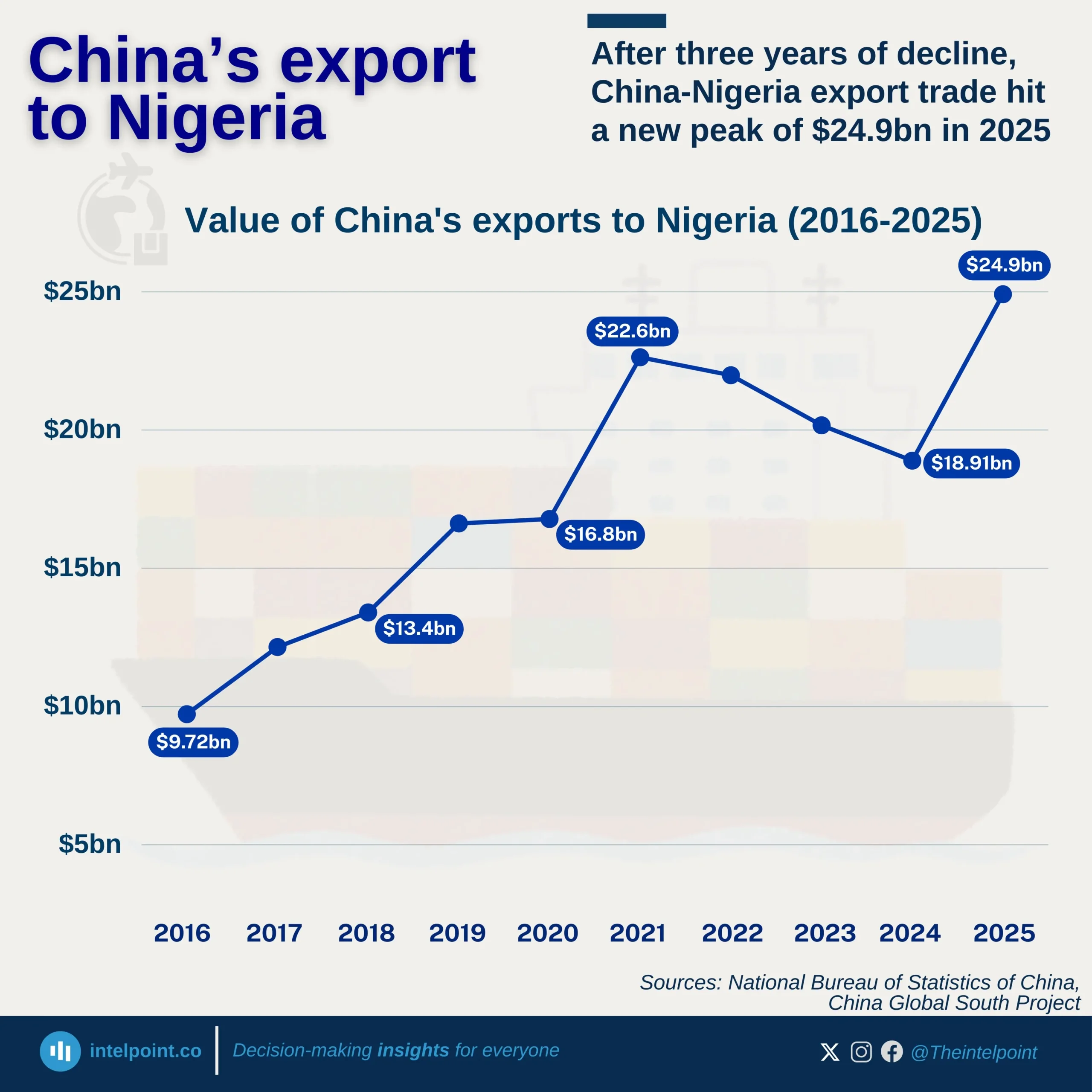
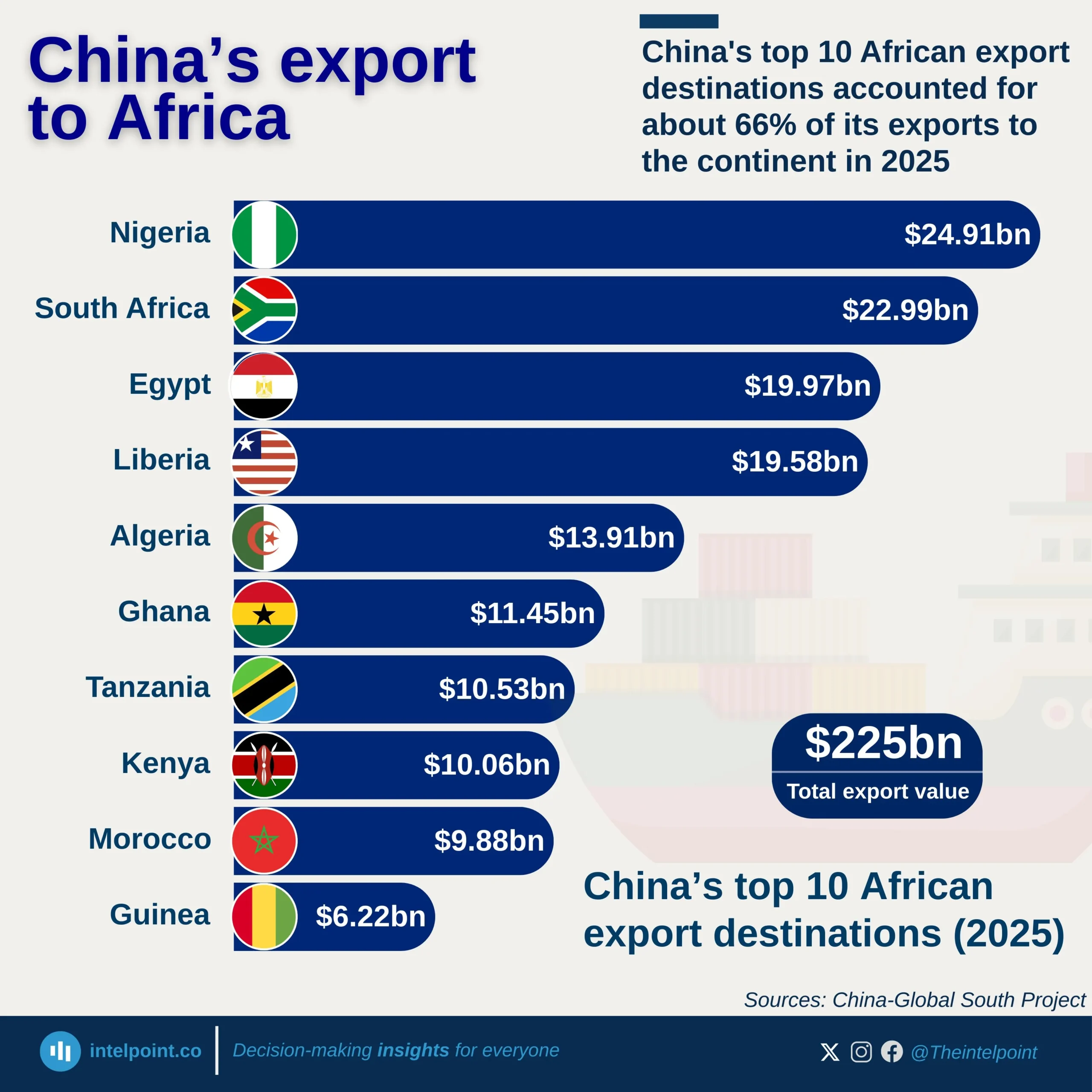
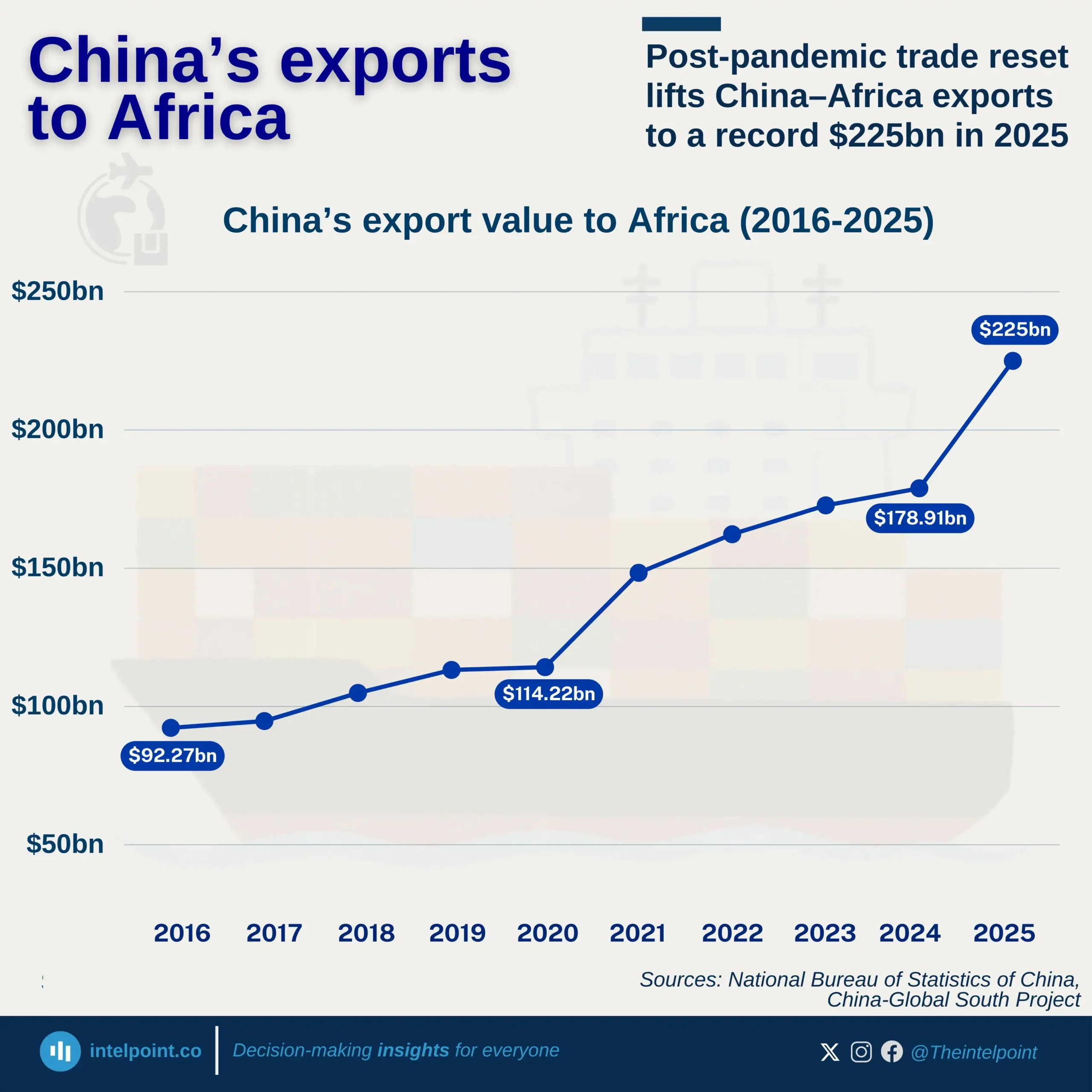
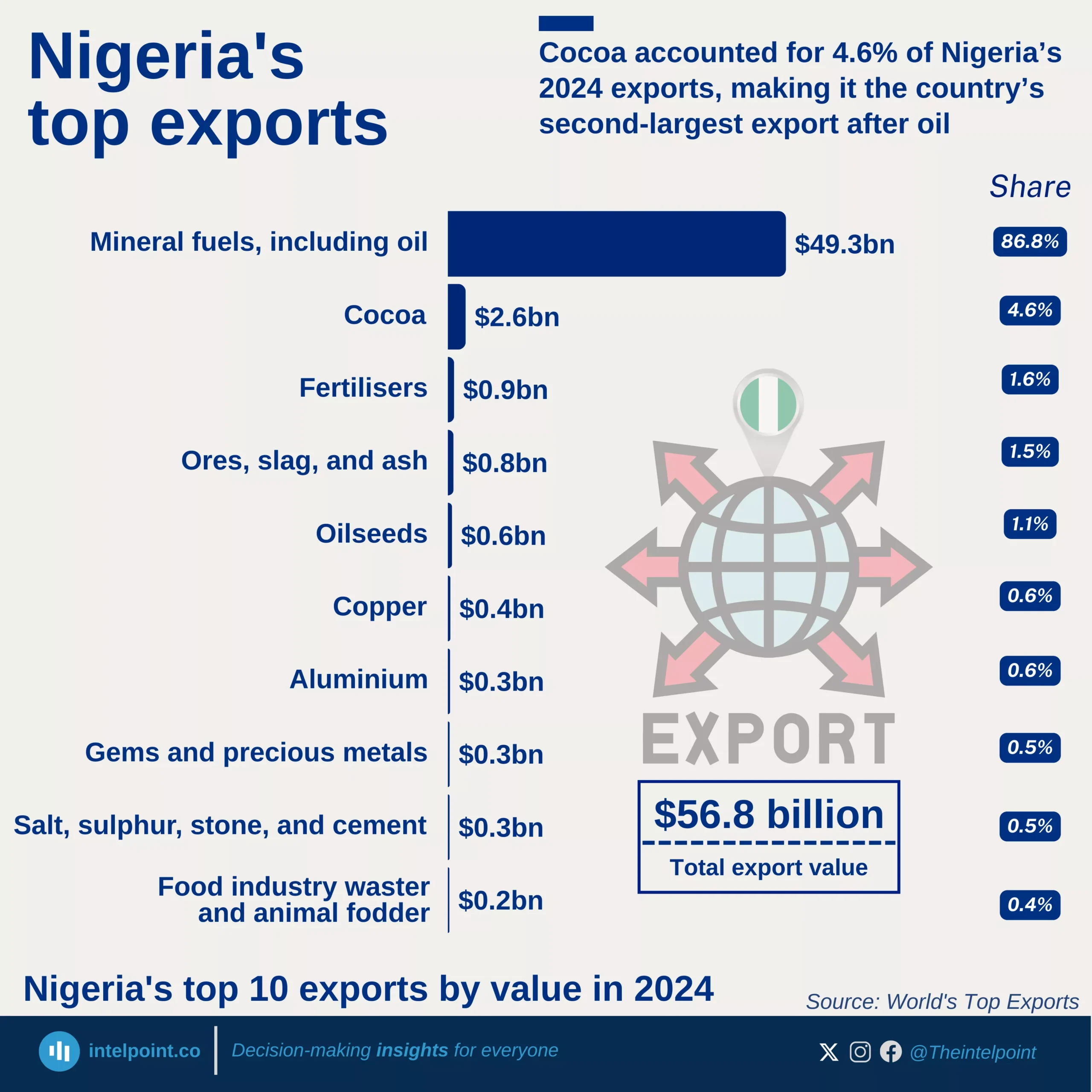
Kenya’s banking sector remains a crucial player in financing international trade, but the balance is heavily tilted towards imports. In the first half of 2024, over 60% of total bank credit allocated to foreign trade went to importing goods, leaving less than 40% for exports. This trend signals a deep reliance on foreign products, raising questions about trade imbalances and the need for export growth.
This pattern is consistent month after month, with March, May, and June peaking above 66% in import financing. Kenyan businesses benefit from import credit, but to ensure long-term economic stability, banks and policymakers might need to explore strategies that promote export financing. A shift towards a more balanced trade credit distribution could strengthen local industries, create jobs, and improve economic resilience.