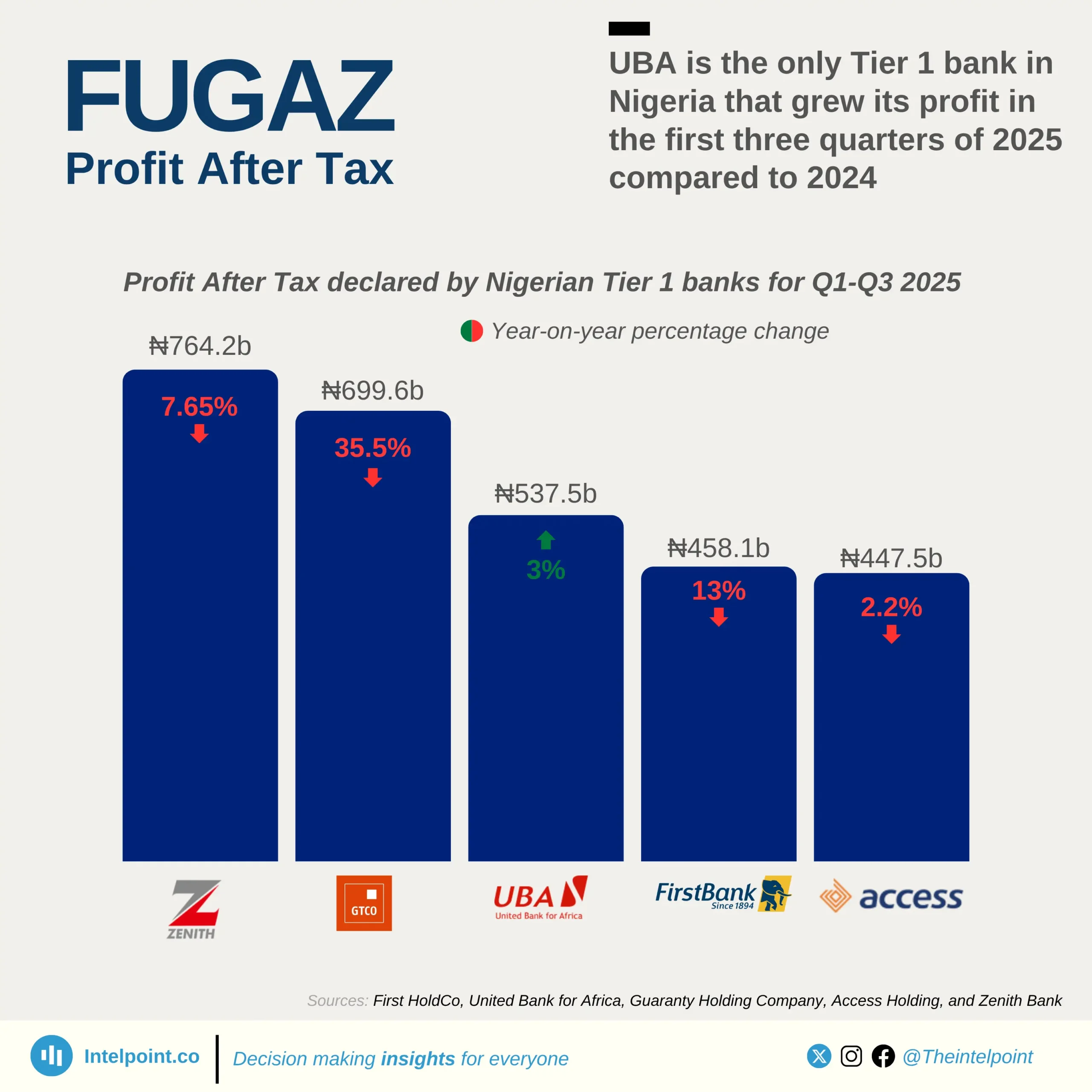
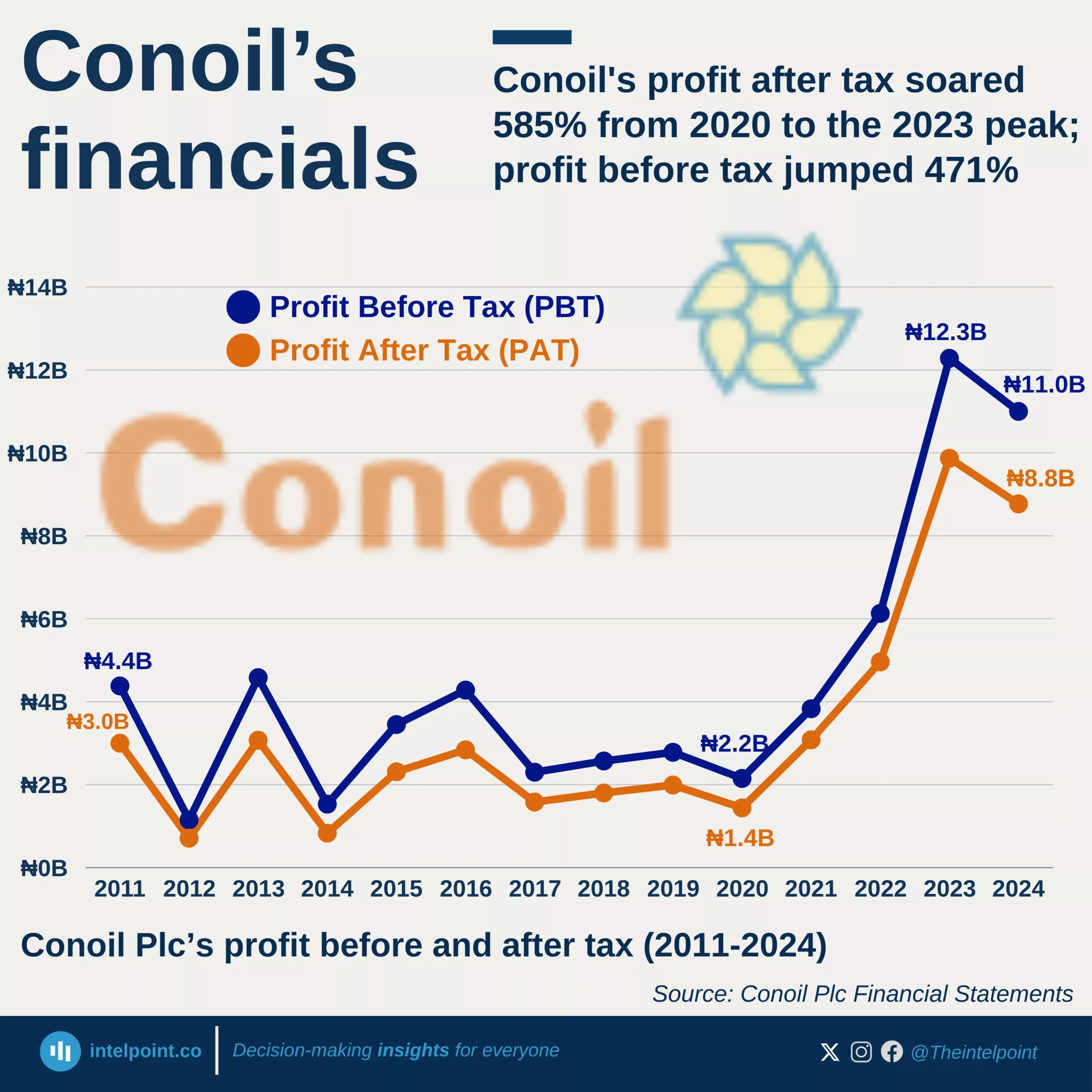
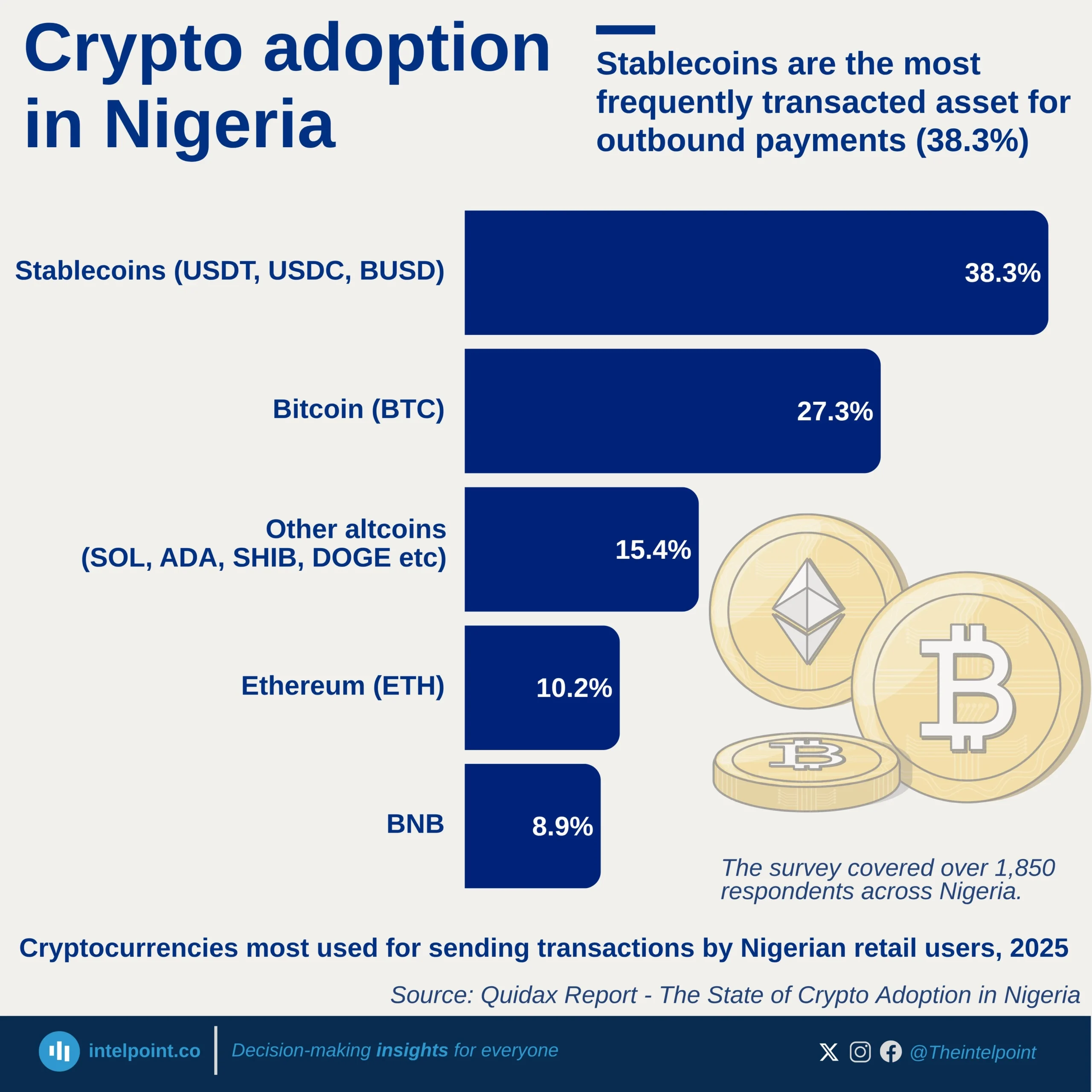
Nigeria's e-commerce space is changing, with digital wallets expected to emerge as the fastest-growing payment method. In 2023, digital wallets accounted for 11% of all e-commerce transactions, but by 2027, it is projected to double its market share to 22%. This rapid shift reflects changing consumer preferences, increased smartphone penetration, and growing confidence in digital payment solutions. While account-to-account (A2A) transfers still hold the largest share (32% in 2023 and projected to rise slightly to 34% in 2027), digital wallets are experiencing the most significant growth in adoption.
Cash-on-delivery, once a dominant force in Nigeria’s e-commerce sector, is steadily declining. It accounted for 15% of transactions in 2023 but is expected to shrink to just 9% by 2027. This indicates that more consumers are embracing digital-first payment methods over traditional cash transactions. Debit and credit cards also maintain a steady presence, with debit cards slightly decreasing from 19% to 16% and credit cards increasing from 12% to 15%.