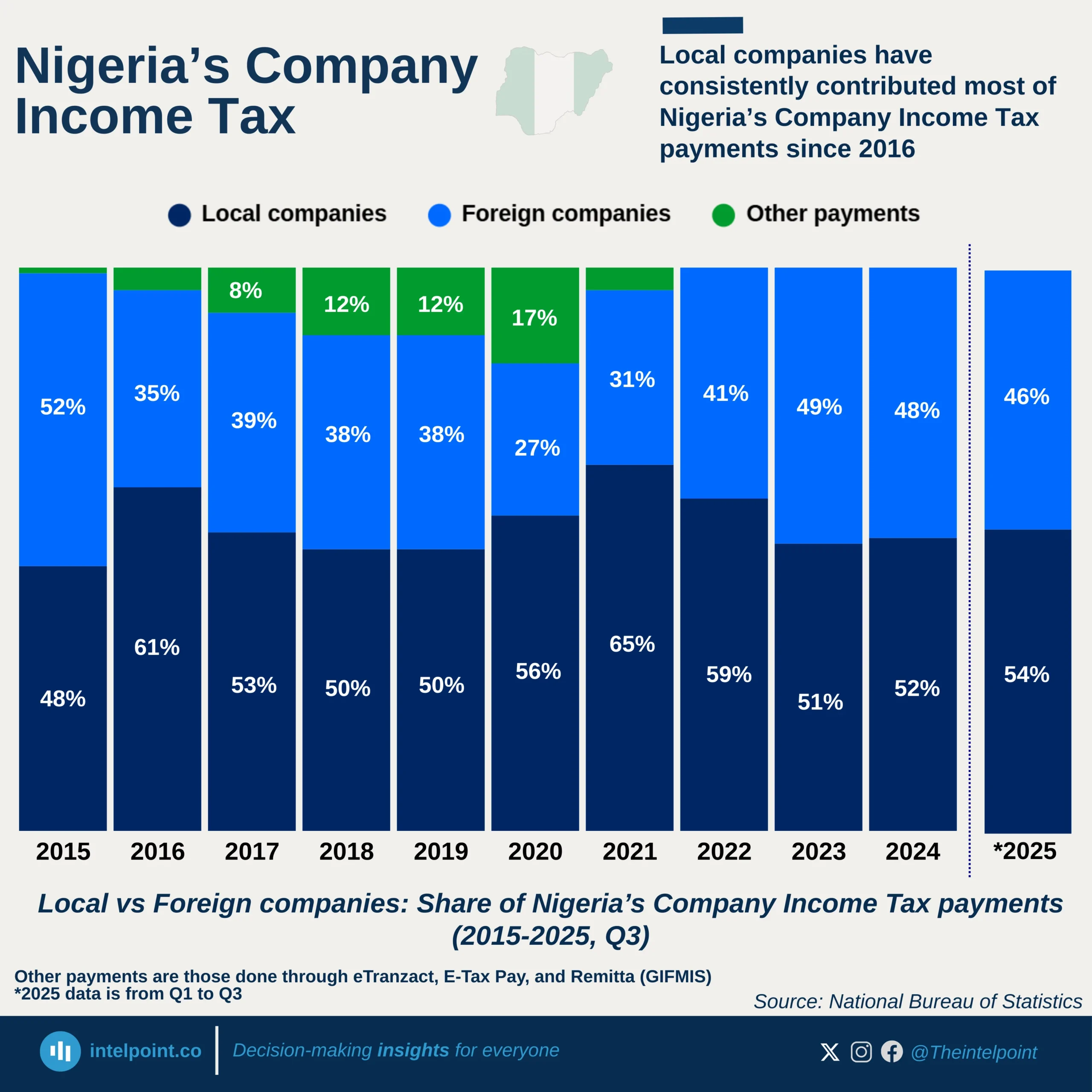
The VAT remittance and sharing pattern in the North-East geopolitical zone of Nigeria reveals a significant reliance on the federal VAT sharing system. The six states collectively remitted ₦14.98 billion but received an allocation of ₦46.68 billion, representing a 211.6% increase in revenue through federal allocation. This trend showcases how the VAT sharing formula, which prioritises equality and population over direct revenue generation, disproportionately benefits states with lower economic activity.
Borno led remittance with ₦3.91 billion (26.1% of the zone’s total VAT), yet it received ₦8.74 billion, a 123% gain. However, the biggest beneficiary in terms of percentage increase was Taraba, which remitted the least (₦0.94 billion, just 6.3% of the total) but received ₦6.91 billion, a massive 635% increase. Bauchi, despite contributing only ₦2.44 billion, received the highest allocation in the region at ₦8.93 billion, a 266% boost, further confirming that VAT allocation is based on sharing metrics beyond just remittance levels.
With every state in the North-East receiving at least double their remittance, this shows a significant fiscal imbalance that continues to drive ongoing discussions about VAT decentralisation. As high revenue states push for VAT retention at the source, states in regions like the North-East, which benefit significantly from sharing, may face economic pressure if the system is altered.