigeria remains dynamic, influenced by both regulatory decisions and customer banking behaviour.