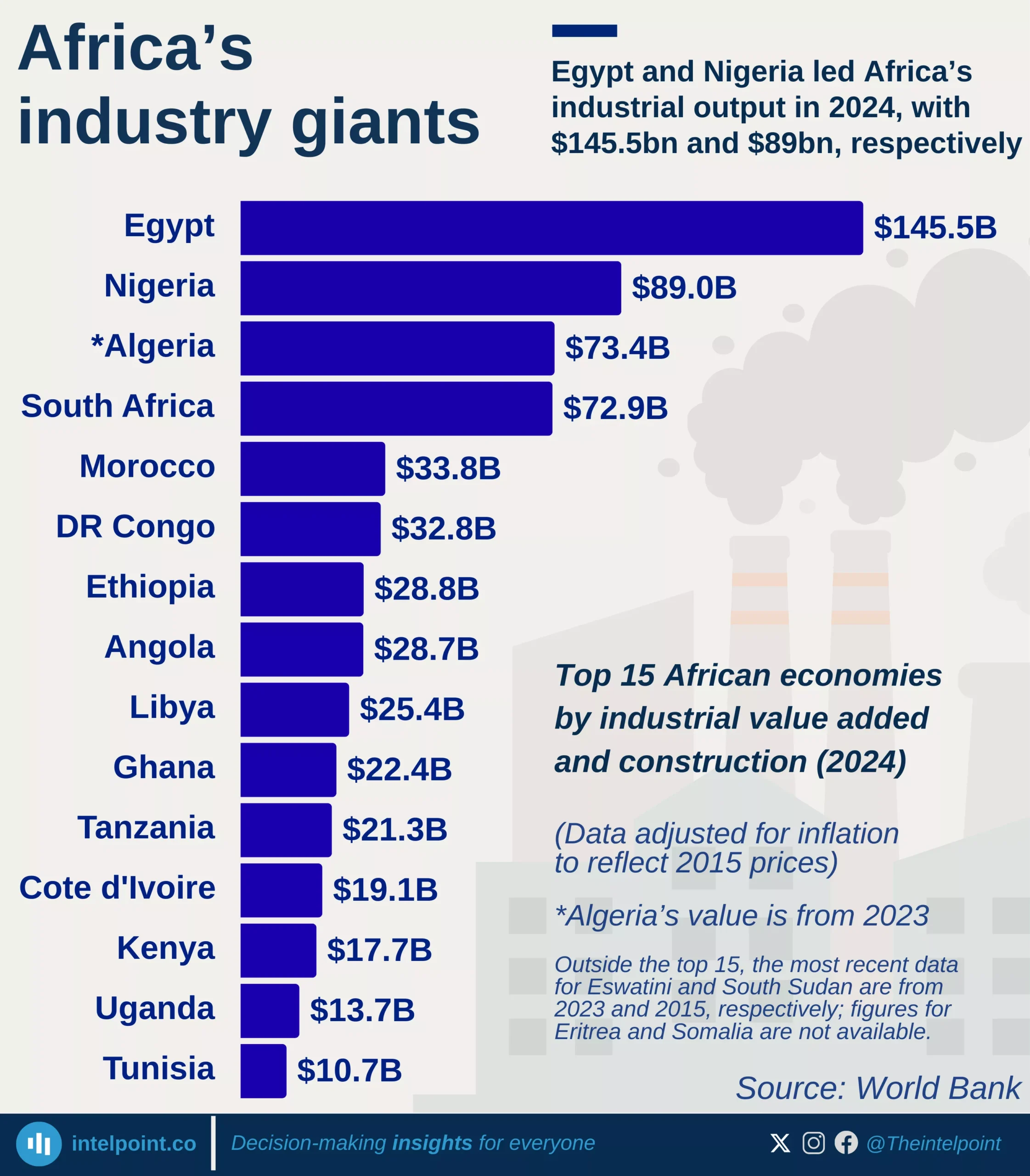
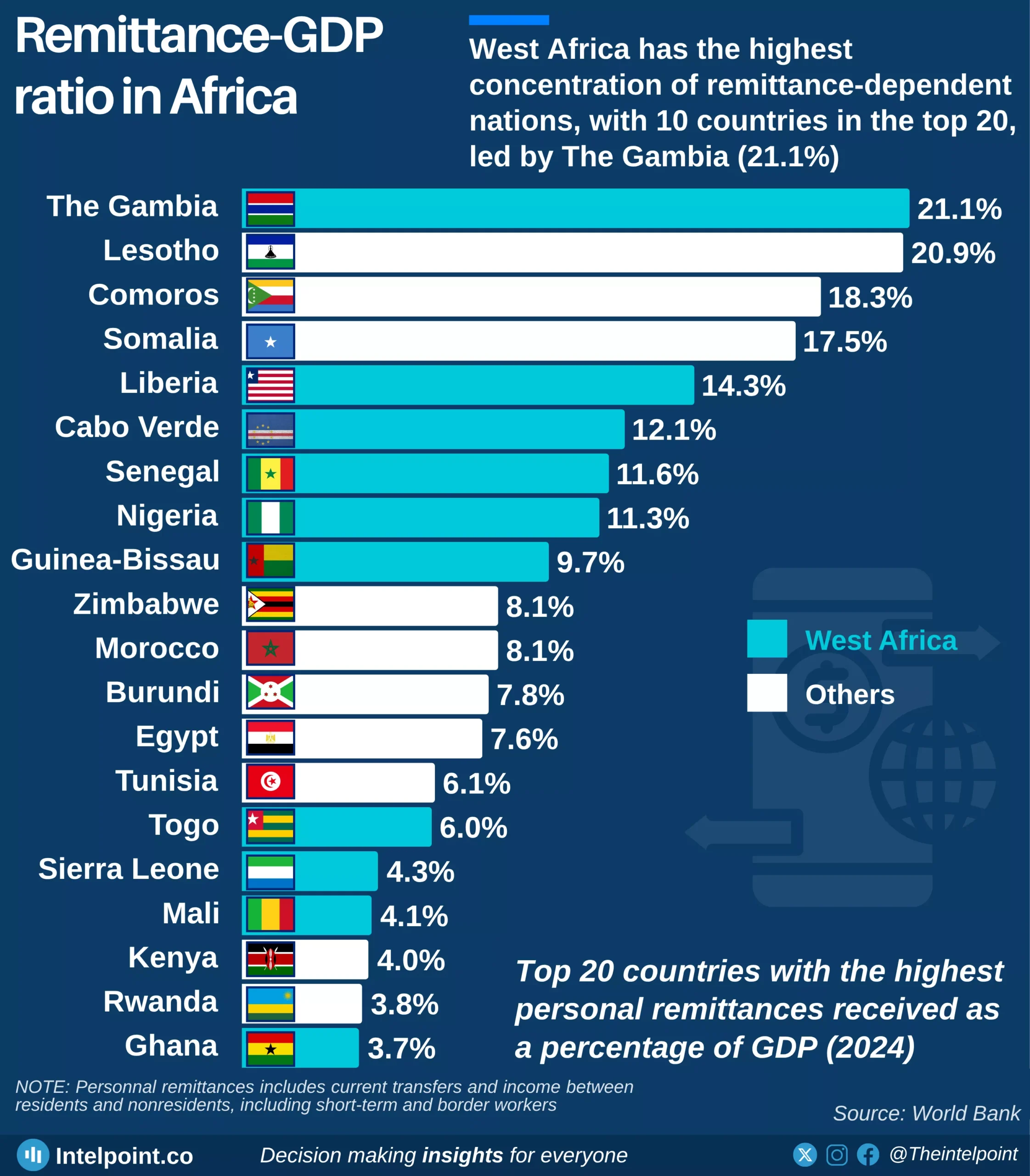
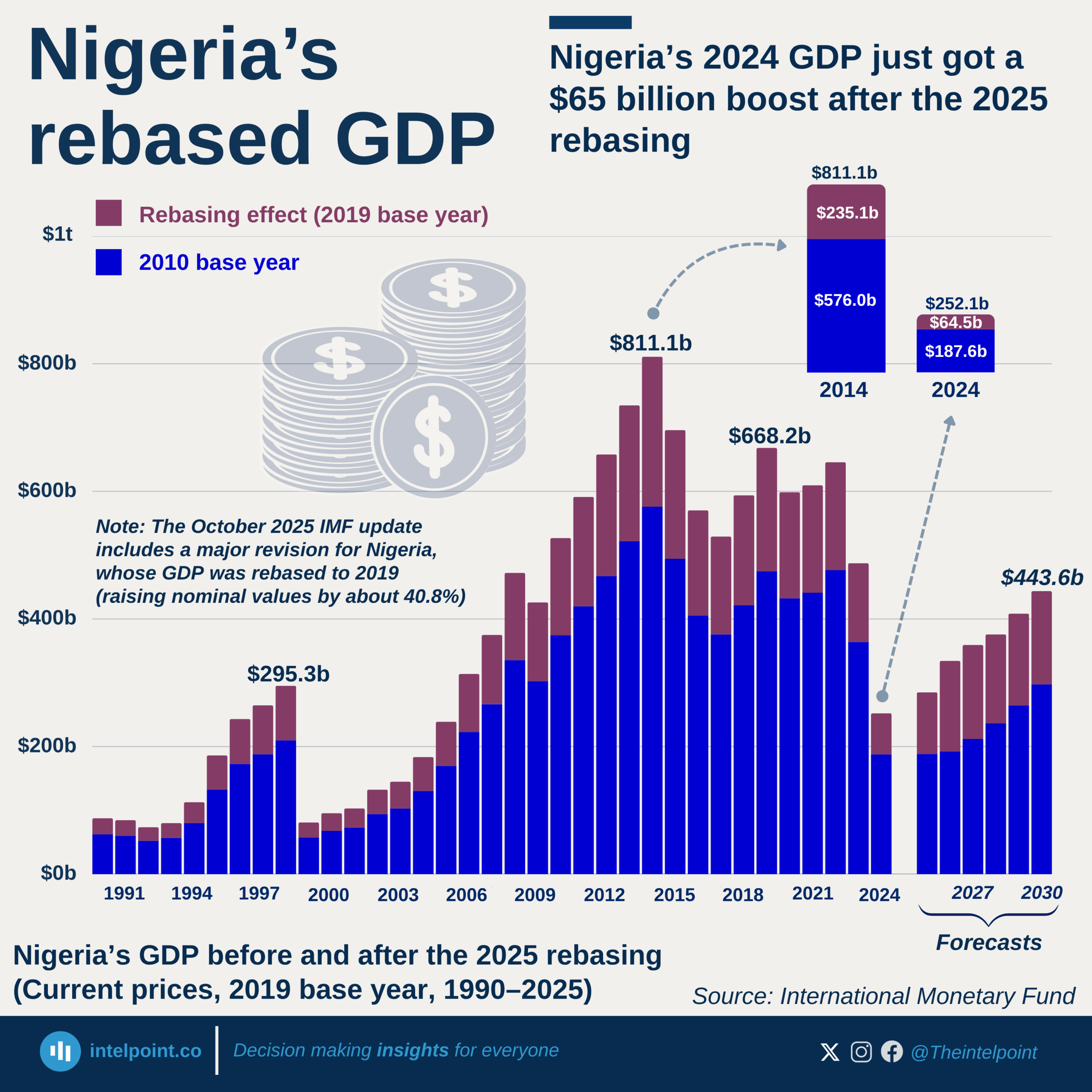
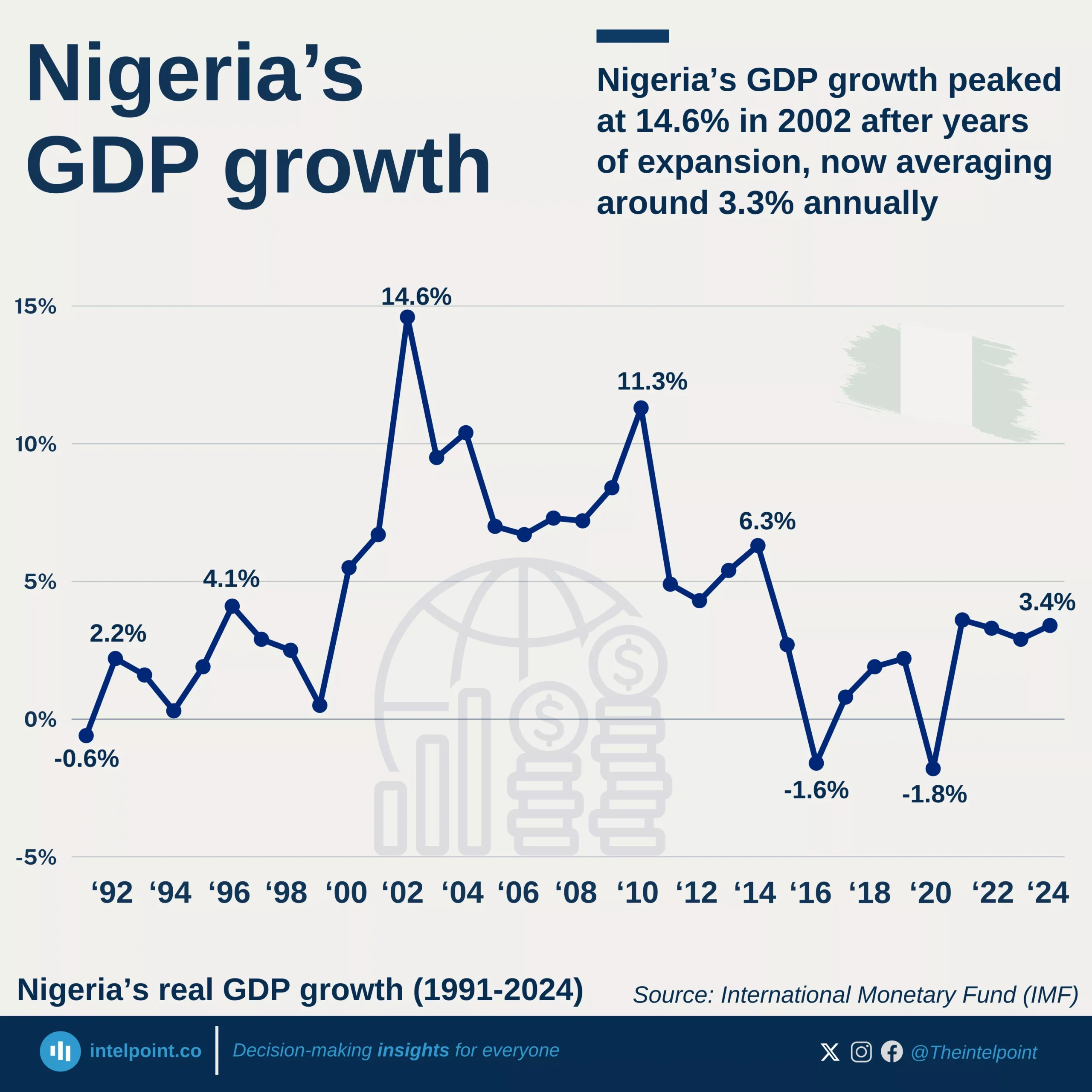
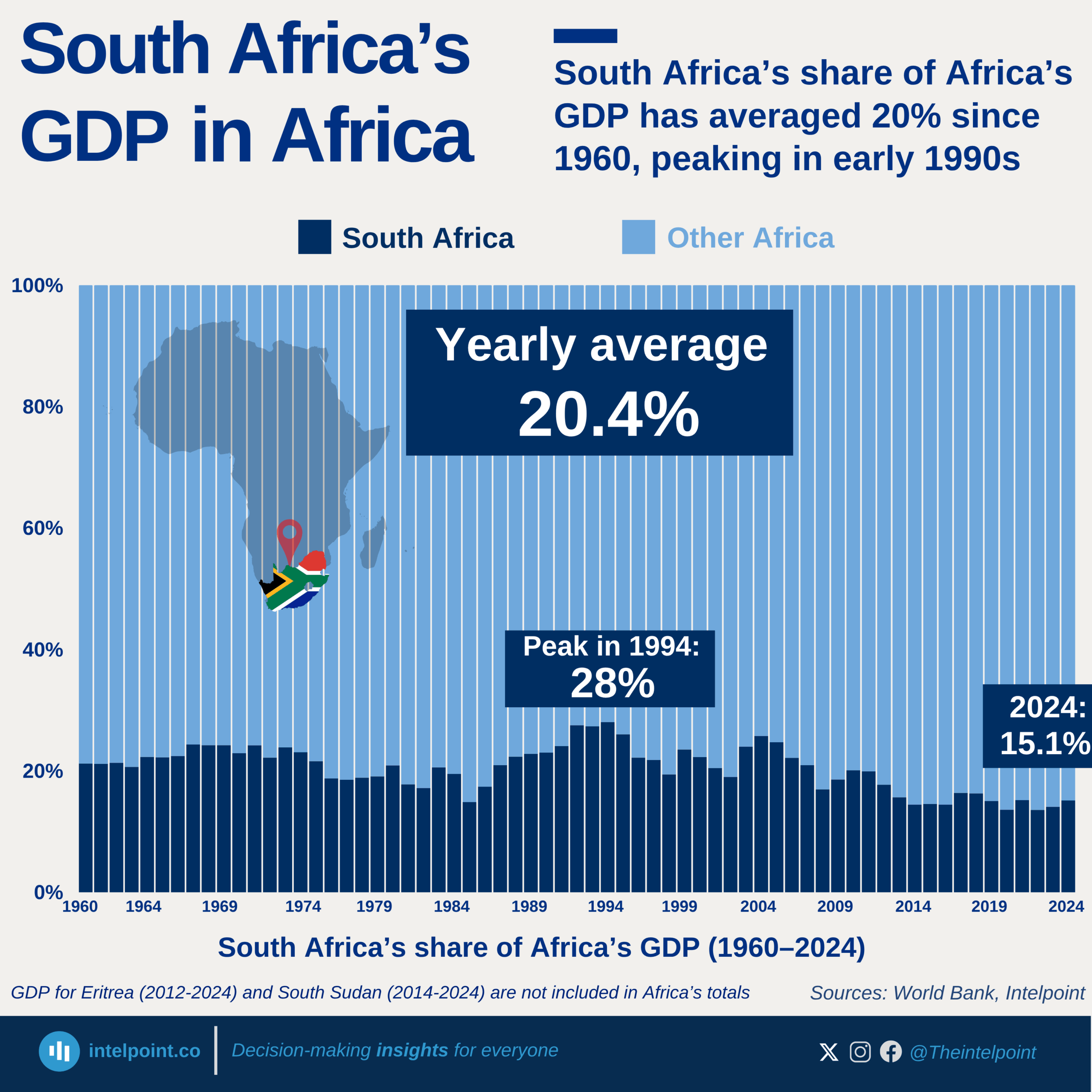
Burkina Faso’s GDP per capita has climbed from $248.9 in 2000 to an all-time high of $987.3 in 2024, a 297% increase over 25 years despite notable swings along the way. After an early 2000s growth and a sharp 2008 surge, the economy contracted during the global financial crisis, hitting a low of $630.1 in 2015. From 2022 onward, the country entered its fastest growth phase in over a decade, with GDP per capita rising from $836.1 to $987.3 in just two years.
This acceleration was fueled by a boom in industrial-scale gold production, which accounts for roughly 70% of export earnings, alongside resilient agricultural performance and stronger cross-border trade. In 2024, Burkina Faso’s GDP per capita placed it in Africa’s lower-middle tier, higher than several West African neighbors such as Mali, Niger, and Sierra Leone, reflecting steady progress despite persistent structural challenges.